Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Morii, Shiori; Yomogida, Takumi; Asai, Shiho*; Ouchi, Kazuki; Oka, Toshitaka; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Bunseki Kagaku, 72(10.11), p.441 - 448, 2023/10
Rapid analytical method for the determination of Zr-93 in radioactive wastes has been developed. Laser ablation (LA)-ICP-MS was applied to the analysis of Zr isotopes in simulated high-level radioactive waste (HLW). Sample preparation time was dramatically reduced by using a DGA resin as the adsorbent for Zr. Direct quantification of Zr isotopes in this resin sample was carried out by LA-ICP-MS. Laser settings were optimized to obtain a reliable isotope ratio of the sample by LA-ICP-MS. Quantification of Zr isotopes in the simulated HLW solution by isotope dilution mass spectrometry (IDMS) was examined. The amount of Zr-90 in the sample obtained by IDMS corresponded to a value calculated from the given concentration of Zr in the sample within uncertainty. Thus, this method can be applied for the quantification of Zr-93 in radioactive wastes.
Igarashi, Hiroshi
JAEA-Review 2020-006, 261 Pages, 2020/09
A literature review was conducted on the increase in surface area of vitrified products of HLW due to the fracturing caused by cooling during glass pouring process and by mechanical impact, from the perspective of a parameter of the radionuclide release model in the performance assessment of geological disposal system studied overseas. The review was focused on the value of surface area increase factor set as a parameter in the model, the experimental work to evaluate an increase in surface area, and how the parameters on surface area were determined based on the experimental results. The surface area obtained from the experiments executed in Japan was also discussed in comparison with the overseas studies. On the basis of the investigation, the effects of various conditions on the surface area were studied, such as a diameter of vitrified product, cooling condition during and after the glass pouring, impact on vitrified products during their handling, environment after the closure of disposal facility, and others. The causes of fracturing are associated with the phenomena or events in the waste management process such as production, transport, storage, and disposal. The surface area increase factors set in the nuclide release model of the glass and their bases were reviewed. In addition, the measured values and the experimental methods for surface increase factors published so far were compared. Accordingly, the methods for measuring surface area as the bases were identified for these factors set in the models. The causes of fracturing and features of these factors were studied with respect to the relation with the waste management process. The results from the review and assessment can contribute to the expanding the knowledge for the conservative and realistic application of these factors to performance assessment, and to the developing and upgrading of safety case as a consequence.
Nishio, Kazuhisa*; Shimizu, Mayuko; Iyatomi, Yosuke; Hama, Katsuhiro
JAEA-Review 2020-013, 59 Pages, 2020/08
The Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting geoscientific study in order to establish a scientific and technological basis for the geological disposal of HLW. Technical information of the result on the geoscientific study conducted at TGC is provided at the annual Information and Opinion Exchange Conference on Geoscientific Study of TGC for exchanging opinions among researchers and engineers from universities, research organizations and private companies. This document compiles the research presentations and posters of the conference in Mizunami on November 20, 2019.
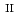 and Si under anoxic and reducing conditions; Structural characteristics of ferrous silicate co-precipitates
and Si under anoxic and reducing conditions; Structural characteristics of ferrous silicate co-precipitatesFrancisco, P. C. M.; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Tachi, Yukio; Doi, Reisuke; Shiwaku, Hideaki
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 270, p.1 - 20, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:74.11(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Nakayama, Masashi
JAEA-Technology 2018-006, 43 Pages, 2018/08
The Horonobe URL Project has being pursued by JAEA to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies through investigations of the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary formation at Horonobe, Hokkaido. The URL Project proceeds in 3 overlapping phases, "Phase I: Surface-based investigations", "Phase II: Investigations during tunnel excavation" and "Phase III: Investigations in the underground facilities", over a period of around 20 years. The OP corrosion test was prepared from 2013 FY at Niche No.3, and heating by electric heater in simulated overpack started in November, 2014. The objective of the test is acquiring data concerned with corrosion of carbon steel OP. These data will be used in order to confirm the performance of engineered barrier system. In the OP corrosion test, the diameter of simulated OP and buffer material are 100 mm and 300 mm, respectively. Concrete support using low alkaline cement was used in order to investigate the effect of cementitious materials to OP corrosion behavior. We will measure corrosion potential of carbon steel, natural potential, pH in buffer material for several years. In this report, we describe how to make simulated OP and buffer material blocks, and set sensors, and so on.
