Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ohashi, Tomonori*; Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Steinle-Neumann, G.*; Hattori, Takanori; Yuan, L.*; Suzuki, Akio*
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences (Internet), 120(1), p.240926a_1 - 240926a_13, 2025/06
We explore the structures of dry and hydrated (H O and D
O and D O) Na
O) Na Si
Si O
O melt at 0-6 GPa and 1000-1300 K and glasses recovered from high pressure and temperatures by in-situ neutron and X-ray diffraction. The structures of the melts at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K are also investigated by ab-initio molecular dynamics simulation. In-situ neutron experiments revealed that the D-O distance increases with compression due to the formation of -O-D-O- bridging species, which is reproduced by the molecular dynamics simulations. The pressure-induced -O-D-O- formation reflects a more rigid incorporation of hydrogen, which acts as a mechanism for the experimentally observed higher solubility of water in silicate melts. Together with shrinking modifier domains, this process dominates the compression behavior of hydrous Na
melt at 0-6 GPa and 1000-1300 K and glasses recovered from high pressure and temperatures by in-situ neutron and X-ray diffraction. The structures of the melts at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K are also investigated by ab-initio molecular dynamics simulation. In-situ neutron experiments revealed that the D-O distance increases with compression due to the formation of -O-D-O- bridging species, which is reproduced by the molecular dynamics simulations. The pressure-induced -O-D-O- formation reflects a more rigid incorporation of hydrogen, which acts as a mechanism for the experimentally observed higher solubility of water in silicate melts. Together with shrinking modifier domains, this process dominates the compression behavior of hydrous Na Si
Si O
O melt, whereas the compression of dry Na
melt, whereas the compression of dry Na Si
Si O
O at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K is governed largely by bending of the Si-O-Si angle. The molecular dynamics simulations on hydrous Na
at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K is governed largely by bending of the Si-O-Si angle. The molecular dynamics simulations on hydrous Na Si
Si O
O melts further suggest that the sodium ions are scavenged from its network-modifying role via 2(
melts further suggest that the sodium ions are scavenged from its network-modifying role via 2(![$$^{[4]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZULV4SI.gif) Si-O
Si-O + Na
+ Na )
) 
![$$^{[4]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZULV4SI.gif) Si-(O-
Si-(O-![$$^{[5]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZVLV4SI.gif) Si-O)
Si-O) + 2Na
+ 2Na and Si-O
and Si-O + Na
+ Na + Si-OH
+ Si-OH  Si-(O-H-O-Si)
Si-(O-H-O-Si) + Na
+ Na with increasing pressure.
with increasing pressure.
 hydridosilicate at high pressures; A Bridge to BaSiH
hydridosilicate at high pressures; A Bridge to BaSiH polyhydride
polyhydrideBeyer, D. C.*; Spektor, K.*; Vekilova, O. Y.*; Grins, J.*; Barros Brant Carvalho, P. H.*; Leinbach, L. J.*; Sannemo-Targama, M.*; Bhat, S.*; Baran, V.*; Etter, M.*; et al.
ACS Omega (Internet), 10(15), p.15029 - 15035, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Hydridosilicates featuring SiH octahedral moieties represent a rather new class of compounds with potential properties relating to hydrogen storage and hydride ion conductivity. Here, we report on the new representative BaSiH
octahedral moieties represent a rather new class of compounds with potential properties relating to hydrogen storage and hydride ion conductivity. Here, we report on the new representative BaSiH obtained from reacting the Zintl phase hydride BaSiH
obtained from reacting the Zintl phase hydride BaSiH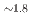 with H
with H fluid at pressures above 4 GPa and subsequent decompression to ambient pressure. It consists of complex SiH
fluid at pressures above 4 GPa and subsequent decompression to ambient pressure. It consists of complex SiH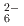 ions, which are octahedrally coordinated by Ba
ions, which are octahedrally coordinated by Ba counterions. The arrangement of Ba and Si atoms deviates only slightly from an ideal fcc NaCl structure. IR and Raman spectroscopy showed SiH
counterions. The arrangement of Ba and Si atoms deviates only slightly from an ideal fcc NaCl structure. IR and Raman spectroscopy showed SiH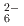 bending and stretching modes in the ranges 800-1200 and 1400-1800 cm
bending and stretching modes in the ranges 800-1200 and 1400-1800 cm , respectively. BaSiH
, respectively. BaSiH is thermally stable up to 95
is thermally stable up to 95 C above which decomposition into BaH
C above which decomposition into BaH and Si takes place. DFT calculations indicated a direct band gap of 2.5 eV. The discovery of BaSiH
and Si takes place. DFT calculations indicated a direct band gap of 2.5 eV. The discovery of BaSiH consolidates the compound class of hydridosilicates, accessible from hydrogenations of silicides at gigapascal pressures (
consolidates the compound class of hydridosilicates, accessible from hydrogenations of silicides at gigapascal pressures (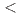 10 GPa). The structural properties of BaSiH
10 GPa). The structural properties of BaSiH suggest that it presents an intermediate (or precursor) for further hydrogenation at considerably higher pressures to the predicted superconducting polyhydride BaSiH
suggest that it presents an intermediate (or precursor) for further hydrogenation at considerably higher pressures to the predicted superconducting polyhydride BaSiH .
