Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Uchida, Shunsuke; Karasawa, Hidetoshi; Kino, Chiaki*; Pellegrini, M.*; Naito, Masanori*; Osaka, Masahiko
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 380, p.111256_1 - 111256_19, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:55.57(Nuclear Science & Technology)It is essential to grasp the long-term distributions of FP as well as fuel debris all over the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F) for safe completion of its decommissioning projects. The fuel debris is going to be removed from the plant under the severe conditions of FP being scattered during major decommissioning work, and then, the decommissioning projects are going to be terminated by storing safely the removed debris as recovered fertile materials or as materials for final radioactive disposal. In order to determine the FP distribution in the plant for the long period from the accident occurrence to the termination of the plant decommissioning, procedures for analyzing multi-term FP behaviors were proposed. The proposed procedures should be improved by applying the FP data measured in the plant and validated based on the feedback data. Then, the accuracy-improved procedures should be applied to estimate FP distribution during each period of the decommissioning projects.
Uchida, Shunsuke; Pellegrini, M.*; Naito, Masanori*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 380, p.111303_1 - 111303_11, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)Multi-term FP analysis procedures were developed to determine FP distribution all over F1 not only for analyzing accident propagation but also for planning its decommissioning projects. They should be validated based on the measured FP data. One of the useful tools for their validation was application of the dose rate data monitored by the containment atmosphere monitoring system (CAMS). However, in order to compare the data with different characteristics and dimensional units, e.g., FP distribution (kg, Bq) and dose rate (Sv/h), application of the conversion factors bridging them would be effective and useful. In order to prepare speedy, easy-to-handle and tractable procedures to calculate radiation dose rates at the CAMS detector locations, dose rate conversion factors were determined for major source locations and major radionuclides. The dose rates could be easily calculated by multiplying FP amounts obtained with the multiterm FP analysis procedures by the conversion factors.
Idomura, Yasuhiro; Ina, Takuya*; Ali, Y.*; Imamura, Toshiyuki*
Dai-34-Kai Suchi Ryutai Rikigaku Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 6 Pages, 2020/12
A new communication avoiding (CA) Krylov solver with a FP16 (half precision) preconditioner is developed for a semi-implicit finite difference solver in the Gyrokinetic Toroidal 5D full-f Eulerian code GT5D. In the solver, the bottleneck of global collective communication is resolved using a CA-Krylov subspace method, and halo data communication is reduced by the FP16 preconditioner, which improves the convergence property. The FP16 preconditioner is designed based on the physics properties of the operator and is implemented using the new support for FP16 SIMD operations on A64FX. The solver is ported also on GPUs, and the performance of ITER size simulations with 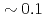 trillion grids is measured on Fugaku (A64FX) and Summit (V100). The new solver accelerates GT5D by
trillion grids is measured on Fugaku (A64FX) and Summit (V100). The new solver accelerates GT5D by 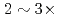 from the conventional non-CA solver, and excellent strong scaling is obtained up to 5,760 CPUs/GPUs both on Fugaku and Summit.
from the conventional non-CA solver, and excellent strong scaling is obtained up to 5,760 CPUs/GPUs both on Fugaku and Summit.
 bus FP results and single effect testing
bus FP results and single effect testingKnebel, K.*; Jokiniemi, J.*; Bottomley, D.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(9-10), p.772 - 789, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:53.17(Nuclear Science & Technology)Revaporisation of the fission products deposited in the primary circuit of a reactor was identified as a possible late source of fission product release during a severe accident: eg. loss of coolant accident (LOCA). Subsequent testing has shown that revaporisation is very likely to occur given a breach of the reactor and is an important contributor for the source term release to the containment and biosphere. The first part reviews the revaporisation mechanisms of Cs and other volatile or semi-volatile fission products transported in the primary circuit that were derived from the Phebus FP and associated programmes. The second part examines the separate effects testing to determine the high temperature chemistry ofvolatile and semi-volatile fission products (I, Mo, Ru) and structural materials (Ag, B) as well as atmospheric effects which substantially affect the source term. Finally, it examines Cs data from reactor accident sites that is providing additional knowledge of longer-term fission product chemistry. The results have been summarised in the form of a table and schematic diagram. This accumulated knowledge and experience has important applications to minimising contamination during decommissioning and site remediation techniques, as well as improving SA simulation codes and raising nuclear safety.
Mizuta, Naoki; Aoki, Takeshi; Ueta, Shohei; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Yan, X.