Amamoto, Ippei
Journal of the Society of Inorganic Materials, Japan, 24(391), p.393 - 401, 2017/11
Glass is a non-crystalline solid, as such, it is relatively easy to change its composition to control its characteristics. The borosilicate glass, which is produced by the addition of boron oxide into sodium-lime glass, possesses excellent heat-resistant properties and mechanical strength. It has a wide variety of uses. The borosilicate glass is applied as the vitrified medium for radioactive wastes to immobilize and stabilize them for long term. The glass form which is loaded with high-level radioactive waste is called the vitrified waste. This paper classified the radioactive waste and describes treatment and production methods of vitrified waste, its characteristics, disposal method and also introduces alternative vitrified medium.
Nakayama, Masashi; Matsuzaki, Tatsuji*; Niunoya, Sumio*
JAEA-Research 2016-010, 57 Pages, 2016/08
The Horonobe URL Project has being pursued by JAEA to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies through investigations of the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary formation at Horonobe, northern Hokkaido. The in-situ experiment for performance confirmation of engineered barrier system (EBS experiment) had been prepared from 2013 to 2014 fiscal year at G.L.-350m gallery, and heating by electric heater in simulated overpack had started in January, 2015. One of objectives of the experiment is acquiring data concerned with Thermal -Hydrological - Mechanical - Chemical coupled behavior. These data will be used in order to confirm the performance of engineered barrier system. In this report, It is summarized the production of casing drilling machine for large diameter, simulated overpack, buffer material blocks and backfilling material for EBS experiment.
Nakayama, Masashi; Ono, Hirokazu; Nakayama, Mariko*; Kobayashi, Masato*
JAEA-Data/Code 2016-005, 55 Pages, 2016/07
The Horonobe URL Project has being pursued by JAEA to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies through investigations of the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary formation at Horonobe, northern Hokkaido. The Project consists of two major research areas, "Geoscientific Research" and "Research and Development on Geological Disposal Technologies", and proceeds in three overlapping phases, "Phase I: Surface-based investigations", "Phase II: Investigations during tunnel excavation" and "Phase III: Investigations in the underground facilities". Phase III investigation was started in 2010 fiscal year. The in-situ experiment for performance confirmation of engineered barrier system (EBS experiment) had been prepared from 2013 to 2014 fiscal year at GL-350m gallery, and heating by electric heater in simulated overpack had started in January, 2015. One of objectives of the experiment is acquiring data concerned with Thermal-Hydrological-Mechanical-Chemical (THMC) coupled behavior. These data will be used in order to confirm the performance of engineered barrier system. This report summarizes the measurement data acquired from the EBS experiment from December, 2014 to March, 2016.
Nakayama, Masashi; Ono, Hirokazu; Tanai, Kenji; Sugita, Yutaka; Fujita, Tomoo
JAEA-Research 2016-002, 280 Pages, 2016/06
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project has being pursued by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies through investigations of the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary formation at Horonobe, northern Hokkaido. The URL Project consists of two major research areas, "Geoscientific Research" and "Research and Development on Geological Disposal Technologies", and proceeds in three overlapping phases, "Phase I: Surface-based investigations", "Phase II: Investigations during tunnel excavation" and "Phase III: Investigations in the underground facilities", over a period of around 20 years. Phase III investigation was started in 2010 fiscal year. The in-situ experiment for performance confirmation of engineered barrier system (EBS experiment) had been prepared from 2013 to 2014 fiscal year at G.L.-350m gallery (Niche No.4), and heating by electric heater in simulated overpack had started in January, 2015. One of objectives of the experiment is acquiring data concerned with Thermal-Hydrological-Mechanical-Chemical (THMC) coupled behavior. These data will be used in order to confirm the performance of engineered barrier system. In EBS experiment, the backfill material using mixture of bentonite and muck from Horonobe URL construction was used for backfilling a part of Niche No.4. This report shows the results of properties of the backfill material, confirmation test of compaction method and making backfill material block, and so on. From these results, it was confirmed that the backfill material would satisfy target value of the permeability and the swelling pressure.
