Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tsubota, Yoichi; Porcheron, E.*; Journeau, C.*; Delacroix, J.*; Suteau, C.*; Lallot, Y.*; Bouland, A.*; Roulet, D.*; Mitsugi, Takeshi
Proceedings of International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM2023) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2023/10
In order to safely remove fuel debris from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), it is necessary to quantitatively evaluate radioactive airborne particulate generated by the cutting of nuclear fuel debris. We fabricated Uranium-bearing simulated fuel debris (SFD) with In/Ex-Vessel compositions and evaluated the physical and chemical properties of aerosols generated by heating the SFDs. Based on these results, we estimated the isotopic composition and radioactivity of aerosols produced when 1F-Unit2 fuel debris is laser cut, which is a typical example of a heating method. Plutonium, mainly  Pu,
Pu, Am, and
Am, and  Cm were found to be the alpha nuclide, and
Cm were found to be the alpha nuclide, and  Pu,
Pu,  Cs-Ba, and
Cs-Ba, and  Sr-Y were found to be the beta nuclide of interest.
Sr-Y were found to be the beta nuclide of interest.
Abe, Tomohisa; Funaki, Hironori; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Shiribiki, Natsu*; Sanada, Yukihisa
JAEA-Data/Code 2023-001, 38 Pages, 2023/05
In this study, commissioned by the Cabinet Office, we conducted a survey on radioactive materials in atmospheric dust in three municipalities (Futaba Town, Okuma Town, and Tomioka Town) in Fukushima Prefecture to contribute to the assessment of internal exposure in the Specified Reconstruction and Revitalization Base (SRRB). Air dust samplers were installed in the targeted municipalities to investigate the atmospheric  Cs concentrations and to evaluate internal exposure doses based on measured value. This report summarizes the results of measurements between 2018 and 2021. A database of information on internal exposure dose assessment results based on atmospheric radioactivity concentrations and actual measurements, and meteorological observation data was compiled.
Cs concentrations and to evaluate internal exposure doses based on measured value. This report summarizes the results of measurements between 2018 and 2021. A database of information on internal exposure dose assessment results based on atmospheric radioactivity concentrations and actual measurements, and meteorological observation data was compiled.
Takahashi, Fumiaki; Manabe, Kentaro; Sato, Kaoru
JAEA-Review 2020-068, 114 Pages, 2021/03
Radiation safety regulations have been currently established based on the 1990Recommendation by the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) in Japan. Meanwhile, ICRP released the 2007 Recommendation that replaces the 1990 Recommendation. Thus, the Radiation Council, which is established under the Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA), has made discussions to incorporate the purpose of the 2007 Recommendation into Japanese regulations for radiation safety. As ICRP also has published effective dose coefficients for internal exposure assessment in accordance with the 2007recommendation, the technical standards are to be revised for the internal exposure assessment method in Japan. Currently, not all of the effective doses have been published to revise concentration limits for internal exposure protections of workers and public. The published effective dose coefficients are applied to radionuclides which are important in radiation protection for internal exposure of a worker. Thus, we review new effective dose coefficients as well as basic dosimetry models and data based upon Occupational Intakes of Radionuclides (OIR) parts 2, 3 and 4 that have been published from 2016 to 2019 by ICRP. In addition, issues are sorted out to provide information for revision of the technical standards for internal exposure assessment based on the 2007 Recommendations in future.
Hosoda, Masahiro*; Nugraha, E. D.*; Akata, Naofumi*; Yamada, Ryohei; Tamakuma, Yuki*; Sasaki, Michiya*; Kelleher, K.*; Yoshinaga, Shinji*; Suzuki, Takahito*; Rattanapongs, C. P.*; et al.
Science of the Total Environment, 750, p.142346_1 - 142346_11, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:85.42(Environmental Sciences)The biological effects of low dose-rate radiation exposures on humans remains unknown. In fact, the Japanese nation still struggles with this issue after the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. Recently, we have found a unique area in Indonesia where naturally high radiation levels are present, resulting in chronic low dose-rate radiation exposures. We aimed to estimate the comprehensive dose due to internal and external exposures at the particularly high natural radiation area, and to discuss the enhancement mechanism of radon. A car-borne survey was conducted to estimate the external doses from terrestrial radiation. Indoor radon measurements were made in 47 dwellings over three to five months, covering the two typical seasons, to estimate the internal doses. Atmospheric radon gases were simultaneously collected at several heights to evaluate the vertical distribution. The absorbed dose rates in air in the study area vary widely between 50 nGy h and 1109 nGy h
and 1109 nGy h . Indoor radon concentrations ranged from 124 Bq m
. Indoor radon concentrations ranged from 124 Bq m to 1015 Bq m
to 1015 Bq m . That is, the indoor radon concentrations measured exceed the reference levels of 100 Bq m
. That is, the indoor radon concentrations measured exceed the reference levels of 100 Bq m recommended by the World Health Organization. Furthermore, the outdoor radon concentrations measured were comparable to the high indoor radon concentrations. The annual effective dose due to external and internal exposures in the study area was estimated to be 27 mSv using the median values. It was found that many residents are receiving radiation exposure from natural radionuclides over the dose limit for occupational exposure to radiation workers. This enhanced outdoor radon concentration might be as a result of the stable atmospheric conditions generated at an exceptionally low altitude. Our findings suggest that this area provides a unique opportunity to conduct an epidemiological study related to health effects due to chronic low dose-rate radiation exposure.