.
 under hydrostatic pressure; A Combined neutron, X-ray, Raman, and first-principles calculation study
under hydrostatic pressure; A Combined neutron, X-ray, Raman, and first-principles calculation studyEfthimiopoulos, I.*; Klotz, S.*; Kunc, K.*; Baptiste, B.*; Chauvigne, P.*; Hattori, Takanori
Physical Review B, 111(13), p.134103_1 - 134103_13, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We present a comprehensive study of the high pressure behaviour of ReO using X-ray and neutron diffraction, Raman scattering and first-principles calculations to 15 GPa. We show that the ambient pressure
using X-ray and neutron diffraction, Raman scattering and first-principles calculations to 15 GPa. We show that the ambient pressure 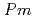
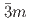 structure converts at 0.7 GPa in a continuous phase transition directly to a cubic phase with space group
structure converts at 0.7 GPa in a continuous phase transition directly to a cubic phase with space group 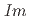
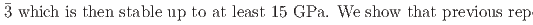 and rhombohedral
and rhombohedral 
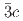 structures in this pressure range are an artifact due to an alteration of the sample by high-flux synchrotron X-ray radiation. The structural pressure dependence of the
structures in this pressure range are an artifact due to an alteration of the sample by high-flux synchrotron X-ray radiation. The structural pressure dependence of the 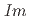
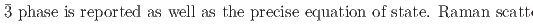 O samples are presented. The data shed light onto the unusual transition and densification mechanism due to progressive tilting of essentially rigid ReO
O samples are presented. The data shed light onto the unusual transition and densification mechanism due to progressive tilting of essentially rigid ReO octahedra.
octahedra.
Xu, J.*; Lang, P.*; Liang, S.*; Zhang, J.*; Fei, Y.*; Wang, Y.*; Gao, D.*; Hattori, Takanori; Abe, Jun*; Dong, X.*; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), p.2445 - 2451, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)The Alder-ene reaction is a chemical reaction between an alkene with an allylic hydrogen, and it provides an efficient method to construct the C-C bond. Traditionally, this reaction requires catalysts, high temperatures, or photocatalysis. In this study, we reported a high-pressure-induced solid-state Alder-ene reaction of 1-hexene at room temperature without a catalyst. 1-Hexene crystallizes at 4.3 GPa and polymerizes at 18 GPa, forming olefins. By exploring gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, we discovered that 1-hexene generates dimeric products through the Alder-ene reaction under high pressures. The in situ neutron diffraction shows that the reaction process did not obey the topochemical rule. A six-membered ring transition state including one C-H  bond and two alkene
bond and two alkene  bonds was evidenced by the theoretical calculation, whose energy obviously decreased when compressed to 20 GPa. Our work offers a novel and promising method to realize the Alder-ene reaction at room temperature without a catalyst, expanding the application of this important reaction.
bonds was evidenced by the theoretical calculation, whose energy obviously decreased when compressed to 20 GPa. Our work offers a novel and promising method to realize the Alder-ene reaction at room temperature without a catalyst, expanding the application of this important reaction.
