Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamada, Ryohei; Odagiri, Taiki*; Iwaoka, Kazuki*; Hosoda, Masahiro*; Tokonami, Shinji*
Radiation Environment and Medicine, 8(1), p.21 - 25, 2019/02
We evaluate radon/thoron and its progeny concentration using passive-type monitors using CR-39 plates. After exposure, it is necessary to do chemical etching for CR-39 plates. In the present study, we considered shortening of chemical etching time for CR-39 and enlargement of the track diameter (i.e. etch pit diameter) aiming for introduction of automatic counting system in the future. Optimum conditions were determined by changing solution concentration, solution temperature and etching time. As a result, the optimized conditions (concentration, temperature and etching time) were determined to be 8 M NaOH solution, 75 degrees Celsius and 10 hours. This result of etching time showed that the chemical etching was completed in less than half of conventional etching time. Furthermore, it was suggested that shorter etching time would be possible if we do not consider the enlargement of conventional track diameter.
Lee, C. G.; Iguchi, Kazunari; Esaka, Fumitaka; Magara, Masaaki; Sakurai, Satoshi; Watanabe, Kazuo; Usuda, Shigekazu
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 245(2), p.440 - 444, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.64(Instruments & Instrumentation)The etching rates of fission track detectors made of polycarbonate containing uranium particles were measured after thermal neutron irradiation with fluence of 8 10
10 n/cm
n/cm , in order to study the influence of uranium enrichment on the etching rate that was calculated from the weight loss by etching. There is a strong correlation between the etching rate of detector and the enrichment E of uranium particle: the former increases as the latter increases. Particularly, the etching rate per particle was proportional to E
, in order to study the influence of uranium enrichment on the etching rate that was calculated from the weight loss by etching. There is a strong correlation between the etching rate of detector and the enrichment E of uranium particle: the former increases as the latter increases. Particularly, the etching rate per particle was proportional to E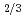 rather than E
rather than E , which is probably due to the overlapping of fission tracks. The etching behaviors of detector revealed that the existence of two different etching rate regions, a nonlinear region in the beginning of etching process and a subsequent constant region, which was explained as the opening of fission tracks and the broadening of opened tracks, respectively.
, which is probably due to the overlapping of fission tracks. The etching behaviors of detector revealed that the existence of two different etching rate regions, a nonlinear region in the beginning of etching process and a subsequent constant region, which was explained as the opening of fission tracks and the broadening of opened tracks, respectively.
Iguchi, Kazunari; Esaka, Konomi; Lee, C. G.; Inagawa, Jun; Esaka, Fumitaka; Onodera, Takashi; Fukuyama, Hiroyasu; Suzuki, Daisuke; Sakurai, Satoshi; Watanabe, Kazuo; et al.
Radiation Measurements, 40(2-6), p.363 - 366, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:58.78(Nuclear Science & Technology)In particle analysis for safeguards environmental samples, the fission track technique is very important to detect sub-micrometer particles containing uranium. In the technique the authors developed, the particles were recovered onto the polycarbonate membrane filter. The filter was dissolved in solvent and dried to form a thin film of detector, in which the particles were confined. After thermal neutron irradiation and etching, the particles of interest in the detector were easily identified with fission tracks, and were picked up for isotope ratio analysis. It was found, however, that the particles in the vicinity of the detector surface may fall off during the etching process. Therefore, optimization of the etching condition is required. In this work, the effects of etching time and enrichment of uranium in particles were investigated. Preliminary results suggest that etching time should be shorter with the increase in the enrichment.
Zhu, Z.; Maekawa, Yasunari; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Suzuki, Yasuyuki; Yonezawa, Noriyuki*; Yoshida, Masaru
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 217(3), p.449 - 456, 2004/05
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:75.84(Instruments & Instrumentation)The pretreatment effects using UV light illumination and DMF soaking on bulk and track etching rates of PET films were investigated. The wavelength of illuminated UV light plays an important role in sensitizing track etching. Illumination with the light at wavelengths longer than 320nm showed strong enhancement in the track etching rates without influence on the bulk etching rates, whereas light with the wavelengths lower than 320nm causes large enhancement in both track and bulk etching rates even in the interior of the material. The track etching rate is found to be not constant along ion tracks, which is attributed to the inhomogeneous distribution of reactive chemical species induced during post-UV light illumination. Furthermore, the DMF soaking of PET after UV light illumination can enhance the etching sensitivity of the track by more than 100 times. The phenomenon is attributed to the high diffusion of organic solution along tracks after UV light illumination.