recommended by the World Health Organization. Furthermore, the outdoor radon concentrations measured were comparable to the high indoor radon concentrations. The annual effective dose due to external and internal exposures in the study area was estimated to be 27 mSv using the median values. It was found that many residents are receiving radiation exposure from natural radionuclides over the dose limit for occupational exposure to radiation workers. This enhanced outdoor radon concentration might be as a result of the stable atmospheric conditions generated at an exceptionally low altitude. Our findings suggest that this area provides a unique opportunity to conduct an epidemiological study related to health effects due to chronic low dose-rate radiation exposure.
Miwa, Kazuji; Takeda, Seiji; Iimoto, Takeshi*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 184(3-4), p.372 - 375, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)The Ministry of the Environment has indicated the policy of recycling the contaminated soil generated by decontamination activity after the Fukushima accident. By recycling to coastal reclamation which is one of effective recycling application, dissolved radiocesium and absorbed radiocesium on soil particles will flow out to the ocean by construction, therefore evaluating radiocesium transition in ocean considering the both types of radiocesium is important for safety assessment. In this study, the radiocesium outflow during constructing and after constructing is modeled, and radiocesium transition in ocean is evaluated by Sediment model suggested in OECD/NEA. The adaptability of sediment model is confirmed by reproducing evaluation of the coastal area of Fukushima. We incorporate the sediment model to PASCLR2 code system to evaluate the doses from radiocesium in ocean.
Hirouchi, Jun; Takahara, Shogo; Komagamine, Hiroshi*; Munakata, Masahiro
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2019 (ASRAM 2019) (USB Flash Drive), 7 Pages, 2019/09
no abstracts in English
Hirouchi, Jun; Takahara, Shogo; Komagamine, Hiroshi*; Munakata, Masahiro
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2018 (ASRAM 2018) (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2018/10
no abstracts in English
Saito, Kimiaki; Takahara, Shogo; Uezu, Yasuhiro
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 60(2), p.111 - 115, 2018/02
, 60(2), p.111 - 115, 2018/02
no abstracts in English
Hirouchi, Jun; Takahara, Shogo; Komagamine, Hiroshi*; Watanabe, Masatoshi*; Munakata, Masahiro
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2017 (ASRAM 2017) (USB Flash Drive), 11 Pages, 2017/11
no abstracts in English
Endo, Akira; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro; Eckerman, K. F.*
JAERI 1347, 114 Pages, 2005/02
no abstracts in English
Endo, Akira; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro; Eckerman, K. F.*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 105(1-4), p.565 - 569, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:61.05(Environmental Sciences)The present paper discusses a strategy for the development of a new radioactive decay database, which will succeed ICRP Publ.38 used for dosimetry calculations. The development of the database requires 1) Consistency checking of the ENSDF used for compilation of the decay data, 2) Improvement of the computer code EDISTR for processing the ENSDF, and 3) Comparison with other decay data prepared from the different computer codes and libraries for the verification of the compiled data. This paper identifies several technical issues that need to be addressed for the development of the new radioactive decay database.
Endo, Akira; Sato, Kaoru; Noguchi, Hiroshi; Tanaka, Susumu; Iida, Takao*; Furuichi, Shinya*; Kanda, Yukio*; Oki, Yuichi*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 256(2), p.231 - 237, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:45.02(Chemistry, Analytical)Size distributions of  Cl,
Cl, 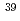 Cl,
Cl, 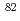 Br and
Br and 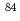 Br aerosols generated by irradiations of argon and krypton gases containing di-octyl phthalate (DOP) aerosols with 45MeV and 65MeV quasi-monoenergetic neutrons were measured to study the formation mechanism of radioactive particles in high energy radiation fields. Effects of the size distribution of the radioactive aerosols on the size of added DOP aerosols, the energy of irradiation neutrons and the kinds of nuclides were studied. The observed size distributions of the radioactive particles were explained by attachment of the radioactive atoms generated by the neutron-induced reactions to the DOP aerosols.
