Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Miwa, Kazuji; Namekawa, Masakazu*; Shimada, Taro; Takeda, Seiji
MRS Advances (Internet), 7(7-8), p.165 - 169, 2022/03
We have developed evaluation method of radiocesium (RCs) migration by surface runoff and soil erosion in considering vertical distribution of RCs in initial contaminated soil and concentration of RCs in different particle size. RCs migration on ground surface during single year has been evaluated in virtual site contaminated uniformly by Cs-137. As a result, RCs has concentrated in the impoundment, and 0.18% of total inventory in the site migrated into the sea. These results suggest that surface migration of RCs effects increasing of external exposure at impoundment and internal exposure from ingestion of marine product.
 Cs washoff from bare land in Fukushima
Cs washoff from bare land in FukushimaIgarashi, Yasunori*; Onda, Yuichi*; Wakiyama, Yoshifumi*; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Kato, Hiroaki*; Kozuka, Shohei*; Manome, Ryo*
Science of the Total Environment, 769, p.144706_1 - 144706_9, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:16.79(Environmental Sciences)Naoe, Takashi; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Wakui, Takashi; Wakai, Eiichi; Haga, Katsuhiro; Takada, Hiroshi
Materials Science Forum, 1024, p.111 - 120, 2021/03
The mercury target vessel for the at the J-PARC neutron source is severely damaged by the cavitation caused by proton beam-induced pressure waves in mercury. To mitigate the cavitation damage, we adopted a double-walled structure with a narrow channel for the mercury at the beam window of the vessel. In addition, gas microbubbles were injected into the mercury to suppress the pressure waves. The front end of the vessel was cut out to inspect the effect of the damage mitigation technologies on the interior surface. The results showed that the double-walled target facing the mercury with gas microbubbles operating at 1812 MWh for an average power of 434 kW had equivalent damage to the single-walled target without microbubbles operating 1048 MWh for average power of 181 kW. The erosion depth due to cavitation in the narrow channel was clearly smaller than it was on the wall facing the bubbling mercury
Naoe, Takashi; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Wakui, Takashi; Wakai, Eiichi; Haga, Katsuhiro; Takada, Hiroshi
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 28, p.081004_1 - 081004_6, 2020/02
The beam window of the mercury target vessel in J-PARC is severely damaged by the cavitation. The cavitation damage is a crucial factor to limit lifetime of the target because it increases with the beam power. Therefore, mitigating cavitation damage is an important issue to operate the target stably for long time at 1 MW. At J-PARC, to mitigate the cavitation damage: gas microbubbles are injected into mercury for suppressing pressure waves, and double-walled structure with a narrow channel of 2 mm in width to form high-speed mercury flow ( 4m/s) has been adopted. After operation, the beam window was cut to inspect the effect of the cavitation damage mitigation on inner wall. We optimized cutting conditions through the cold cutting tests, succeeding in cutting the target No.2 (without damage mitigation technologies) smoothly in 2017, and target No.8 with damage mitigation technologies. In the workshop, progress of cavitation damage observation for the target vessel will be presented.
4m/s) has been adopted. After operation, the beam window was cut to inspect the effect of the cavitation damage mitigation on inner wall. We optimized cutting conditions through the cold cutting tests, succeeding in cutting the target No.2 (without damage mitigation technologies) smoothly in 2017, and target No.8 with damage mitigation technologies. In the workshop, progress of cavitation damage observation for the target vessel will be presented.
 Cs, and their time dependence
Cs, and their time dependenceWakiyama, Yoshifumi*; Onda, Yuichi*; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Igarashi, Yasunori*; Kato, Hiroaki*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 210, p.105990_1 - 105990_12, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:60.05(Environmental Sciences)Naoe, Takashi; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Tanaka, Nobuatsu*; Futakawa, Masatoshi
Advanced Experimental Mechanics, 4, p.17 - 21, 2019/08
We have introduced the following two techniques to mitigate the pressure wave-induced cavitation damage in the mercury target. One is the gas microbubble injection into the flowing mercury, and the other is the double-walled structure with a narrow gap channel at the proton beam entrance portion of the mercury vessel. The latter is expected to mitigate the cavitation damage due to the high-speed liquid flow ( 4 m/s) and the narrow gap boundary (2 mm). To quantitatively investigate the effect of double-walled structure on cavitation damage, cavitation damage tests were conducted by parametrically changing mercury flow velocity and gap width of the channel wall. The results showed that the damage evaluated as a surface roughness was reduced by increasing the flow velocity. By contrast, the effect of gap width on cavitation damage was hardly observed under flowing conditions.
