Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ding, H.*; Ito, Keita*; Endo, Yasushi*; Takanashi, Koki; Seki, Takeshi*
Journal of Physics D; Applied Physics, 57(38), p.385002_1 - 385002_10, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:37.90(Physics, Applied)Yamazaki, Takumi*; Seki, Takeshi*; Kubota, Takahide*; Takanashi, Koki
Applied Physics Express, 16(8), p.083003_1 - 083003_4, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.86(Physics, Applied)Yamamoto, Shunya; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Yoshikawa, Masahito
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 129, 2015/03
no abstracts in English
Takeyama, Akinori; Yamamoto, Shunya; Ito, Hiroshi; Yoshikawa, Masahito
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 232(1-4), p.333 - 337, 2005/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Cu precipitates were formed on Si(100) by 200 keV Cu ion implantation and subsequent annealing at 773 K. The shape of the Cu precipitates evolved from a large rectangle to a small elongated pyramid with increasing annealing time. This shape evolution seemed to result from the epitaxial formation of Cu precipitates to minimize the interfacial energy between the precipitate and the Cu implanted substrate. The average density of Cu precipitates monotonously increased and the average diameter of Cu precipitates decreased with increasing annealing time up to 1 h. These indicate that the morphology, size and average density of Cu precipitates can be controlled by varying annealing time, and that Cu ion implantation and subsequent annealing were effective in producing a substrate dispersed with catalytic particles for oxide nanorods growth.
Takeda, Masayasu; Mibu, Ko*; Shinjo, Teruya*; Endo, Yasuo*; Suzuki, Junichi
Physical Review B, 70(10), p.104408_1 - 104408_9, 2004/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:40.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Detailed magnetic structure of spin-density waves (SDWs) in epitaxial Cr(001)/Sn multilayer was investigated by neutron scattering combined with M ssbauer spectroscopic studies. Monatomic Sn layers were embedded in 240 nm thick Cr(001) films with varying the periodic spacing from 4.2 to 16.2 nm. All samples were revealed to be a commensurate antiferromagnetic (CAF) phase at 300 K. The CAF structures changed to incommensurate SDW states with complex waveforms whose wavelength are controlled by the artificial periodicity at low temperatures although the CAF structure in the sample with the period of 4.2 nm persisted even at 10 K. The phase transition depends on the thickness of the Cr layers intervening between Sn monatomic layers. An appreciable phase slip in the SDW was observed during the phase transition in the sample with the period of 10.2 nm. The SDW structure is discussed by taking account of the competing forces between the nesting of Fermi surface and a pinning of antinodes at the Sn monatomic layers.
ssbauer spectroscopic studies. Monatomic Sn layers were embedded in 240 nm thick Cr(001) films with varying the periodic spacing from 4.2 to 16.2 nm. All samples were revealed to be a commensurate antiferromagnetic (CAF) phase at 300 K. The CAF structures changed to incommensurate SDW states with complex waveforms whose wavelength are controlled by the artificial periodicity at low temperatures although the CAF structure in the sample with the period of 4.2 nm persisted even at 10 K. The phase transition depends on the thickness of the Cr layers intervening between Sn monatomic layers. An appreciable phase slip in the SDW was observed during the phase transition in the sample with the period of 10.2 nm. The SDW structure is discussed by taking account of the competing forces between the nesting of Fermi surface and a pinning of antinodes at the Sn monatomic layers.
 thin films grown on
thin films grown on  -Al
-Al O
O substrates by pulsed laser deposition
substrates by pulsed laser depositionShinohara, Ryuji*; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Yamamoto, Shunya; Ito, Hisayoshi; Asai, Keisuke*
Journal of Materials Science Letters, 21(12), p.967 - 969, 2002/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:38.57(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 -anatase film on Si(001) substrate with TiN and SrTiO
-anatase film on Si(001) substrate with TiN and SrTiO as buffer layers
as buffer layersSugiharuto; Yamamoto, Shunya; Sumita, Taishi; Miyashita, Atsumi
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 13(13), p.2875 - 2881, 2001/04
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:60.82(Physics, Condensed Matter)An epitaxial TiO -anatase thin film was grown on the Si(001) substrate with SrTiO
-anatase thin film was grown on the Si(001) substrate with SrTiO /TiN as the buffer layers by pulsed laser deposition technique under an oxygen gas supply. The characterization of the epitaxial TiO
/TiN as the buffer layers by pulsed laser deposition technique under an oxygen gas supply. The characterization of the epitaxial TiO -anatase film was performed using the X-ray diffraction method. The crystallographic relationships between the TiO
-anatase film was performed using the X-ray diffraction method. The crystallographic relationships between the TiO -anatase film and SrTiO
-anatase film and SrTiO /TiN buffer layers were analyzed by the
/TiN buffer layers were analyzed by the  -2
-2 scan and pole figure measurement. The growth direction of the films was determined as
scan and pole figure measurement. The growth direction of the films was determined as 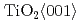 /
/ 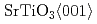 /
/ 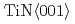 /
/ 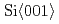 and their in-plane relationship
and their in-plane relationship 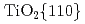 //
// 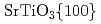 //
// 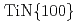 //
// 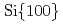 . The crystalline quality of TiO
. The crystalline quality of TiO -anatase was examined by the rocking curve analysis. The composition of the thin film packaging was characterized by Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) using 2.0 MeV
-anatase was examined by the rocking curve analysis. The composition of the thin film packaging was characterized by Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) using 2.0 MeV  He beam.
He beam.
Dai, Z.*; Naramoto, Hiroshi; Narumi, Kazumasa; Yamamoto, Shunya
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 11(43), p.8511 - 8516, 1999/11
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:56.18(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
Dai, Z.*; Miyashita, Atsumi; Yamamoto, Shunya; Narumi, Kazumasa; Naramoto, Hiroshi
Thin Solid Films, 347(1-2), p.117 - 120, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:77.74(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 -SiC by multiple-energy ion implantation
-SiC by multiple-energy ion implantationZ.J.Zhang*; Naramoto, Hiroshi; Miyashita, Atsumi; B.Stritzker*; J.K.N.Lindner*
Physical Review B, 58(19), p.12652 - 12654, 1998/11
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:62.58(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 /BaTiO
/BaTiO multilayer films
multilayer filmsYoneda, Yasuhiro*; ; Sakaue, Kiyoshi*; Terauchi, Hikaru*
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 32, p.S1636 - S1638, 1998/02
no abstracts in English