Br aerosols generated by irradiations of argon and krypton gases containing di-octyl phthalate (DOP) aerosols with 45MeV and 65MeV quasi-monoenergetic neutrons were measured to study the formation mechanism of radioactive particles in high energy radiation fields. Effects of the size distribution of the radioactive aerosols on the size of added DOP aerosols, the energy of irradiation neutrons and the kinds of nuclides were studied. The observed size distributions of the radioactive particles were explained by attachment of the radioactive atoms generated by the neutron-induced reactions to the DOP aerosols.
Kawai, Katsuo; Endo, Akira; Noguchi, Hiroshi
JAERI-Data/Code 2002-013, 66 Pages, 2002/05
Effective dose coefficients by inhalation and ingestion have been calculated for 334 nuclides, including (1) nuclides with half-lives 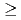 10min and their daughters that are not listed in ICRP Publications and (2) nuclides with half-lives
10min and their daughters that are not listed in ICRP Publications and (2) nuclides with half-lives  10min that are produced in a spallation target. Dose calculation was carried out using a nuclear decay database DECDC and a decay data library newly compiled from the ENSDF. The dose coefficients were calculated with the computer code DOCAP based on the respiratory tract model and biokinetic model of ICRP. The calculated results are presented as tables, which are the same forms as those in ICRP Publs.68 and 72. The complete listings of the dose coefficients are arranged on a CD-ROM, DoseCD, as indexed tables for inhalation of ten particle sizes, ingestion and injection into blood for workers and members of the public. The dose coefficients calculated in the present study are useful to calculate internal doses for a variety of radionuclides produced in high energy proton accelerator facilities.
10min that are produced in a spallation target. Dose calculation was carried out using a nuclear decay database DECDC and a decay data library newly compiled from the ENSDF. The dose coefficients were calculated with the computer code DOCAP based on the respiratory tract model and biokinetic model of ICRP. The calculated results are presented as tables, which are the same forms as those in ICRP Publs.68 and 72. The complete listings of the dose coefficients are arranged on a CD-ROM, DoseCD, as indexed tables for inhalation of ten particle sizes, ingestion and injection into blood for workers and members of the public. The dose coefficients calculated in the present study are useful to calculate internal doses for a variety of radionuclides produced in high energy proton accelerator facilities.
Endo, Akira; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro
JAERI-Data/Code 2001-004, 157 Pages, 2001/03
New nuclear decay data used for dose calculation have been compiled for 817 radionuclides that are listed in ICRP Publication 38 (Publ.38) and for 6 additional isomers. The decay data were prepared using decay data sets from the Evaluated Nuclear Structure Data File (ENSDF), the latest version in August 1997. Basic nuclear properties in the decay data sets that are important for calculating energies and intensities of emissions were updated by referring to NUBASE. In addition, possible revisions of partial and incomplete decay data sets were done for their format and syntax errors, level schemes, normalization records, and so on. After that, the decay data sets were processed by EDISTR in order to compute the energies and intensities of  particles,
particles,  particles,
particles,  rays, internal conversion electrons, X rays, and Auger electrons. The compiled data were prepared in two different types of format: Publ.38 and NUCDECAY formats. The decay data will be widely used for dose calculations in radiation protection and will be beneficial to a future revision of ICRP Publ.38.
rays, internal conversion electrons, X rays, and Auger electrons. The compiled data were prepared in two different types of format: Publ.38 and NUCDECAY formats. The decay data will be widely used for dose calculations in radiation protection and will be beneficial to a future revision of ICRP Publ.38.
 N species and noxious gases produced at the 12GeV proton synchrotron
N species and noxious gases produced at the 12GeV proton synchrotronKanda, Yukio*; Oki, Yuichi*; Endo, Akira; Numajiri, Masaharu*; Kondo, Kenjiro*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 247(1), p.25 - 31, 2001/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:55.14(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
 C produced in the air in high energy proton accelerator tunnels
C produced in the air in high energy proton accelerator tunnelsEndo, Akira; Oki, Yuichi*; Kanda, Yukio*; Oishi, Tetsuya; Kondo, Kenjiro*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 93(3), p.223 - 230, 2001/00
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:43.30(Environmental Sciences)no abstracts in English
Endo, Akira; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro
Proceedings of 10th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA-10) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2000/05
no abstracts in English
 C,
C,  N and
N and  O produced in air through nuclear spallation reactions by high energy protons
O produced in air through nuclear spallation reactions by high energy protonsEndo, Akira; Oki, Yuichi*; Kanda, Yukio*; Kondo, Kenjiro*
Proceedings of 10th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA-10) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2000/05
no abstracts in English
Department of Health Physics; Safety Division, Naka; Safety Division, Takasaki; Radiation Control Division, Oarai; Utilities and Safety Division, Kansai; Operation Safety Administration Division, Mutsu
JAERI-Review 2000-001, p.225 - 0, 2000/03
no abstracts in English
Endo, Akira; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro
JAERI-Data/Code 99-047, p.24 - 0, 1999/12
no abstracts in English