Proceedings of 27th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-27) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2019/05
Enhancement of safety and cooling performance of fuel elements are desired for a commercial High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR). Applying sleeveless fuel elements and dual side directly cooling structures with oxidation resistant SiC-matrix fuel compact has a possibility of improving safety and cooling performance at the pin-in-block type HTGR. The irradiated effective thermal conductivity of a fuel compact is an important physical property for core thermal design of the pin-in-block type HTGR. In order to discuss the irradiated effective thermal conductivity of the SiC-matrix fuel compact which could improve the cooling performance of the reactor, the maximum fuel temperature during normal operation of the pin-in-block type HTGR with dual side directly cooling structures are analytically evaluated. From these results, the desired irradiated thermal conductivity of SiC matrix are discussed. In addition, the suitable fabrication method of SiC-matrix fuel compact is examined from viewpoints of the sintering temperature, the purity and the mass productivity.
Nishihara, Kenji
ImPACT Fujita Puroguramu Kokai Seika Hokokukai "Kaku Henkan Niyoru Koreberu Hoshasei Haikibutsu No Ohaba Na Teigen, Shigenka" Seika Hokokusho, Shiryoshu, p.28 - 31, 2019/03
In this project, long-lived fission products (LLFP) contained in conventional high-level radioactive wastes are separated and their life is reduced, and elements that can be used as resources are separated. By shortening the life of LLFP, it has been shown that it may be possible to dispose in intermediate depth of several tens of meters, meeting safety requirements, instead of geological disposal. In addition, for reassuring recycling of usable elements, possible exposure pathways were evaluated to estimate the safe concentration level of radioactivity.
Nishihara, Kenji
ImPACT Fujita Puroguramu Kokai Seika Hokokukai "Kaku Henkan Niyoru Koreberu Hoshasei Haikibutsu No Ohaba Na Teigen, Shigenka" Seika Hokokusho, Shiryoshu, p.130 - 133, 2019/03
High level radioactive waste contains elements with various characteristics. It is possible to reduce the load on the disposal site by separating them according to those characteristics and appropriately dealing with them. In this project, we are working to shorten the life span of long-lived fission products (LLFP). When this technology is realized, high-level radioactive wastes will become new radioactive wastes with low radioactivity. As a result of investigation of disposal concept of new radioactive waste, it turned out that intermediate-depth disposal currently considered for low level radioactive waste may be suitable. Intermediate-depth disposal is a method of small-scale disposal in shallow locations as compared to geological disposal for conventional high-level radioactive waste. We conducted a safety assessment when this disposal is applied to new radioactive wastes, and found that it is possible to safely dispose of for the four LLFPs addressed by this project.
 Zr
ZrKawase, Shoichiro
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (122), p.75 - 80, 2019/02
Zirconium-93 is one of major long-lived fission products contained in high-level radioactive waste. This report introduces an experimental study of proton-and deuteron-induced spallation reactions on  Zr at 105 MeV per nucleon in inverse kinematics carried out at RIKEN RI Beam Factory. The isotopic production cross sections for a wide range of isotopes including stable ones were obtained. The experimental results were compared to the PHITS calculations considering both the intra-nuclear cascade and evaporation processes.
Zr at 105 MeV per nucleon in inverse kinematics carried out at RIKEN RI Beam Factory. The isotopic production cross sections for a wide range of isotopes including stable ones were obtained. The experimental results were compared to the PHITS calculations considering both the intra-nuclear cascade and evaporation processes.
Ishikawa, Jun; Zheng, X.; Shiotsu, Hiroyuki; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2018 (ASRAM 2018) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2018/10
Usami, Shin; Kishimoto, Yasufumi*; Taninaka, Hiroshi; Maeda, Shigetaka
JAEA-Technology 2018-003, 97 Pages, 2018/07
The decay heat used for effectiveness evaluation of the prevention measures against severe accidents in the prototype fast breeder reactor Monju was evaluated by applying the updated nuclear data libraries based on JENDL-4.0, reflecting the realistic core operation pattern, and setting the rational extent of uncertainty. The decay heats of fission products, the actinide nuclides such as Cm-242, and radioactive structural materials were calculated by FPGS code. The decay heat of U-239 and Np-239 was evaluated based on ANSI/ANS-5.1-1994. The calculation uncertainty of each decay heat was evaluated based on summation of uncertainty factors, C/E values of reaction rates obtained in Monju system startup test, and so on. Furthermore, the decay heat evaluation method based on the FPGS90 was verified by the comparison of the results of the decay heat measurement of the two spent MOX fuel subassemblies in the experimental fast reactor Joyo MK-II core.