Geoscientific Research Department, Tono Geoscience Center
JAEA-Review 2015-015, 39 Pages, 2015/09
In 2014, the JAEA presented the remaining critical issues based on synthesizing R&D results up to date, performed in the approach of whole JAEA reform reflecting the maintenance problems at the fast-breeder reactor "Monju". In this revision, research program of Phase III are restructured based on the critical issues presented in the approach of the whole JAEA reform.
Nakayama, Masashi; Ono, Hirokazu; Nakayama, Mariko*; Kobayashi, Masato*
JAEA-Data/Code 2015-013, 53 Pages, 2015/09
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project has being pursued by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies through investigations of the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary formation at Horonobe, northern Hokkaido. The URL Project consists of two major research areas, "Geoscientific Research" and "Research and Development on Geological Disposal Technologies", and proceeds in three overlapping phases, "Phase I: Surface-based investigations", "Phase II: Investigations during tunnel excavation" and "Phase III: Investigations in the underground facilities", over a period of around 20 years. Phase III investigation was started in 2010 fiscal year. The in-situ experiment for performance confirmation of engineered barrier system (EBS experiment) had been prepared from 2013 to 2014 fiscal year at G.L.-350m gallery, and heating by electric heater in simulated overpack had started in January, 2015. One of objectives of the experiment is acquiring data concerned with Thermal-Hydrological-Mechanical-Chemical (THMC) coupled behavior. These data will be used in order to confirm the performance of engineered barrier system. This report summarizes the measurement data acquired from the EBS experiment. The period of data acquisition is from December, 2014 to March, 2015. It will be periodically published summarized data of EBS experiment.
Takeda, Seiji; Kimura, Hideo
JAERI-Research 2002-014, 20 Pages, 2002/07
no abstracts in English
Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Maeda, Toshikatsu; Ogawa, Hiromichi; Itonaga, Fumio
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.713, p.589 - 596, 2002/00
A large number of studies on HLW glass corrosion have shown that the glass reacts with water to form more stable mineral phases (alteration phases) during the long-term geological disposal. The phase formation is essential to evaluate the radionuclide release from the glass during the long-term disposal. The purpose of this study is to evaluate, experimentally, the mineral phase formation from HLW glass and the associated cesium release. Static corrosion tests were performed on powdered R7T7 glass in alkalline solutions at elevated temperatures to accelerate the reaction, and mineral phases formed were analyzed by XRD. The results showed that analcime (zeolite) is formed as the dominant phase coexisting with SiO (am), and beidellite(smectite) or gibbsite coexists dependiting on the conditions. The solution analysis indicated that most of the cesium is retained in the phases of beidellite and analcime by sorption.
(am), and beidellite(smectite) or gibbsite coexists dependiting on the conditions. The solution analysis indicated that most of the cesium is retained in the phases of beidellite and analcime by sorption.
Ono, Takahiro*; Higuchi, Takanao*; Kazama, T.*; Hashimoto, T.*; Seito, Y.*; Hattori, Tomomi*; Kanamori, Miwa*
JNC TJ1420 2000-005, 257 Pages, 2000/03
None
Kazama, T.*; Hashimoto, T.*; Seito, Y.*; ; Kanamori, Miwa*; ;
JNC TJ1450 2000-001, 160 Pages, 1999/12
no abstracts in English