Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kido, Kentaro; Kaneko, Masashi
Journal of Computational Chemistry, 44(4), p.546 - 558, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.83(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Miyakawa, Kazuya; Kashiwaya, Koki*; Komura, Yuto*; Nakata, Kotaro*
Geochemical Journal, 57(5), p.155 - 175, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:30.17(Geochemistry & Geophysics)In the thick marine sediments, groundwater altered from seawater during the burial diagenesis may exist. Such altered ancient seawater will be called fossil seawater. In such a field, groundwater flow is considered extremely slow because it is not affected by the seepage of meteoric water even after the uplift. During diagenesis, dehydration from silicates causes changes such as a decrease in the salinity of the porewater. However, dehydration reactions alone cannot quantitatively explain water chemistry changes. In this study, we developed an analytical model that considers the dehydration reaction from silicates during the burial process and the upward migration of porewater due to compaction and examined the possible evolution of porewater chemistry. The results showed that the water chemistry, which was strongly influenced by the dehydration reaction from opal-A to quartz and from smectite, was similar to the observations from boring surveys. The results suggest that the fossil seawater formed during the diagenesis may have been preserved since the uplift and strongly supports the slow groundwater flow in the area where the fossil seawater exists.
Noguchi, Hiroki; Kamiji, Yu; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Takegami, Hiroaki; Iwatsuki, Jin; Kasahara, Seiji; Myagmarjav, O.; Imai, Yoshiyuki; Kubo, Shinji
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 46(43), p.22328 - 22343, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:64.60(Chemistry, Physical)An iodine-sulfur process offers the potential for mass producing hydrogen with high-efficiency, and it uses high-temperature heat sources, including HTGR, solar heat, and waste heat of industries. R&D tasks are essential to confirm the integrity of the components that are made of industrial materials and the stability of hydrogen production in harsh working conditions. A test facility for producing hydrogen was constructed from corrosion-resistant components made of industrial materials. For stable hydrogen production, technical issues for instrumental improvements (i.e., stable pumping of the HIx solution, improving the quality control of glass-lined steel, prevention of I precipitation using a water removal technique in a Bunsen reactor) were solved. The entire process was successfully operated for 150 h at the rate of 30 L/h. The integrity of components and the operational stability of the hydrogen production facility in harsh working conditions were demonstrated.
precipitation using a water removal technique in a Bunsen reactor) were solved. The entire process was successfully operated for 150 h at the rate of 30 L/h. The integrity of components and the operational stability of the hydrogen production facility in harsh working conditions were demonstrated.
Yotsuji, Kenji*; Tachi, Yukio; Sakuma, Hiroshi*; Kawamura, Katsuyuki*
Applied Clay Science, 204, p.106034_1 - 106034_13, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:102 Percentile:99.77(Chemistry, Physical)Kato, Aitaro*; Saiga, Atsushi; Takeda, Tetsuya*; Iwasaki, Takaya*; Matsuzawa, Toru*
Earth, Planets and Space (Internet), 66(1), p.86_1 - 86_8, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:56.50(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)To understand the mechanism of an intensive non-volcanic seismic swarm in the Kii Peninsula, Japan, we used a dense seismic linear array to measure fine-scale variations of seismic velocities and converted teleseismic waves. A low-velocity anomaly confined to just beneath the seismic swarm area is clearly imaged, which spatially correlates with an uplifted surface area, and a highly conductive and strong attenuative body. These results suggest that fluids such as partial melt or water are present beneath this non-volcanic seismic swarm area. It is notable that the island arc Moho below the seismic swarm area is at depths of ca. 32 km in the northern part of the seismic swarm area, and shallows to ca. 20 km towards the south, due to an upwardly raised structure of serpentinized mantle wedge. In addition, we show that hydrated oceanic crust of the subducting Philippine Sea slab is characterized by low-velocities with a high Poisson's ratio at depths shallower than 40 km. Water released from the subducting oceanic crust could cause serpentinization of the mantle wedge and infiltration into the forearc base of the overlying plate. The interaction between dehydration of the subducting oceanic crust and hydration of the mantle wedge and overlying plate exerts an important role in driving the non-volcanic seismic swarm activity in the Kii Peninsula.
Niimura, Nobuo; Arai, Shigeki; Kurihara, Kazuo; Chatake, Toshiyuki*; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Bau, R.*
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 63(3), p.285 - 300, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:36.83(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Neutron diffraction provides an experimental method of directly locating hydrogen atoms in proteins and DNA oligomers. Three different types of high resolution neutron diffractometers for biological macromolecules have been constructed in Japan, France and the U.S.A., and they have all been actively used in recent years to determine the crystal structures of numerous proteins. Examples include the detailed geometries of hydrogen bonds, information on H/D exchange in proteins, the unambiguous location of protons, the role of key hydrogen atoms in enzymatic activity and thermostability, and the dynamical behavior of hydration structures, all of which have been extracted from these structural results and reviewed in this article. Other important techniques, such as the optimization of growth of large single crystals using phase diagrams, the preparation of fully deuterated proteins, the introduction of cryogenic techniques to neutron protein crystallography, and the establishment of a "hydrogen and hydration in proteins" database, will also be described in this paper.