Aihara, Jun; Ueta, Shohei; Goto, Minoru; Inaba, Yoshitomo; Shibata, Taiju; Ohashi, Hirofumi
JAEA-Technology 2018-002, 70 Pages, 2018/06
HTFP code is code for calculation of additional release amount of fission product (FP) from fuel rod in high temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR) after stop of fission. Minory changed Fornax-A code also can calculate that. Therefore, release behavior of Cs calculated with HTFP code was compared with that calculated with minory modified FORNAX-A code in this report. Release constants of Cs evaluated with minory modified FORNAX-A code are rather different from default values for HTFP code.
Hidaka, Akihide; Yokoyama, Hiroya
Proceedings of Symposium on Water Chemistry and Corrosion in Nuclear Power Plants in Asia 2017 (AWC 2017) (USB Flash Drive), p.29 - 42, 2017/09
no abstracts in English
Matsuki, Takuya; Yamanaka, Atsushi; Sekine, Megumi; Suzuki, Satoshi*; Yasuda, Takeshi; Tsutagi, Koichi; Tomikawa, Hirofumi; Nakamura, Hironobu; LaFleur, A. M.*; Browne, M. C.*
Proceedings of INMM 58th Annual Meeting (Internet), 8 Pages, 2017/07
The Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP) has been developing a new detector from 2015 to 2017 for purpose to monitor Pu amount in High Active Liquid Waste (HALW) containing FP. It can make a contribution to an advanced approach to effectively and efficiently conduct safeguards for reprocessing facilities because it becomes available to monitor and verify nuclear material movement continuously by a new detector, which has proposed by IAEA. For the second step of this project, we conducted dose rate measurement on the guide rail installing in the cell storing the HALW tank and comparison between measured dose rate distribution and calculation result by MCNP simulation in order to investigate the dose rate distribution which is needed for shielding design of a new detector that is used for radiation (neutron/ spectrum) measurement in the cell and inquest on the monitoring position of the detector for Pu monitoring. In this paper, we report the result of the dose rate measurement in the cell, improvement of the simulation model which is cleared by comparison between measurement result and calculation result and our future plan.
spectrum) measurement in the cell and inquest on the monitoring position of the detector for Pu monitoring. In this paper, we report the result of the dose rate measurement in the cell, improvement of the simulation model which is cleared by comparison between measurement result and calculation result and our future plan.
Ho, H. Q.; Honda, Yuki; Goto, Minoru; Takada, Shoji
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 103, p.114 - 121, 2017/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:55.98(Nuclear Science & Technology)Osaka, Masahiko; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Miwa, Shuhei; Di Lemma, F. G.*; Miyahara, Naoya; Suzuki, Chikashi; Suzuki, Eriko; Okane, Tetsuo; Kobata, Masaaki
Proceedings of 8th European Review Meeting on Severe Accident Research (ERMSAR 2017) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2017/05
Fundamental research on fission product (FP) chemistry is underway at Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The purpose is to establish a FP chemistry database in each region of a LWR under severe accident conditions. Improvement of FP chemical models based on this database is also an important task of the research. Research outputs are reflected to the research and development of decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) and the enhancement of LWR safety. Four research items have thus been established considering the specific issues of 1F and the priority in the source term research area, as follows: - Effects of boron (B) release kinetics and thermal-hydraulic conditions on FP behavior, - Cesium (Cs) chemisorption and reactions with structural materials, - Establishment of a thermodynamic and thermophysical properties database for FP compounds, - Development of experimental and analytical techniques for the reproduction of FP behavior. In this paper, results and progress of the research are presented.
Usami, Shin; Kishimoto, Yasufumi; Taninaka, Hiroshi; Maeda, Shigetaka
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors; Unifying Theory and Experiments in the 21st Century (PHYSOR 2016) (USB Flash Drive), p.3263 - 3274, 2016/05
The present paper describes the validation of the new decay heat evaluation method using FPGS90 code with both the updated nuclear data library and the rational extent of uncertainty, by comparing the results of the decay heat measurement of the spent fuel subassemblies in Joyo MK-II core and by comparing with the calculation results of ORIGEN2.2 code. The calculated values of decay heat (C) by FPGS90 based on the JENDL-4.0 library were coincident with the measured ones (E) within the calculation uncertainties, and the C/E ranged from 1.01 to 0.93. FPGS90 evaluated the decay heat almost 3% larger than ORIGEN2.2, and it improved the C/E in comparison with the ORIGEN2.2 code. Furthermore, The C/E by FPGS90 based on the JENDL-4.0 library was improved than that based on the JENDL-3.2 library, and the contribution of the revision of reaction cross section library to the improvement was dominant rather than that of the decay data and fission yield data libraries.