Miura, Taito*; Miyamoto, Shintoro*; Maruyama, Ippei*; Aili, A.*; Sato, Takumi; Nagae, Yuji; Igarashi, Go*
Case Studies in Construction Materials, 21, p.e03571_1 - e03571_14, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Construction & Building Technology) 4 simulated fuel bundle for validation of thermal-hydraulics simulation codes
4 simulated fuel bundle for validation of thermal-hydraulics simulation codesOno, Ayako; Nagatake, Taku; Uesawa, Shinichiro; Shibata, Mitsuhiko; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of Specialist Workshop on Advanced Instrumentation and Measurement Techniques for Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics and Severe Accidents (SWINTH-2024) (USB Flash Drive), 7 Pages, 2024/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is developing a neutronics/thermal-hydraulics coupling simulation code for light-water reactors. Thermal-hydraulic simulation codes applied to the coupling code are expected to calculate the void fraction distribution in a rod bundle under operational conditions, which are necessary for neutron transport simulation, and need to be validated using void fraction distribution data in a rod bundle under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions. Therefore, we have conducted the measurement of the instantaneous void distribution in the 4  4 simulated fuel bundle using a developed wire mesh sensor, which is installed in the pressurized two-phase flow experimental loop of JAEA to obtain the data for code validation.
4 simulated fuel bundle using a developed wire mesh sensor, which is installed in the pressurized two-phase flow experimental loop of JAEA to obtain the data for code validation.
 structure transition under high pressure
structure transition under high pressureYamanaka, Takamitsu*; Nakamoto, Yuki*; Sakata, Masafumi*; Shimizu, Katsuya*; Hattori, Takanori
Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 51(1), p.4_1 - 4_10, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Neutron and synchrotron X-ray diffraction and electric conductivity measurements of FeTiO ilmenite were performed under pressures. Ilmenite structure is retained up to 28 GPa. Structure analysis revealed that FeO
ilmenite were performed under pressures. Ilmenite structure is retained up to 28 GPa. Structure analysis revealed that FeO and TiO
and TiO are compressible and less compressible below 8 GPa, respectively. The resistivity is lowest along the Fe-Ti direction that has shortest interatomic distance among all the metal ion pairs. The resistivity in the direction normal to c-axis monotonically decreases with pressure, whereas that along c-axis shows hallow-shape with pressure. Maximum entropy analysis shows that electron configuration of Fe
are compressible and less compressible below 8 GPa, respectively. The resistivity is lowest along the Fe-Ti direction that has shortest interatomic distance among all the metal ion pairs. The resistivity in the direction normal to c-axis monotonically decreases with pressure, whereas that along c-axis shows hallow-shape with pressure. Maximum entropy analysis shows that electron configuration of Fe (3
(3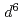 ) is more strongly changed than Ti
) is more strongly changed than Ti (3
(3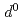 ) under compression. The anisotropic electrical conductivity and non-uniform structure change of Fe-Ti interatomic distance can be explained by the possible spin transition from high-spin state to intermediate-spin state of Fe cation.
) under compression. The anisotropic electrical conductivity and non-uniform structure change of Fe-Ti interatomic distance can be explained by the possible spin transition from high-spin state to intermediate-spin state of Fe cation.
 S-nuclear magnetic resonance measurements
S-nuclear magnetic resonance measurementsYoshida, Shogo*; Haga, Yoshinori; Fujii, Takuto*; Nakai, Yusuke*; Mito, Takeshi*; 8 of others*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(1), p.013702_1 - 013702_5, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Yoshida, Shogo*; Koyama, Takehide*; Yamada, Haruhiko*; Nakai, Yusuke*; Ueda, Koichi*; Mito, Takeshi*; Kitagawa, Kentaro*; Haga, Yoshinori
Physical Review B, 103(15), p.155153_1 - 155153_5, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Temleitner, L.*; Hattori, Takanori; Abe, Jun*; Nakajima, Yoichi*; Pusztai, L.*
Molecules (Internet), 26(5), p.1218_1 - 1218_12, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:8.76(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Total structure factors of per-deuterated methanol and heavy water, CD OD and D
OD and D O, have been determined across the entire composition range at pressures of up to 1.2 GPa, by neutron diffraction. Largest variations due to increasing pressure were observed below
O, have been determined across the entire composition range at pressures of up to 1.2 GPa, by neutron diffraction. Largest variations due to increasing pressure were observed below 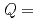 5
5 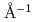 , mostly as shifts of the first and second maxima. Molecular dynamics computer simulations been conducted at the experimental pressures to interpret neutron diffraction results. The peak shifts mentioned above could be qualitatively reproduced by simulations. In order to reveal the influence of changing pressure on the local intermolecular structure, simulated structures have been analyzed in terms of hydrogen bond related partial radial distribution functions and size distributions of hydrogen bonded cyclic entities. Distinct differences between pressure dependent structures of water-rich and methanol-rich composition regions have been revealed.