Naganawa, Hirochika; Suzuki, Hideya*; Noro, Junji*; Kimura, Takaumi
Chemical Communications, (23), p.2963 - 2965, 2005/06
A "superweak" anion, TFPB-, gives rise to a field effect on the selectivity for Am over Ln
over Ln in their extraction from aqueous HNO
in their extraction from aqueous HNO solution into benzene containing a "hard donor" extractant that shows no selectivity for these metal ions in traditional solvent extraction.
solution into benzene containing a "hard donor" extractant that shows no selectivity for these metal ions in traditional solvent extraction.
 and La
and La compared; An Application of metadynamics
compared; An Application of metadynamicsIkeda, Takashi; Hirata, Masaru; Kimura, Takaumi
Journal of Chemical Physics, 122(24), p.244507_1 - 244507_5, 2005/06
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:83.51(Chemistry, Physical)We studied the hydration structures of Y and La
and La in aqueous solutions by applying the metadynamics method recently introduced as a tool to explore reaction pathways based on the Car-Parrinello molecular dynamics. By employing the metal-water oxygen coordination number as a collective variable of the metadynamics a couple of aqua and chloro-aqua complexes are successfully generated within the time scales of 10 ps. The reconstructed free energy surface captures the characteristics of the hydration of the light and heavy trivalent rare-earth ions. The present study demonstrates that the metadynamics based on the Car-Parrinello molecular dynamics is a promising tool for exploring the free energy surface of complicated systems such as solutions.
in aqueous solutions by applying the metadynamics method recently introduced as a tool to explore reaction pathways based on the Car-Parrinello molecular dynamics. By employing the metal-water oxygen coordination number as a collective variable of the metadynamics a couple of aqua and chloro-aqua complexes are successfully generated within the time scales of 10 ps. The reconstructed free energy surface captures the characteristics of the hydration of the light and heavy trivalent rare-earth ions. The present study demonstrates that the metadynamics based on the Car-Parrinello molecular dynamics is a promising tool for exploring the free energy surface of complicated systems such as solutions.
Niimura, Nobuo; Arai, Shigeki; Kurihara, Kazuo; Chatake, Toshiyuki*; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Bau, R.*
Hydrogen- and Hydration-Sensitive Structural Biology, p.17 - 35, 2005/00
At the JAERI, we have constructed several high-resolution neutron diffractometers dedicated to biological macromolecules (called BIX-type diffractometers), which use a monochromatized neutron beam and a neutron imaging plate detector. In this paper, we review several interesting results regarding hydrogen positions and hydration in proteins, obtained using the two BIX-type diffractometers in JAERI. The general subject of neutron protein crystallography has been reviewed by several authors, and several selected topics have been discussed.
 resolution
resolutionChatake, Toshiyuki*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Tsyba, I.*; Bau, R.*; Jenney, F. E. Jr.*; Adams, M. W. W.*; Niimura, Nobuo
Acta Crystallographica Section D, 60(8), p.1364 - 1373, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:88.49(Biochemical Research Methods)A neutron diffraction study has been carried out at 1.6  resolution on a mutant rubredoxin from
resolution on a mutant rubredoxin from 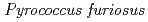 using the BIX-3 single-crystal diffractometer at the JRR-3 reactor of JAERI. In order to study the unusual thermostability of rubredoxin from
using the BIX-3 single-crystal diffractometer at the JRR-3 reactor of JAERI. In order to study the unusual thermostability of rubredoxin from 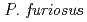 , the hydrogen-bonding patterns were compared between the native and a 'triple-mutant' variant where three residues were changed so that they are identical to those in a mesophilic rubredoxin. In the present study, some minor changes were found between the wild-type and mutant proteins in the hydrogen-bonding patterns of the Trp3/Tyr3 region. The H/D-exchange ratios in the protein were also studied. The results suggest that the backbone amide bonds near the four Cys residues of the FeS
, the hydrogen-bonding patterns were compared between the native and a 'triple-mutant' variant where three residues were changed so that they are identical to those in a mesophilic rubredoxin. In the present study, some minor changes were found between the wild-type and mutant proteins in the hydrogen-bonding patterns of the Trp3/Tyr3 region. The H/D-exchange ratios in the protein were also studied. The results suggest that the backbone amide bonds near the four Cys residues of the FeS redox center are most resistant to H/D exchange. In addition, the 1.6
redox center are most resistant to H/D exchange. In addition, the 1.6  resolution of the present neutron structure determination has revealed a more detailed picture than previously available of some portions of the water structure, including ordered and disordered O-D bonds.
resolution of the present neutron structure determination has revealed a more detailed picture than previously available of some portions of the water structure, including ordered and disordered O-D bonds.