4 m/s) and the narrow gap boundary (2 mm). To quantitatively investigate the effect of double-walled structure on cavitation damage, cavitation damage tests were conducted by parametrically changing mercury flow velocity and gap width of the channel wall. The results showed that the damage evaluated as a surface roughness was reduced by increasing the flow velocity. By contrast, the effect of gap width on cavitation damage was hardly observed under flowing conditions.
Jo, Mayumi*; Ono, Makoto*; Nakayama, Masashi; Asano, Hidekazu*; Ishii, Tomoko*
Geological Society Special Publications, 482, 16 Pages, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.76(Geology)Yang, B.*; Onda, Yuichi*; Wakiyama, Yoshifumi*; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Sekimoto, Hitoshi*; Ha, Y.*
Environmental Pollution, 208(Part B), p.562 - 570, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:45.67(Environmental Sciences)Ishimoto, Yuki; Goto, Yoshitaka*; Arai, Takashi; Masaki, Kei; Miya, Naoyuki; Oyama, Naoyuki; Asakura, Nobuyuki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 350(3), p.301 - 309, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:79.97(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Thermal properties of the redeposition layer on the inner plate of the W-shaped divertor of JT-60U have been measured with laser flash method for the first time so as to estimate transient heat loads onto the divertor. Measurement of a redeposition layer sample of more than 200 m thick showed following results: (1) the bulk density of the redeposition layer is about half of that of carbon fiber composite material; (2) the specific heat of the layer is roughly equal to that of the isotropic graphite; (3) the thermal conductivity of the redeposition layer is two orders of magnitude smaller than that of the carbon fiber composite. The difference between the divertor heat loads and the loss of the plasma stored energy becomes smaller taking account of thermal properties of the redeposition layer on the inner divertor, whereas estimated heat loads due to the ELMs is still larger than the loss. This is probably caused by the poloidal distribution of the thermal properties and heat flux asymmetry inherent in the device.
Hayashi, Takao; Ochiai, Kentaro; Masaki, Kei; Goto, Yoshitaka*; Kutsukake, Chuzo; Arai, Takashi; Nishitani, Takeo; Miya, Naoyuki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 349(1-2), p.6 - 16, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:55.89(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Deuterium concentrations and depth profiles in plasma-facing graphite tiles used in the divertor of JT-60U were investigated by NRA. The highest deuterium concentration of D/ C of 0.053 was found in the outer dome wing tile, where the deuterium accumulated probably through the deuterium-carbon co-deposition. In the outer and inner divertor target tiles, the D/
C of 0.053 was found in the outer dome wing tile, where the deuterium accumulated probably through the deuterium-carbon co-deposition. In the outer and inner divertor target tiles, the D/ C data were lower than 0.006. Additionally, the maximum (H+D)/
C data were lower than 0.006. Additionally, the maximum (H+D)/ C in the dome top tile was estimated to be 0.023 from the results of NRA and SIMS. OFMC simulation showed energetic deuterons caused by NBI were implanted into the dome region with high heat flux. Furthermore, the surface temperature and conditions such as deposition and erosion significantly influenced the accumulation process of deuterium. The deuterium depth profile, SEM observation and OFMC simulation indicated the deuterium was considered to accumulate through three processes: the deuterium-carbon co-deposition, the implantation of energetic deuterons and the deuterium diffusion into the bulk.
C in the dome top tile was estimated to be 0.023 from the results of NRA and SIMS. OFMC simulation showed energetic deuterons caused by NBI were implanted into the dome region with high heat flux. Furthermore, the surface temperature and conditions such as deposition and erosion significantly influenced the accumulation process of deuterium. The deuterium depth profile, SEM observation and OFMC simulation indicated the deuterium was considered to accumulate through three processes: the deuterium-carbon co-deposition, the implantation of energetic deuterons and the deuterium diffusion into the bulk.
