Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
小野田 雄一; 松場 賢一; 飛田 吉春; 鈴木 徹
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 4(3), p.16-00597_1 - 16-00597_14, 2017/06
For the prototype sodium-cooled fast reactor, MONJU, the mechanical energy and structural response under energetics caused by neutronic power excursion during Unprotected Loss of Flow accident (ULOF) were preliminarily analyzed. The objective of this study is to demonstrate the integrity of the reactor vessel against the mechanical load induced by the energetics. Conservative energy production was assumed in order to confirm the robustness of the safety design of MONJU. Mechanical energy was evaluated with the code in which mechanistic modelling of core expansion was implemented. The mechanical energy, which were obtained by analyzing the expanding behavior of core materials after energetics, were about one order of magnitude below the thermodynamic work potential calculated by assuming isentropic expansion of the fuel vapor to one atmosphere, which was often used as an indicator to express the severity of the energetics. Structural integrity was then evaluated with coupled fluid-structure dynamics code using the obtained mechanical energy. No or very small circumferential residual strain of the reactor vessel was evaluated in most analytical cases, and even in the most conservative energy production case, the residual strain was only 0.008 % so that the integrity of the reactor vessel is maintained. The result obtained in the present study shows that MONJU has enough robustness against the mechanical load under energetics.
小野田 雄一; 松場 賢一; 飛田 吉春; 鈴木 徹
Proceedings of 24th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-24) (DVD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2016/06
For the prototype sodium-cooled fast reactor, MONJU, the mechanical energy and structural response under energetics caused by neutronic power excursion during Unprotected Loss of Flow accident were preliminarily analyzed. The objective of this study is to demonstrate the integrity of the reactor vessel against the mechanical load induced by the energetics. Conservative energy production was assumed in order to confirm the robustness of the safety design of MONJU. Mechanical energy was evaluated with the code in which mechanistic modelling of core expansion was implemented. The mechanical energy, which were obtained by analyzing the expanding behavior of core materials after energetics, were about one order of magnitude below the thermodynamic work potential calculated by assuming isentropic expansion of the fuel vapor to one atmosphere, which was often used as an indicator to express the severity of the energetics. Structural integrity was then evaluated with coupled fluid-structure dynamics code using the obtained mechanical energy. No or very small circumferential residual strain of the reactor vessel was evaluated in most analytical cases, and even in the most conservative energy production case, the residual strain was only 0.008 % so that the integrity of the reactor vessel is maintained. The result obtained in the present study shows that MONJU has enough robustness against the mechanical load under energetics.
 (OH)
(OH)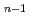 (n=2-5) clusters deduced from photoionization efficiency curves
(n=2-5) clusters deduced from photoionization efficiency curves田中 宏昌; 横山 啓一; 工藤 博司*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 114(1), p.152 - 159, 2001/01
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:15.25(Chemistry, Physical)レーザーアブレーションした金属リチウムと水蒸気との反応により生成した過剰なリチウムを有するLi (OH)
(OH)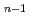 (n=2-5)クラスターについて、光イオン化効率曲線(IEC)を測定した。実測したIECはイオン化におけるフランク-コンドン因子をもとにしたシミュレーションでよく再現できた。両IECの比較から、測定にかかったLi
(n=2-5)クラスターについて、光イオン化効率曲線(IEC)を測定した。実測したIECはイオン化におけるフランク-コンドン因子をもとにしたシミュレーションでよく再現できた。両IECの比較から、測定にかかったLi (OH)
(OH)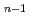 クラスターの構造が密度汎関数法を用いた理論計算から得られた最安定構造と一致することがわかった。
クラスターの構造が密度汎関数法を用いた理論計算から得られた最安定構造と一致することがわかった。