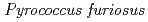 by BIX-3, a single-crystal diffractometer for biomacromolecules
by BIX-3, a single-crystal diffractometer for biomacromoleculesKurihara, Kazuo; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Chatake, Toshiyuki*; Adams, M. W. W.*; Jenney, F. E. Jr.*; Moiseeva, N.*; Bau, R.*; Niimura, Nobuo
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101(31), p.11215 - 11220, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:60.08(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The structure of a rubredoxin (Rd) from 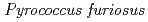 , an organism that grows optimally at 100
, an organism that grows optimally at 100  C, was determined using the neutron single-crystal diffractometer for biological macromolecules (BIX-3) at the JRR-3 reactor of JAERI. Data were collected at room temperature up to a resolution of 1.5
C, was determined using the neutron single-crystal diffractometer for biological macromolecules (BIX-3) at the JRR-3 reactor of JAERI. Data were collected at room temperature up to a resolution of 1.5  , and the completeness of the data set was 81.9 %. The model contains 306 H atoms and 50 D atoms. A total of 37 hydration water molecules were identified. The model has been refined to final agreement factors of
, and the completeness of the data set was 81.9 %. The model contains 306 H atoms and 50 D atoms. A total of 37 hydration water molecules were identified. The model has been refined to final agreement factors of  = 18.6 % and
= 18.6 % and 
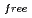 = 21.7 %. Several orientations of the O-D bonds of side chains, whose assignments from X-ray data were previously ambiguous, were clearly visible in the neutron structure. While most backbone N-H bonds had undergone some degree of H/D exchange throughout the molecule, five H atom positions still had distinctly negative (H) peaks. The neutron Fourier maps clearly showed the details of an extensive set of H bonds involving the ND
= 21.7 %. Several orientations of the O-D bonds of side chains, whose assignments from X-ray data were previously ambiguous, were clearly visible in the neutron structure. While most backbone N-H bonds had undergone some degree of H/D exchange throughout the molecule, five H atom positions still had distinctly negative (H) peaks. The neutron Fourier maps clearly showed the details of an extensive set of H bonds involving the ND
 terminus that may contribute to the unusual thermostability of this molecule.
terminus that may contribute to the unusual thermostability of this molecule.
Tian, G.*; Kimura, Takaumi; Yoshida, Zenko; Zhu, Y.*; Rao, L.*
Radiochimica Acta, 92(8), p.495 - 499, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:71.02(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Niimura, Nobuo; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tanaka, Ichiro
Kagaku, 59(2), p.46 - 47, 2004/02
no abstracts in English
Pinak, M.
JAERI-Research 2001-038, 30 Pages, 2001/07
no abstracts in English
Kurihara, Kazuo; Tanaka, Ichiro; Adams, M. W. W.*; Jenney, F. E. Jr.*; Moiseeva, N.*; Bau, R.*; Niimura, Nobuo
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, Vol.70, Supplement A, p.400 - 402, 2001/05
With the new single-crystal diffractometer BIX-3 at the JRR-3M reactor of JAERI, a single-crystal neutron diffraction analysis of the structure of the small protein rubredoxin from the hyperthermophile Pyrococcus furiosus is currently under way. Data were collected at room temperature up to a resolution of 1.5  intervals in
intervals in  and exposure times ranging from 60 to 77 minutes per frame. The completeness factor of the 1.5-
and exposure times ranging from 60 to 77 minutes per frame. The completeness factor of the 1.5- . Included in the refinement are 301 hydrogen atoms and 40 deuterium atoms, and 29 water molecules were also identified. In the present model, the current value for R and R
. Included in the refinement are 301 hydrogen atoms and 40 deuterium atoms, and 29 water molecules were also identified. In the present model, the current value for R and R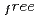 are 24.0
are 24.0  and 26.3
and 26.3  , respectively.
, respectively.
Pinak, M.
JAERI-Research 99-077, p.31 - 0, 2000/02
no abstracts in English

 in X-irradiated frozed aqueous solutions; Similar hydration shells for Cd
in X-irradiated frozed aqueous solutions; Similar hydration shells for Cd
 and Cd
and Cd
 species
speciesFujimura, Takashi; L.Kevan*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 19(6), p.435 - 437, 1982/00
no abstracts in English
Nakashima, Mikio; Tachikawa, Enzo; Saeki, Masakatsu;
Journal of Inorganic and Nuclear Chemistry, 43(2), p.369 - 373, 1981/00
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:37.49(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Yamagami, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
Miyakawa, Kazuya; Kashiwaya, Koki*; Komura, Yuto*; Nakata, Kotaro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English