, mostly as shifts of the first and second maxima. Molecular dynamics computer simulations been conducted at the experimental pressures to interpret neutron diffraction results. The peak shifts mentioned above could be qualitatively reproduced by simulations. In order to reveal the influence of changing pressure on the local intermolecular structure, simulated structures have been analyzed in terms of hydrogen bond related partial radial distribution functions and size distributions of hydrogen bonded cyclic entities. Distinct differences between pressure dependent structures of water-rich and methanol-rich composition regions have been revealed.
Takeda, Takeshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-019, 58 Pages, 2021/01
An experiment denoted as SB-SL-01 was conducted on March 27, 1990 using the Large Scale Test Facility (LSTF) in the Rig of Safety Assessment-IV (ROSA-IV) Program. The ROSA/LSTF experiment SB-SL-01 simulated a main steam line break (MSLB) accident in a pressurized water reactor (PWR). The test assumptions were made such as auxiliary feedwater (AFW) injection into secondary-side of both steam generators (SGs) and coolant injection from high pressure injection (HPI) system of emergency core cooling system into cold legs in both loops. The MSLB led to a fast depressurization of broken SG, which caused a decrease in the broken SG secondary-side wide-range liquid level. The broken SG secondary-side wide-range liquid level recovered because of the AFW injection into the broken SG secondary-side. The primary pressure temporarily decreased a little just after the MSLB, and increased up to 16.1 MPa following the closure of the SG main steam isolation valves. Coolant was manually injected from the HPI system into cold legs in both loops a few minutes after the primary pressure reduced to below 10 MPa. The primary pressure raised due to the HPI coolant injection, but was kept at less than 16.2 MPa by fully opening a power-operated relief valve of pressurizer. The core was filled with subcooled liquid through the experiment. Thermal stratification was seen in intact loop cold leg during the HPI coolant injection owing to the flow stagnation. On the other hand, significant natural circulation prevailed in broken loop. When the continuous core cooling was ensured by the successive coolant injection from the HPI system, the experiment was terminated. The experimental data obtained would be useful to consider recovery actions and procedures in the multiple fault accident with the MSLB of PWR. This report summarizes the test procedures, conditions, and major observations in the ROSA/LSTF experiment SB-SL-01.
Saito, Hiroyuki*; Machida, Akihiko*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Sato, Toyoto*; Orimo, Shinichi*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 587, p.412153_1 - 412153_6, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:24.90(Physics, Condensed Matter)The site occupancy of deuterium (D) atoms in face-centered-cubic nickel (fcc Ni) was measured along a cooling path from 1073 to 300 K at an initial pressure of 3.36 GPa via in situ neutron powder diffraction. Deuterium atoms predominantly occupy the octahedral (O) sites and slightly occupy the tetrahedral (T) sites of the fcc metal lattice. The O-site occupancy increases from 0.4 to 0.85 as the temperature is lowered from 1073 to 300 K. Meanwhile, the T-site occupancy remains c.a. 0.02. The temperature-independent behavior of the T-site occupancy is unusual, and its process is not yet understood. From the linear relation between the expanded lattice volume and D content, a D-induced volume expansion of 2.09(13) 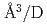 atom was obtained. This value is in agreement with the values of 2.14-2.2
atom was obtained. This value is in agreement with the values of 2.14-2.2 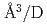 atom previously reported for Ni and Ni
atom previously reported for Ni and Ni Fe
Fe alloy.
alloy.