Kubo, Hirotaka; JT-60 Team
Plasma Science and Technology, 8(1), p.50 - 54, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.73(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Hiroo; Takemura, Morio*; Yamauchi, Michinori*; Fischer, U.*; Ida, Mizuho*; Mori, Seiji*; Nishitani, Takeo; Simakov, S.*; Sugimoto, Masayoshi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 75-79, p.1169 - 1172, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:39.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the IFMIF, activated erosion/corrosion materials of Li target back wall deposits on a surface of the Li loop. Therefore, accessibility during maintenance of the Li loop pipings will depend on the activation level of the deposition materials. This paper evaluates effect of target activation on the accessibility of the Li loop pipings. Activation level is calculated by the ACT-4 code. High energy cross section above 15 MeV is introduced using IEAF-2001 data. In this calculation, target material is stainless steel 316. Area of the erosion/corrosion in the back wall is 100 cm . The erosion/corrosion rate is 1 micron/y. Dose rate around the Li loop after one year IFMIF operation is evaluated assuming 1% deposition of the erosion/corrosion materials and uniform deposition on surface area of 33 m
. The erosion/corrosion rate is 1 micron/y. Dose rate around the Li loop after one year IFMIF operation is evaluated assuming 1% deposition of the erosion/corrosion materials and uniform deposition on surface area of 33 m . Permissible level for hands-on maintenance is 10 microSv/hr. As the results, after 1 week from shutdown, close maintenance work 8 cm to the Li loop is possible. Also, after 1 month, hands-on maintenance becomes possible.
. Permissible level for hands-on maintenance is 10 microSv/hr. As the results, after 1 week from shutdown, close maintenance work 8 cm to the Li loop is possible. Also, after 1 month, hands-on maintenance becomes possible.
Naoe, Takashi; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Oi, Toshiyuki; Ishikura, Shuichi*; Ikeda, Yujiro
Zairyo, 54(11), p.1184 - 1190, 2005/11
High power spallation targets for neutron sources are being developed in the world. Mercury target will be installed at the material science and life facility in J-PARC, which will promote innovative science. The mercury target is subject to the pressure wave caused by the proton bombarding in the mercury. The pressure wave propagation induces the cavitation in mercury that imposes localized impact damage on the target vessel. The impact erosion is a critical issue to decide the lifetime of the target. The electro Magnetic IMpact Testing Machine, MIMTM, was developed to reproduce the localized impact erosion damage and evaluate the damage formation. Additionally, droplet impact analysis was carried out to investigate the correlation between isolate pit profile and micro-jet velocity. We confirmed that value of depth/radius was able to estimate micro jet-velocity. And the velocity at 560W in MIMTM was estimated to be 225 325 m/s. Furthermore, surface-hardening treatments were inhibited pit formation in plastic deformation.
325 m/s. Furthermore, surface-hardening treatments were inhibited pit formation in plastic deformation.
Futakawa, Masatoshi; Naoe, Takashi*; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Date, Hidefumi*; Ikeda, Yujiro
JSME International Journal, Series A, 48(4), p.234 - 239, 2005/10
Mercury target will be installed at the material science and life facility in J-PARC, which will promote innovative science. The mercury target will be subjected to the pressure wave caused by proton bombarding in the mercury. The pressure wave propagation induces the cavitation in mercury that imposes localized impact damage on the target vessel. The impact erosion is a critical issue to decide the lifetime of target. An electromagnetic impact testing machine, MIMTM, was developed to reproduce the localized impact erosion damage and evaluate the damage formation. Additionally, droplet impact analyses were carried out to investigate the correlation between isolate pit profile and micro-jet velocity. We confirmed that the value of depth/radius was applicable to estimate micro-jet velocity, and the velocity at 560 W in MIMTM equivalent to 1MW proton beam injection was 300 m/s approximately.
Naoe, Takashi*; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Koyama, Tomofumi*; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Ikeda, Yujiro
Jikken Rikigaku, 5(3), p.280 - 285, 2005/09
no abstracts in English
Roth, J.*; Kirschner, A.*; Bohmeyer, W.*; Brezinsek, S.*; Cambe, A.*; Casarotto, E.*; Doerner, R.*; Gauthier, E.*; Federici, G.*; Higashijima, Satoru; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 337-339, p.970 - 974, 2005/03
Times Cited Count:97 Percentile:98.47(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In the frame work of the EU Task Force on Plasma-Wall Interaction and the International Tokamak Physics Activity an attempt was made to establish a possible dependence of the chemical erosion yield of carbon on the ion flux,  , involving ion beam experiments, plasma simulators, and fusion devices. After data normalization a fit using Bayesian probability analysis was performed yielding a decrease of the erosion yield with
, involving ion beam experiments, plasma simulators, and fusion devices. After data normalization a fit using Bayesian probability analysis was performed yielding a decrease of the erosion yield with 
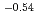 at high ion fluxes. With this dependence on ion flux a comprehensive description is available for chemical erosion as function of energy, temperature and ion flux. Using this dependence the erosion and redeposition of carbon in the ITER divertor can be calculated using the ERO code and the steady-state plasma scenario given by the ITER team. The resulting gross and net erosion rates are compared to previous estimates using a constant erosion yield of 1.5%. The use of the complete parameter dependence results in an order of magnitude lower erosion, most strongly determined by the temperature dependence and the reduction at the highest fluxes.
at high ion fluxes. With this dependence on ion flux a comprehensive description is available for chemical erosion as function of energy, temperature and ion flux. Using this dependence the erosion and redeposition of carbon in the ITER divertor can be calculated using the ERO code and the steady-state plasma scenario given by the ITER team. The resulting gross and net erosion rates are compared to previous estimates using a constant erosion yield of 1.5%. The use of the complete parameter dependence results in an order of magnitude lower erosion, most strongly determined by the temperature dependence and the reduction at the highest fluxes.
