Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 = 0.01-600
= 0.01-600 C,
C,  = 1-3000 bars,
= 1-3000 bars, 
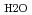 = 0.35-1.1 g cm
= 0.35-1.1 g cm , and
, and 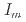 = 0
= 0
Walker, C. S.*; Arthur, R. C.*; Anraku, Sohtaro; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Mihara, Morihiro
Applied Geochemistry, 175, p.106086_1 - 106086_17, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The thermodynamic properties and revised Helgeson-Kirkham-Flowers equation of state (r-H-K-F EoS) parameters of the hydrated (Si(OH) (aq), SiO(OH)
(aq), SiO(OH)
 and SiO
and SiO (OH)
(OH)
 ) and fictive dehydrated (SiO
) and fictive dehydrated (SiO (aq), HSiO
(aq), HSiO
 and SiO
and SiO
 ) monomeric silicon species are used extensively to describe the pH, composition, temperature, and pressure dependence of formation/breakdown reactions of all silicon-bearing compounds globally. Experimental log10 equilbrium constant, K values describing the formation reactions of the hydrated and dehydrated monomeric silicon species were therefore compiled from the literature, extrapolated to zero ionic strength by specific ion interaction theory as required and used to derive their thermodynamic properties and r-H-K-F EoS parameters. Consideration of all formation reactions in the same study provides a collective, internally consistent update to the thermodynamic properties and r-H-K-F EoS parameters of the monomeric silicon species that can provide a satisfactory match to the experimental log10 K values at
) monomeric silicon species are used extensively to describe the pH, composition, temperature, and pressure dependence of formation/breakdown reactions of all silicon-bearing compounds globally. Experimental log10 equilbrium constant, K values describing the formation reactions of the hydrated and dehydrated monomeric silicon species were therefore compiled from the literature, extrapolated to zero ionic strength by specific ion interaction theory as required and used to derive their thermodynamic properties and r-H-K-F EoS parameters. Consideration of all formation reactions in the same study provides a collective, internally consistent update to the thermodynamic properties and r-H-K-F EoS parameters of the monomeric silicon species that can provide a satisfactory match to the experimental log10 K values at  = 0.01-600
= 0.01-600 C,
C,  = 1-3000 bars,
= 1-3000 bars, 
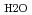 = 0.35-1.1 g cm
= 0.35-1.1 g cm , and zero ionic strength. These temperature and pressure limits comfortably bracket t=0.01-100
, and zero ionic strength. These temperature and pressure limits comfortably bracket t=0.01-100 C and P =1-270 bars relecant to the geological disposal of radioactive wastes at depths of up to 1 km.
C and P =1-270 bars relecant to the geological disposal of radioactive wastes at depths of up to 1 km.
Yamada, Raiki; Takahashi, Toshiro*; Ogita, Yasuhiro
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences (Internet), 118(1), p.221219a_1 - 221219a_26, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:32.60(Mineralogy)Oligocene to Miocene volcanic rocks from the Toyama basin of the SW Japan arc, that were formed during back-arc spreading in the Japan Sea, were examined to reveal their petrogeneses and temporal change of arc volcanism during the Japan Sea opening. We reported whole-rock major and trace element and Sr-Nd isotopic compositions of andesites and rhyolites (23-16 Ma) and quantitatively discussed their petrogenesis, based on comparison with the results of model calculations, in this paper. Main concluding remarks are as follows: (1) Rhyolite magmas were generated by crustal assimilation of basaltic to andesitic magmas. (2) Andesites consist of high-Mg andesite, high-Sr, and tholeiitic andesite, generated by interaction among slab fluid, slab melt, and crustal material. (3) Upwelling of the asthenospheric mantle into the mantle wedge caused melting of the subducting Pacific plate, and andesitic magmatism induced rhyolitic magmatism.
Takeda, Seiji; ; Kimura, Hideo; Matsuzuru, Hideo
JAERI-Research 95-069, 47 Pages, 1995/11
no abstracts in English
; Sato, Tsutomu; Nagano, Tetsushi; Yanase, Nobuyuki; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Isobe, Hiroshi; Onuki, Toshihiko; Sekine, Keiichi
JAERI-Review 95-011, 94 Pages, 1995/07
no abstracts in English
Kimura, Hideo; Takahashi, Tomoyuki; ; Matsuzuru, Hideo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 32(5), p.439 - 449, 1995/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:17.20(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
; ; ; ; Sakamoto, Yoshiaki; ; ; ; Nagasaki, Shinya*; ; et al.
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 37(1), p.59 - 77, 1995/00
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:73.48(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Kimura, Hideo; Takahashi, Tomoyuki; ; Matsuzuru, Hideo
JAERI-Research 94-028, 50 Pages, 1994/11
no abstracts in English
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 32(10), p.970 - 974, 1990/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:56.87(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Nichifutsu Rikoka Kaishi, (44), p.1 - 28, 1988/00
no abstracts in English
Watanabe, Takahiro; Nara, Fumiko*; Matsunaka, Tetsuya*; Minoura, Koji*; Kakegawa, Takeshi*; Yamasaki, Shinichi*; Tsuchiya, Noriyoshi*; Nakamura, Toshio*; Junbo, W.*; Liping, Z.*
no journal, ,
Understanding of past environmental and geochemical changes is significant issues to estimate global climate variation. Therefore, these changes have been studied by continuous terrestrial sediments. The high-time resolution past environmental changes, especially monsoon fluctuations, have been reported in previous studies using geochemical signatures in stalagmites from Asian caves. However, continuous climate records in Tibetan plateau have not yet been cleared, which a key area to understand mechanism of monsoon fluctuations. In this study, mean grain size and geochemical proxies from lake sediment cores from south Tibetan plateau were used for estimation of past monsoon changes during Holocene. Spectral analysis of the mean grain size in the Tibetan lake indicated 1000-1500 years climate cycles, which might be caused by the changes in solar activities. These monsoon fluctuations based on the mean grain size were also supported by geochemical proxies in this study.
Nara, Fumiko*; Yamasaki, Shinichi*; Watanabe, Takahiro; Tsuchiya, Noriyoshi*; Miyahara, Hiroko*; Kato, Takenori*; Minoura, Koji*; Kakegawa, Takeshi*
no journal, ,
High-time resolution measurements of the major and trace inorganic elements, such as Rb and Sr, from the Lake Baikal sediment core was carried out to estimate the weathering response and the material provenance in the lake watershed. The fluctuations of the Rb/Sr ratio and mean grain size (MGS) during the Holocene were corresponding with each other. The similar profiles between the Rb/Sr ratio and the MGS from loess sediment in China have been observed in previous study. These results imply that the Rb/Sr ratio can be used as the proxy to estimate the East Asian winter monsoon intensity.
Kawasaki, Yohei*; Yagisawa, Makoto*; Granata, G.*; Tokoro, Chiharu*; Ohara, Yoshiyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English