Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Mochizuki, Akihito; Matsui, Hiroya; Nakayama, Masashi; Sakamoto, Ryo*; Shibata, Masahito*; Motoshima, Takayuki*; Jo, Mayumi*
Case Studies in Construction Materials, 22, p.e04648_1 - e04648_20, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Construction & Building Technology)The properties of low-pH cement used in the geological disposal of radioactive waste may change through atmospheric carbonation and degradation caused by groundwater during the long-term operation of a repository. In this study, we investigated the effects of atmospheric carbonation and groundwater contact on the chemical, microstructural, and transport properties of shotcrete made from low-pH, high-fly-ash silica-fume cement (HFSC) over a period of 16 years in an underground research laboratory. In both carbonated and degraded zones of the HFSC shotcrete, capillary porosity increased for pores of  300 nm in diameter, and the total porosity was higher than in undegraded zones. These changes in porosity may be associated with the decalcification of calcium-silicate-hydrate and decomposition of ettringite. Such changes were minor in altered zones of OPC shotcrete, indicating that HFSC shotcrete is less resistant to atmospheric carbonation and groundwater leaching under the studied conditions. However, the hydraulic conductivity in HFSC was low enough to fulfill the specific functional requirements of low-pH cements for geological disposal.
300 nm in diameter, and the total porosity was higher than in undegraded zones. These changes in porosity may be associated with the decalcification of calcium-silicate-hydrate and decomposition of ettringite. Such changes were minor in altered zones of OPC shotcrete, indicating that HFSC shotcrete is less resistant to atmospheric carbonation and groundwater leaching under the studied conditions. However, the hydraulic conductivity in HFSC was low enough to fulfill the specific functional requirements of low-pH cements for geological disposal.
 and Na
and Na O additives on properties synthetic rock of fly ash from municipal waste incinerator
O additives on properties synthetic rock of fly ash from municipal waste incineratorMitamura, Hisayoshi; Bamba, Tsunetaka; Maeda, Toshikatsu
Nihon Seramikkusu Kyokai Gakujutsu Rombunshi, 110(1277), p.55 - 59, 2002/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:19.00(Materials Science, Ceramics)Influence of additives and hot-pressing temperature on properties of the synthetic rock was investigated, which was developed for making harmless and stabilizing fly ash from municipal waste incinerator. Sintering test at 1200 C for 16 h revealed that addition of 20 and 1.5 wt% of TiO
C for 16 h revealed that addition of 20 and 1.5 wt% of TiO and Na
and Na O, respectively, is necessary for preparation of dense products. X-ray diffractometry showed that these additives promoted the formation of perovskite (CaTiO
O, respectively, is necessary for preparation of dense products. X-ray diffractometry showed that these additives promoted the formation of perovskite (CaTiO ) and gehlenite (Ca
) and gehlenite (Ca Al
Al SiO
SiO ) minerals. During hot pressing, bulk density of the synthetic rock increased steeply with temperature between 1000 and 1100
) minerals. During hot pressing, bulk density of the synthetic rock increased steeply with temperature between 1000 and 1100 C. On the other hand, its open porosity decreased rapidly with temperature between 1050 and 1150
C. On the other hand, its open porosity decreased rapidly with temperature between 1050 and 1150 C. These facts imply that the temperature of 1100
C. These facts imply that the temperature of 1100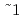 150
150 C is practical in hot pressing of fly ash.
C is practical in hot pressing of fly ash.
Yanase, Shinichiro*; Sugitsue, Noritake; Ishimori, Yuu; Yokoyama, Kaoru; Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Takahashi, Nobuo; Rong, D.*; Takeda, Hiroshi*; Kochi, Toshinori*; Takami, Toshihiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Otake, Yoshinori; Tambo, Masaki; Kabir, M.*; Inada, Arisa; Fukaya, Hiroyuki; Kida, Takashi
no journal, ,
In March 2011, a large amount of radioactive cesium (hereinafter referred to as Cs) was dispersed over a wide area as a result of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident after the devastating earthquake that occurred in Japan. The incinerated ash containing Cs generated by environmental decontamination has become a problem due to lack of storage space. The purpose of this study is to reduce the volume of designated waste that needs to be preserved by removing Cs from incinerator ash using Electrokinetic (EK) method. Two electrodes are placed in the polluted materials (i.e. incinerator ash for this study) with electrolyte solution and a DC voltage is applied in between the electrodes. It can be understood that the Cs ions will move to the cathode side and thus it will be removed from the incinerator ash. At first, a preliminary experiment was conducted with commercially available ash polluted with stable Cs with the concentration ratio 50 mg/kg. We found that more than 80% of stable Cs was separated from the ash with the EK treatment. Then we performed the EK treatment with two types of radioactive contaminated ashes (i.e. fly ash and bottom ash). The radioactive concentration of Cs was about 3,000 Bq/kg to 5,000 Bq/kg for the ashes. We succeeded in the separation of Cs from the ashes. Further works will be carried out with various test conditions, such as, the type of electrolyte and the structure of the test apparatus etc.