Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Idomura, Yasuhiro
Physics of Plasmas, 26(12), p.120703_1 - 120703_5, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:32.66(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This Letter presents the impacts of the hydrogen isotope mass and the normalized gyroradius 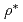 on L-mode like hydrogen (H) and deuterium (D) plasmas dominated by ion temperature gradient driven (ITG) turbulence using global full-f gyrokinetic simulations. In ion heated numerical experiments with adiabatic electrons, the energy confinement time shows almost no isotope mass dependency, and is determined by Bohm like
on L-mode like hydrogen (H) and deuterium (D) plasmas dominated by ion temperature gradient driven (ITG) turbulence using global full-f gyrokinetic simulations. In ion heated numerical experiments with adiabatic electrons, the energy confinement time shows almost no isotope mass dependency, and is determined by Bohm like 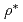 scaling. Electron heated numerical experiments with kinetic electrons show clear isotope mass dependency caused by the isotope effect on the collisional energy transfer from electrons to ions, and the H and D plasmas show similar ion and electron temperature profiles at an H to D heating power ratio of
scaling. Electron heated numerical experiments with kinetic electrons show clear isotope mass dependency caused by the isotope effect on the collisional energy transfer from electrons to ions, and the H and D plasmas show similar ion and electron temperature profiles at an H to D heating power ratio of 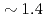 . The normalized collisionless ion gyrokinetic equations for H and D plasmas become identical at the same
. The normalized collisionless ion gyrokinetic equations for H and D plasmas become identical at the same 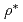 , and collisions weakly affect ITG turbulence. Therefore, the isotope mass dependency is mainly contributed by the
, and collisions weakly affect ITG turbulence. Therefore, the isotope mass dependency is mainly contributed by the 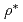 scaling and the heating sources.
scaling and the heating sources.
Nakamura, Hirofumi; Nishi, Masataka; Sugisaki, Masayasu*
JAERI-Research 2003-018, 32 Pages, 2003/09
Tritium transport behavior in materials, which is essential for the safety evaluation of the fusion reactor, has to be evaluated by either tritium properties or extrapolated value from protium or deuterium (D) to tritium (T) using the isotope effect theory. However, there are still some uncertainties on estimation of T behavior in materials, because there are only a few T transport properties data in materials, and it is not completely proven the application of the isotope effect theory to T due to the lack of T data. Therefore, in order to understand the tritium transport properties in materials, isotope effects on diffusion and surface recombination between T and D in/on nickel, whose hydrogen transport properties were well known, were investigated by comparing the obtained properties of T with those of D measured under the same conditions with the ion driven permeation method. Though obtained diffusion coefficient of T was larger than that of D, and activation energy of diffusion of T was smaller than that of D as the contrary to the classical diffusion theory, those were shown to be explained with a modified diffusion theory by introducing higher vibration temperatures in nickel than previous reported values. In addition, the isotope effect on surface recombination coefficient between D and T was shown to be explained using a modified solution model as well as diffusion.
Advanced Radiation Technology Center
JAERI-Review 2001-039, 328 Pages, 2001/11
no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Hirofumi; Hayashi, Takumi; Kakuta, Toshiya*; Suzuki, Takumi; Nishi, Masataka
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 297(3), p.285 - 291, 2001/09
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:78.30(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The isotope effect on the implantation-driven permeation of pure tritium (T) and deuterium (D) through nickel was investigated, respectively. The rate-determining processes of backward flow at the upstream surface and permeation at the down-stream surface were found to be as follows: recombination on up-stream surface and diffusion at down-stream side in a lower temperature region, whereas recombination on both surfaces in a higher temperature region for T and D, respectively. The diffusion coefficients of T and D derived by analyzing the obtained transient data of permeation in the lower temperature region were in good agreement with literature data of deuterium. The obtained activation energy of diffusion for T and D suggested the tendency of mass dependence. The surface recombination coefficients for both isotopes were also derived and showed in good agreement with literature data. As a result, the experimental results indicated the surface recombination could be attributed to the isotope effect of the permeation between T and D rather than the diffusion.
Advanced Radiation Technology Center
JAERI-Review 2000-024, 326 Pages, 2000/10
no abstracts in English
Advanced Radiation Technology Center
JAERI-Review 99-025, p.298 - 0, 1999/10
no abstracts in English
 Cs following the decay of
Cs following the decay of  Xe atoms implanted in metals
Xe atoms implanted in metals; ; ; ; ; ; Muto, Suguru*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Osa, Akihiko; Sekine, Toshiaki; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 239(2), p.251 - 255, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
 Cs
Cs; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; Muto, Suguru*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; et al.
Physical Review B, 58(17), p.11313 - 11321, 1998/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:31.82(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 laser
laserIkezoe, Yasumasa; Soga, Takeshi; Suzuki, Kazuya; Ono, Shinichi*
Journal of the Mass Spectometry Society of Japan, 43(5), p.257 - 263, 1995/00
no abstracts in English
Noguchi, Hiroshi; Murata, Mikio
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 33(4), p.360 - 362, 1991/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:50.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 laser photolysis of clustered ions, I
laser photolysis of clustered ions, IIkezoe, Yasumasa; Soga, Takeshi; Suzuki, Kazuya; Ono, Shinichi
JAERI-M 90-141, 55 Pages, 1990/09
no abstracts in English
Yamashita, Kiyonobu; Shindo, Ryuichi; Murata, Isao; Nakata, Tetsuo*
JAERI-M 89-198, 42 Pages, 1989/12
no abstracts in English
K.W.Lee*; ; ; ; ; ; Saeki, Masakatsu; Tachikawa, Enzo
J.Phys.Chem., 90, p.5343 - 5347, 1986/00
no abstracts in English
Fujie, Makoto; ; ;
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 23(4), p.330 - 337, 1986/00
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:96.61(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
;
Bunseki Kagaku, 34(11), p.677 - 681, 1985/00
no abstracts in English
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 136, p.1 - 5, 1985/00
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:94.14(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
;
Radioisotopes, 34(6), p.266 - 269, 1985/00
no abstracts in English
Saeki, Masakatsu; Tachikawa, Enzo; ; ;
J.Phys.Chem., 88(14), p.3108 - 3110, 1984/00
no abstracts in English
;
Environ.Exp.Bot., 23(4), p.361 - 364, 1983/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:22.10(Plant Sciences)no abstracts in English