Kora, Kazuki*; Nakaya, Hiroyuki*; Matsuura, Hideaki*; Goto, Minoru; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Shimakawa, Satoshi*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 300, p.330 - 338, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:45.07(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to investigate the potential of high temperature gas-cooled reactors (HTGRs) for transmutation of long-lived fission products (LLFPs), numerical simulation of four types of HTGRs were carried out. In addition to the gas-turbine high temperature reactor system "GTHTR300", a small modular HTGR plant "HTR50S" and two types of plutonium burner HTGRs "Clean Burn with MA" and "Clean Burn without MA" were considered. The simulation results show that an early realization of LLFP transmutation using a compact HTGR may be possible since the HTR50S can transmute fair amount of LLFPs for its thermal output. The Clean Burn with MA can transmute a limited amount of LLFPs. However, an efficient LLFP transmutation using the Clean Burn without MA seems to be convincing as it is able to achieve very high burn-ups and produce LLFP transmutation more than GTHTR300. Based on these results, we propose utilization of variety of HTGRs for LLFP transmutation and storage.
Takai, Toshihide; Sato, Isamu*; Yamashita, Shinichiro; Furukawa, Tomohiro
JAEA-Technology 2015-043, 56 Pages, 2016/02
Fundamental research on FP-chemistry for fission product release behaviors under severe accident was carried out for reinforcement of source term evaluation, and implementation of the 1F decommissioning R&D project. There were subjects to clarified (1) FP chemistry behavior between vapor species release and aerosol formation and (2) physical parameters which would be affect subsequent aerosol's chemical behavior, for improvement of FP transport model. Applicability of measuring/analyzing techniques presently used was studied for evaluating foregoing properties. And the validity was verified by trial measurements. In conclusion, Raman spectrometry and high temperature X-ray diffraction were hopeful to determine FP-chemical form against vapor/aerosol species and aerosol species, respectively. Combination use of cascade impactor and scanning type electron microscope with energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometry was hopeful to determine physical parameters of aerosol.
Nomoto, Yasunobu; Aihara, Jun; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Isaka, Kazuyoshi; Ohashi, Hirofumi
JAEA-Data/Code 2015-008, 39 Pages, 2015/06
HTFP is a calculation code for amount of additionally released fission product (FP) from fuel rods of pin-in-type according to transient of core temperature at the accident of high temperature gas-cooled reactors (HTGRs). This code analyzes FP release inventory from core according to the transient of core temperature at the accident as an input data and considering FP release rate from a fuel compact and a graphite sleeve and radioactive decay of FP. This report describes the outline of HTFP code and its input data. The computed solutions using the HTFP code were compared to those of HTCORE code, which was used for the design of the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) to validate the analysis models of the HTFP code. The comparison of HTFP code results with HTCORE code results showed the good agreement.
Sato, Isamu; Onishi, Takashi; Tanaka, Kosuke; Iwasaki, Maho; Koyama, Shinichi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 461, p.22 - 28, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:56.39(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In order to evaluate B influence on the release and transport of Cs and I during severe accidents, basic experiments have been performed on the interaction between deposited Cs/I compounds and vapor/aerosol B compounds. CsI and B O
O were utilized as a Cs/I compound and a B compound, respectively. Deposited CsI on the thermal gradient tube (TGT), which is exposed to temperatures ranging from 423 K to 1023 K was reacted with vapor/aerosol B
were utilized as a Cs/I compound and a B compound, respectively. Deposited CsI on the thermal gradient tube (TGT), which is exposed to temperatures ranging from 423 K to 1023 K was reacted with vapor/aerosol B O
O , and then observed to determine how it changed Cs/I decomposition profiles. As a result, vapor/aerosol B
, and then observed to determine how it changed Cs/I decomposition profiles. As a result, vapor/aerosol B O
O stripped a portion of deposited CsI within a temperature range from 830 K to 920 K to make gaseous CsBO
stripped a portion of deposited CsI within a temperature range from 830 K to 920 K to make gaseous CsBO and I
and I . In addition, gaseous I
. In addition, gaseous I was re-deposited at a temperature range from 530 K to 740 K, while CsBO
was re-deposited at a temperature range from 530 K to 740 K, while CsBO travelled through the sampling tubes and filters without deposition. It is implied that B influences Cs carriers such as CsBO
travelled through the sampling tubes and filters without deposition. It is implied that B influences Cs carriers such as CsBO to transport Cs to the colder regions.
to transport Cs to the colder regions.