Futakawa, Masatoshi; Naoe, Takashi*; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Ikeda, Yujiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(11), p.1059 - 1064, 2004/11
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:60.50(Nuclear Science & Technology)High power spallation targets for neutron sources are developing in the world. Mercury target will be installed at the material and life science facility in J-PARC, which will promote innovative science. The mercury target is subject to the pressure wave caused by the proton bombarding mercury. The pressure wave propagation induces the cavitation in mercury that imposes localized impact damage on the target vessel. The impact erosion is a critical issue to decide the lifetime of the target. The electric Magnetic Impact Testing Machine, MIMTM, was developed to produce the localized impact erosion damage and evaluate the damage formation. Acoustic vibration measurement was carried out to investigate the correlation between damage and acoustic vibration. It was confirmed that the acoustic vibration is useful to predict the damage due to the localized impact erosion and to diagnose the structural integrity.
Roth, J.*; Preuss, R.*; Bohmeyer, W.*; Brezinsek, S.*; Cambe, A.*; Casarotto, E.*; Doerner, R.*; Gauthier, E.*; Federici, G.*; Higashijima, Satoru; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 44(11), p.L21 - L25, 2004/11
Times Cited Count:99 Percentile:89.66(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Chemical erosion of carbon has been studied in ion beam experiments, and the yield values are available as a function of ion energy and surface temperature. ITER divertor condition, however, cannot be simulated by ion beam. For extrapolating to ITER, the erosion must be investigated in plasma simulators and in SOL or divertors of present fusion devices. In the past, erosion values were reported, but the values showed a wide scatter as a function of ion flux,  . Therefore, a joint attempt was made through the EU Task Force on Plasma-Wall Interaction and the International Tokamak Physics Activity (ITPA) to clarify the flux dependence. For each data point the local plasma conditions were normalized to impact energy of 30 eV, the data were selected for a surface temperature close to the maximum yield or to room temperature, and the diagnostic was calibrated in-situ. Through this procedure, the previous large scatter could be drastically reduced. A fit using Bayesian probability analysis was performed yielding a decrease of the erosion yield with
. Therefore, a joint attempt was made through the EU Task Force on Plasma-Wall Interaction and the International Tokamak Physics Activity (ITPA) to clarify the flux dependence. For each data point the local plasma conditions were normalized to impact energy of 30 eV, the data were selected for a surface temperature close to the maximum yield or to room temperature, and the diagnostic was calibrated in-situ. Through this procedure, the previous large scatter could be drastically reduced. A fit using Bayesian probability analysis was performed yielding a decrease of the erosion yield with 
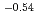 at high ion fluxes.
at high ion fluxes.
Nakamura, Hiroo; Riccardi, B.*; Loginov, N.*; Ara, Kuniaki*; Burgazzi, L.*; Cevolani, S.*; Dell'Ocro, G.*; Fazio, C.*; Giusti, D.*; Horiike, Hiroshi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 329-333(1), p.202 - 207, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:64.92(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF), being developed by EU, JA, RF and US, is a deuteron-lithium (Li) reaction neutron source for fusion materials testing. In the end of 2002, 3 year Key Element technology Phase (KEP) to reduce the key technology risk factors has been completed. This paper describes these KEP tasks results. To evaluate Li flow characteristics, a water and Li flow experiments have been done. To develop Li purification system, evaluation of nitrogen and tritium gettering materials have been done. Conceptual design of remote handling and basic experiment have been donde. In addition, safety analysis and diganostics design have been done. In the presentation, the latest design and future prospects will be also summarized.
Soyama, Hitoshi*; Futakawa, Masatoshi
Tribology Letters, 17(1), p.27 - 30, 2004/07
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:58.59(Engineering, Chemical)Estimation have been made, resulting in a general method for the prediction of the incubation time for cavitation erosion using various cavitating conditions and materials. From a single erosion test, the incubation time can be estimated for various conditions and materials by plotting the mass loss as a function of exposure time to cavitation on a log-log scale.