Aihara, Jun; Goto, Minoru; Ueta, Shohei; Tachibana, Yukio
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-018, 22 Pages, 2020/01
Concept of Pu-burner high temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR) was proposed for purpose of more safely reducing amount of recovered Pu. In Pu-burner HTGR concept, coated fuel particle (CFP), with ZrC coated yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) containing PuO (PuO
(PuO -YSZ) small particle and with tri-structural isotropic (TRISO) coating, is employed for very high burn-up and high nuclear proliferation resistance. ZrC layer is oxygen getter. On the other hand, we have developed Code-B-2.5.2 for prediction of pressure vessel failure probabilities of SiC-tri-isotropic (TRISO) coated fuel particles for HTGRs under operation by modification of an existing code, Code-B-2. The main purpose of modification is preparation of applying code for CFPs of Pu-burner HTGR. In this report, basic formulae are described.
-YSZ) small particle and with tri-structural isotropic (TRISO) coating, is employed for very high burn-up and high nuclear proliferation resistance. ZrC layer is oxygen getter. On the other hand, we have developed Code-B-2.5.2 for prediction of pressure vessel failure probabilities of SiC-tri-isotropic (TRISO) coated fuel particles for HTGRs under operation by modification of an existing code, Code-B-2. The main purpose of modification is preparation of applying code for CFPs of Pu-burner HTGR. In this report, basic formulae are described.
 baddeleyite involving softenings of bulk modulus and atom vibrations
baddeleyite involving softenings of bulk modulus and atom vibrationsFukui, Hiroshi*; Fujimoto, Manato*; Akahama, Yuichi*; Sano, Asami; Hattori, Takanori
Acta Crystallographica Section B; Structural Science, Crystal Engineering and Materials (Internet), 75(4), p.742 - 749, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:76.15(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Monoclinic ZrO baddeleyite exhibits anomalous softenings of bulk modulus and atom vibrations with compression. We have investigated the pressure evolution of the structure by neutron powder diffraction combined with ab-initio calculations. The present results showed that the anomalous pressure response of the bulk modulus is related not to the change in the bonding characters but to the deformation of an oxygen sublattice, especially one of layers made of oxygens in the crystallographic
baddeleyite exhibits anomalous softenings of bulk modulus and atom vibrations with compression. We have investigated the pressure evolution of the structure by neutron powder diffraction combined with ab-initio calculations. The present results showed that the anomalous pressure response of the bulk modulus is related not to the change in the bonding characters but to the deformation of an oxygen sublattice, especially one of layers made of oxygens in the crystallographic  * plane. The layer consists of two parallelograms; one is rotating with little distortion and the other is being distorted with increasing pressure. This deformation of this layer makes one of Zr-O distances long, resulting in the softening of some atom vibrational modes.
* plane. The layer consists of two parallelograms; one is rotating with little distortion and the other is being distorted with increasing pressure. This deformation of this layer makes one of Zr-O distances long, resulting in the softening of some atom vibrational modes.
 Al
Al (O
(O D
D )
) , with temperature at high pressure
, with temperature at high pressureKyono, Atsushi*; Kato, Masato*; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori
Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 46(5), p.459 - 469, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:16.12(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To reveal the decomposition mechanism with temperature under high-pressure, crystal structure of a hydrogrossular, katoite Ca Al
Al (O
(O D
D )
) has been studied by in-situ neutron diffraction at 8 GPa. Although unusual expansion behavior was discerned at 200-400
has been studied by in-situ neutron diffraction at 8 GPa. Although unusual expansion behavior was discerned at 200-400 C, the unit cell was continuously expanded up to 850
C, the unit cell was continuously expanded up to 850 C. At 900
C. At 900 C, katoite was decomposed, indicating that pressure strongly increases dehydration temperature from 300
C, katoite was decomposed, indicating that pressure strongly increases dehydration temperature from 300 C to 900
C to 900 C. On release of pressure, the katoite reappear together with corundum and portlandite. At 8 GPa, CaO
C. On release of pressure, the katoite reappear together with corundum and portlandite. At 8 GPa, CaO and AlO
and AlO polyhedra expand with temperature up to 850
polyhedra expand with temperature up to 850 C by about 8% and 13%, respectively. On the other hand, tetrahedral interstices are isotopically squeezed by about 10%: due to the expansion of above polyhedra. The neighboring D-D distance remains almost unchanged in this temperature range, while the O-D bond distance shrinks drastically just before decomposition. This finding suggests that the shortening of O-D distance caused by the D-D repulsion destabilizes the O-D bond, which induces the thermal decomposition of katoite.
