Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Inoue, Rintaro*; Kanaya, Toshiji*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Shibata, Kaoru; Fukao, Koji*
Physical Review E, 97(1), p.012501_1 - 012501_6, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:60.88(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In this study, we investigate the  process of a polystyrene thin film using inelastic neutron scattering (INS), dielectric relaxation spectroscopy (DRS), and thermal expansion spectroscopy (TES). The DRS and TES measurements exhibited a decrease in glass transition temperature (
process of a polystyrene thin film using inelastic neutron scattering (INS), dielectric relaxation spectroscopy (DRS), and thermal expansion spectroscopy (TES). The DRS and TES measurements exhibited a decrease in glass transition temperature (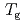 ) with film thickness. On the other hand, an increase in
) with film thickness. On the other hand, an increase in 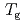 was observed in INS studies. In order to interpret this contradiction, we investigated the temperature dependence of the peak frequency (
was observed in INS studies. In order to interpret this contradiction, we investigated the temperature dependence of the peak frequency (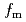 ) of the
) of the  process probed by DRS and TES. The experiments revealed an increase in the peak frequency (
process probed by DRS and TES. The experiments revealed an increase in the peak frequency (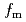 ) with decreasing film thickness in the frequency region. This observation is consistent with the observed decrease in
) with decreasing film thickness in the frequency region. This observation is consistent with the observed decrease in 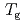 with thickness. The discrepancy between INS and DRS or TES descriptions of the
with thickness. The discrepancy between INS and DRS or TES descriptions of the  process is likely to be attributed to a decrease in the apparent activation energy with film thickness and reduced mobility, due to the impenetrable wall effect.
process is likely to be attributed to a decrease in the apparent activation energy with film thickness and reduced mobility, due to the impenetrable wall effect.
Katayama, Yoshinori; Inamura, Yasuhiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 238(1-4), p.154 - 159, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:52.13(Instruments & Instrumentation)It is well know that many substances have different structures in the crystalline state and they exhibit first-order structural phase transitions by a change in pressure. On the other hand, pressure-induced structural changes in the liquid and glassy states were supposed to be monotonous. The recent development of synchrotron radiation sources enables us to perform structural studies on liquids and glasses under high pressure and high temperature conditions. These studies revealed that the changes in the liquid and glassy states are not necessarily monotonous. We will present recent results on liquid phosphorus and silica glass.
Yokota, Terufumi
Physical Review B, 70(17), p.174422_1 - 174422_14, 2004/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:13.17(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Phase transitions in the infinite-range p-state Potts glass model is studied in the presence of a field. Phase transition line into the transverse ordered phase is a straight line in a field-temperature phase diagram for small field and small effective ferromagnetic interaction. This is in contrast with the Gabay-Toulouse line for the vector spin-glass model. Replica symmetry breaking pattern is discussed near the phase transition line. Replica symmetry for the longitudinal order parameter is weakly broken at higher temperature than the transition line to the transverse ordered phase for p 3.2. For p
3.2. For p 4.6, the transition to the transverse ordered phase reveals discontinuity in the order parameter just as the p
4.6, the transition to the transverse ordered phase reveals discontinuity in the order parameter just as the p 4 case without a field.
4 case without a field.
Katayama, Yoshinori; Inamura, Yasuhiro
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 15(1), p.S343 - S350, 2003/01
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:60.46(Physics, Condensed Matter)Combination of synchrotron radiation sources and large volume presses enable us to make in-situ observations of structural change in liquids and glasses at high pressures up to several GPa and high temperatures up to 1500K. A number of methods, X-ray diffraction, XAFS, density measurement by means of X-ray absorption, viscosity measurements by means of radiography, are now applicable for this purpose. We have systematically studied elemental liquid and found that a characteristic structural change occurs in a narrow pressure-temperature range in liquid selenium. Moreover we have found a sudden structural change in liquid phosphorus. Experimental results on phosphorus support a view that the change is a first-order liquid-liquid transition. In the talk, results of current attempt to detect sudden structural change in silica glass will be presented. A preliminary result of X-ray diffraction study on liquid water under high-pressure will be also reported.
Physics Letters A, 212, p.109 - 114, 1996/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:30.23(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Tabata, Yoneho*; ; ; Seguchi, Tadao
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 48(5), p.563 - 568, 1996/00
no abstracts in English
Physical Review B, 51(2), p.962 - 971, 1995/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.11(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
JAERI-M 92-181, 126 Pages, 1992/12
no abstracts in English
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 4, p.2615 - 2622, 1992/00
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:56.62(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
Physica A, 185, p.336 - 339, 1992/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
;
Physical Review A, 42(4), p.2176 - 2183, 1990/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.26(Optics)no abstracts in English
;
Physical Review A, 41(4), p.1990 - 1996, 1990/02
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:67.86(Optics)no abstracts in English
;
Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 117-118, p.92 - 95, 1990/00
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:43.26(Materials Science, Ceramics)no abstracts in English
;
Proc. of the Yamada Conf. XXIV on Strongly Coupled Plasma Physics, p.683 - 686, 1990/00
no abstracts in English