Teraoka, Yuden
Nano Tekunoroji Daijiten, p.340 - 351, 2003/12
The current status of microprocesses using synchrotron radiation in Japan was reviewed. The SR-excited process is followed by SR-excited surface modification, SR-excited crystal growth and SR-excited etching. The SR-excited surface modification is followed by SR-gas-excited surface modification and SR-direct-excited surface modification. The SR-excited crystal growth is followed by SR-excited atomic layer epitaxy and SR-excited chemical vapor deposition. THe SR-excited etching is followed by SR-direct-excited etching, SR-gas-excited etching and SR ablation.
 and YVO
and YVO laser crystal integration by a direct bonding technique
laser crystal integration by a direct bonding techniqueSugiyama, Akira; Fukuyama, Hiroyasu; Katsumata, Masaki*; Okada, Yukikatsu*
Integrated Optical Devices: Fabrication and Testing (Proceedings of SPIE Vol.4944), p.361 - 368, 2003/00
We report recent progress in bonding of crystals used in microchip lasers, Nd:YVO and non-doped YVO
and non-doped YVO crystal that functions as a cold finger. The bonding technique consists of a dry etching process for polished crystal surfaces to be bonded and a successive transformation from hydrogen bonding to oxygen-bridged bonding at temperature below half of the melting point of crystal. Roughness of the surfaces was less than 0.2-lambda at 633 nm. After the etching of around 30 nm by an argon ion beam, the surfaces were contacted in the clean ambient, then heat treatment was done for 50 hours in a vacuum furnace. To evaluate the bonded region, we made optical scattering measurements, and laser oscillation tests pumped by a laser diode with the output power of 20 W. From these experiments, it was clear that the number of defects on the bonded surface is much smaller than that of the intrinsic defects, and the integrated crystal, improving thermal conductivity, can produce twice of laser output power compared with a usual one.
crystal that functions as a cold finger. The bonding technique consists of a dry etching process for polished crystal surfaces to be bonded and a successive transformation from hydrogen bonding to oxygen-bridged bonding at temperature below half of the melting point of crystal. Roughness of the surfaces was less than 0.2-lambda at 633 nm. After the etching of around 30 nm by an argon ion beam, the surfaces were contacted in the clean ambient, then heat treatment was done for 50 hours in a vacuum furnace. To evaluate the bonded region, we made optical scattering measurements, and laser oscillation tests pumped by a laser diode with the output power of 20 W. From these experiments, it was clear that the number of defects on the bonded surface is much smaller than that of the intrinsic defects, and the integrated crystal, improving thermal conductivity, can produce twice of laser output power compared with a usual one.
J.Vacik*; J.Cervena*; V.Hnatowicz*; S.Posta*; D.Fink*; Naramoto, Hiroshi; Kobayashi, Yoshinori*; Hirata, K.*; P.Strauss*
Radiat. Eff. Defects Solids, 147, p.177 - 186, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
;
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 67(12), p.4302 - 4303, 1998/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:50.96(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Shiwaku, Hideaki; Yoda, Yoshitaka*; Harami, Taikan; ; Ono, Hideo
JAERI-Research 94-032, 44 Pages, 1994/11
no abstracts in English
Komaki, Yoshihide; ; Sakurai, Tsutomu; Matsumoto, Yasuyo*
Radiat. Meas., 23(4), p.725 - 729, 1994/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 on fission tracks in polyvinylidene fluoride
on fission tracks in polyvinylidene fluoride; ; Ishikawa, Niro;
J.Electron Microsc., 31(2), p.191 - 193, 1982/00
no abstracts in English
;
J.Electron Microsc., 30(4), p.292 - 297, 1981/00
no abstracts in English
Nucl.Tracks, 13(1-2), p.33 - 44, 1979/00
no abstracts in English
;
Science, 199(4327), p.421 - 422, 1978/00
Times Cited Count:14no abstracts in English
;
Journal of Applied Physics, 47(4), p.1355 - 1358, 1976/04
Times Cited Count:13no abstracts in English
; ; Izui, Kazuhiko;
Journal of Applied Physics, 46(3), p.1155 - 1158, 1975/03
Times Cited Count:6no abstracts in English
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 26(1), p.143 - 148, 1969/01
Times Cited Count:5no abstracts in English
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 26(1), p.143 - 148, 1969/00
no abstracts in English
Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Yamamoto, Shunya; Sugimoto, Masaki; Kitamura, Akane; Sawada, Shinichi; Yamaki, Tetsuya
no journal, ,
Chemical etching of polymer films irradiated with heavy ions leads to the formation of ion-track membranes with nanoscale pores in different shapes. Particularly, conically-shaped pores are expected to have a potential to create metallic nanoneedles by combination of vapor-deposition and electroplating methods. In this study, we prepared copper nanoneedles inside the conical pores of polyimide (PI)-based ion-track membranes and investigated their morphology. The PI films were irradiated with  Ar ions. The irradiated films were etched in a sodium hypochlorite solution at 60
Ar ions. The irradiated films were etched in a sodium hypochlorite solution at 60 C for 0.5 h, leading to the formation of conical pores with a surface diameter of ca. 500 nm. A very thin Au layer was deposited on this pore side of the ion-track membranes; then, it was used as a cathode for electroplating copper into the pores. After dissolving the PI templates, we obtained the copper needles ca. 500 nm in base diameter and 1.2
C for 0.5 h, leading to the formation of conical pores with a surface diameter of ca. 500 nm. A very thin Au layer was deposited on this pore side of the ion-track membranes; then, it was used as a cathode for electroplating copper into the pores. After dissolving the PI templates, we obtained the copper needles ca. 500 nm in base diameter and 1.2  m in height on copper plates.
m in height on copper plates.
 O
O thin films by ion beam sputter deposition method
thin films by ion beam sputter deposition methodFujita, Masaya*; Yamaguchi, Kenji; Asaoka, Hidehito; Mao, W.*; Chikada, Takumi*; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Terai, Takayuki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English