C by about 8% and 13%, respectively. On the other hand, tetrahedral interstices are isotopically squeezed by about 10%: due to the expansion of above polyhedra. The neighboring D-D distance remains almost unchanged in this temperature range, while the O-D bond distance shrinks drastically just before decomposition. This finding suggests that the shortening of O-D distance caused by the D-D repulsion destabilizes the O-D bond, which induces the thermal decomposition of katoite.
Ono, Ayako; Suzuki, Takayuki*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 26th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-26) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2018/07
The mechanism of critical heat flux (CHF) for higher system pressure remains to be clarified, even though it is important to evaluate the CHF for the light water reactor (LWR) which is operated under the high pressure condition. In this study, the process of bubble coalescence was simulated by using a computational multi-fluid dynamics (CMFD) simulation code TPFIT under various system pressure in order to investigate the behavior of bubbles as a basic study. The growth of bubbles was simulated by blowing of vapor from a tiny orifice simulating bubble bottom. One or four orifices were located on the bottom surface in this simulation study. The numerical simulations were conducted by varying the pressure and temperature.
Ishii, Yusuke*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Nakano, Satoshi*; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Kagi, Hiroyuki*
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 20(24), p.16650 - 16656, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:19.53(Chemistry, Physical)The structure of an aluminum layered hydroxide, boehmite ( -AlOOH), as a function of pressure was studied by using
-AlOOH), as a function of pressure was studied by using  synchrotron X-ray and neutron diffraction. Peak broadening and subsequent splitting, which are only found for hkl (h
synchrotron X-ray and neutron diffraction. Peak broadening and subsequent splitting, which are only found for hkl (h 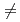 0) peaks in the X-ray diffraction patterns above 25 GPa, are explained by stacking disorder accompanied with a continuously increasing displacement of the AlO
0) peaks in the X-ray diffraction patterns above 25 GPa, are explained by stacking disorder accompanied with a continuously increasing displacement of the AlO octahedral layer along a-axis. This finding could be the first experimental result for the pressure-induced stacking disorder driven by the continuous layer displacement. The magnitude of the layer displacement was estimated from the X-ray scattering profile calculation based on the stacking disordered structure model. Hydrogen bond geometries of boehmite, obtained by structure refinements on the observed neutron diffraction patterns for deuterated sample up to 10 GPa, show linearly approaching O-D covalent and D
octahedral layer along a-axis. This finding could be the first experimental result for the pressure-induced stacking disorder driven by the continuous layer displacement. The magnitude of the layer displacement was estimated from the X-ray scattering profile calculation based on the stacking disordered structure model. Hydrogen bond geometries of boehmite, obtained by structure refinements on the observed neutron diffraction patterns for deuterated sample up to 10 GPa, show linearly approaching O-D covalent and D O hydrogen bond distances and they could merge below 26 GPa. The pressure-induced stacking disorder would make the electrostatic potential of hydrogen bonds asymmetric, yielding less chance for the proton-tunnelling.
O hydrogen bond distances and they could merge below 26 GPa. The pressure-induced stacking disorder would make the electrostatic potential of hydrogen bonds asymmetric, yielding less chance for the proton-tunnelling.
Chanyshev, A. D.*; Litasov, K. D.*; Rashchenko, S.*; Sano, Asami; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Hattori, Takanori; Shatskiy, A. F.*; Dymshits, A. M.*; Sharygin, I. S.*; Higo, Yuji*
Crystal Growth & Design, 18(5), p.3016 - 3026, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:83.76(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The high-temperature structural properties of solid benzene were studied at 1.5-8.2 GPa up to melting or decomposition using multi-anvil apparatus and in situ neutron and X-ray diffraction. The crystal structure of deuterated benzene phase II (P2 /c unit cell) was refined at 3.6-8.2 GPa and 473-873 K. Our data show a minor temperature effect on the change in the unit cell parameters of deuterated benzene at 7.8-8.2 GPa. At 3.6-4.0 GPa, we observed the deviation of deuterium atoms from the benzene ring plane and minor zigzag deformation of the benzene ring, enhancing with the temperature increase caused by the displacement of benzene molecules and decrease of van der Waals bond length between the
/c unit cell) was refined at 3.6-8.2 GPa and 473-873 K. Our data show a minor temperature effect on the change in the unit cell parameters of deuterated benzene at 7.8-8.2 GPa. At 3.6-4.0 GPa, we observed the deviation of deuterium atoms from the benzene ring plane and minor zigzag deformation of the benzene ring, enhancing with the temperature increase caused by the displacement of benzene molecules and decrease of van der Waals bond length between the  -conjuncted carbon skeleton and the deuterium atom of adjacent molecule. Deformation of benzene molecule at 723-773 K and 3.9-4.0 GPa could be related to the benzene oligomerization at the same conditions. In the pressure range of 1.5-8.2 GPa, benzene decomposition was defined between 773-923 K. Melting was identified at 2.2 GPa and 573 K. Quenched products analyzed by Raman spectroscopy consist of carbonaceous material. The defined benzene phase diagram appears to be consistent with those of naphthalene, pyrene, and coronene at 1.5-8 GPa.
-conjuncted carbon skeleton and the deuterium atom of adjacent molecule. Deformation of benzene molecule at 723-773 K and 3.9-4.0 GPa could be related to the benzene oligomerization at the same conditions. In the pressure range of 1.5-8.2 GPa, benzene decomposition was defined between 773-923 K. Melting was identified at 2.2 GPa and 573 K. Quenched products analyzed by Raman spectroscopy consist of carbonaceous material. The defined benzene phase diagram appears to be consistent with those of naphthalene, pyrene, and coronene at 1.5-8 GPa.
Takeda, Takeshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2018-004, 64 Pages, 2018/03
Experiment SB-SG-10 was conducted on November 17, 1992 using LSTF. Experiment simulated recovery actions from multiple steam generator (SG) tube rupture accident in PWR. Primary pressure was kept higher than broken SG secondary-side pressure due to coolant injection from high pressure injection (HPI) system into cold and hot legs even after start of full opening of intact SG relief valve (RV). Full opening of power-operated relief valve (PORV) in pressurizer (PZR) resulted in pressure equalization between primary and broken SG systems as well as PZR liquid level recovery. Broken SG RV opened once after start of intact SG RV full opening. Core was filled with saturated or subcooled liquid through experiment. Significant natural circulation prevailed in intact loop after start of intact SG RV full opening. Significant thermal stratification appeared in hot legs especially during time period of HPI coolant injection into hot legs.
Klotz, S.*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Kunc, K.*; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori
Physical Review B, 95(17), p.174111_1 - 174111_7, 2017/05
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:82.84(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The compression behaviour of deuterated ice VII and VIII was investigated by high pressure neutron scattering in the pressure range 2-13.7 GPa between 93 K and 300 K. We establish equations-of-state which contain accurate values for the bulk moduli B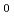 , their pressure derivatives B'
, their pressure derivatives B'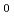 , as well as the ambient pressure volumina V
, as well as the ambient pressure volumina V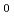 . These equations-of-state hold over a large part of the stability domain of ice VII, by comparison with available X-ray data, and to at least
. These equations-of-state hold over a large part of the stability domain of ice VII, by comparison with available X-ray data, and to at least 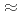 13 GPa for ice VIII. They are indistinguishable at low pressures, but beyond
13 GPa for ice VIII. They are indistinguishable at low pressures, but beyond 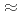 7 GPa and at low temperatures ice VIII appears to become stiffer than expected. This might be related to an anomalous phonon hardening observed previously in ice VIII in this
7 GPa and at low temperatures ice VIII appears to become stiffer than expected. This might be related to an anomalous phonon hardening observed previously in ice VIII in this 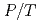 range [D.D. Klug et al., Physical Review B, 70, 144113 (2004)].
range [D.D. Klug et al., Physical Review B, 70, 144113 (2004)].