Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shimomura, Koichiro*; Koda, Akihiro*; Pant, A. D.*; Sunagawa, Hikaru*; Fujimori, Hiroshi*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Fujihara, Masayoshi; Tampo, Motonobu*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.31_1 - 31_6, 2024/12
Kobayashi, Fuminori; Kamiya, Junichiro; Takahashi, Hiroki; Suzuki, Yasuo*; Tasaki, Ryuta*
JAEA-Technology 2024-007, 28 Pages, 2024/07
In J-PARC LINAC, the vacuum system is in place to maintain an ultra-high vacuum in the beam transport line (LINAC to 3GeV RCS beam transportation line: L3BT) between the LINAC to the 3GeV synchrotron. The vacuum system is installed in the LINAC and L3BT buildings and consists of vacuum pumps, vacuum gauges, beam line gate valves (BLGVs), and other vacuum. In existing vacuum systems, vacuum equipment is controlled independently for each area, and vacuum equipment can be operated regardless of the status of adjacent areas. This makes it impossible to eliminate erroneous operation due to human error. In addition, when a vacuum deterioration occurs in the beam transport line, the vacuum deterioration ILK signal is transmitted to the BLGV relay unit via the MPS transmission signal, which causes the BLGVs to be forcibly closed. Because the ILK signal transmission range extends to all BLGVs in the L3BT, however, BLGVs in areas unaffected by vacuum deterioration are also forced to close. This could cause problems such as unnecessary open/close operations leading to more frequent maintenance cycles of the BLGVs. In addition, since the BLGV is operated using the MPS signal path, maintenance of the vacuum control system requires work involving the MPS signal path, making it difficult to maintain the vacuum control system alone and making the work complicated. To solve these problems, it is necessary to improve maintainability by separating the signal paths and automatically controlling BLGV separately. Therefore, the vacuum control system was modified and constructed with the aim of realizing a control system that takes into account the safety and efficient maintenance and operation of the L3BT vacuum system. This report summarizes the development and use of the L3BT vacuum system control system.
 Ta
TaEndo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Toh, Yosuke; Segawa, Mariko; Maeda, Makoto
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 198(4), p.786 - 803, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:63.33(Nuclear Science & Technology)Saito, Shigeru; Meigo, Shinichiro; Makimura, Shunsuke*; Hirano, Yukinori*; Tsutsumi, Kazuyoshi*; Maekawa, Fujio
JAEA-Technology 2023-025, 48 Pages, 2024/03
JAEA has been developing Accelerator-Driven Systems (ADS) for research and development of nuclear transmutation using accelerators in order to reduce the volume and hazardousness of high-level radioactive waste generated by nuclear power plants. In order to prepare the material irradiation database necessary for the design of ADS and to study the irradiation effects in Lead-Bismuth Eutectic (LBE) alloys, a proton irradiation facility is under consideration at J-PARC. In this proton irradiation facility, 250 kW proton beams will be injected into the LBE spallation target, and irradiation tests under LBE flow will be performed for candidate structural materials for ADS. Furthermore, semiconductor soft-error tests, medical RI production, and proton beam applications will be performed. Among these, Post Irradiation Examination (PIE) of irradiated samples and RI separation and purification will be carried out in the PIE facility to be constructed near the proton irradiation facility. In this PIE facility, PIE of the equipment and samples irradiated in other facilities in J-PARC will also be performed. This report describes the conceptual study of the PIE facility, including the items to be tested, the test flow, the facilities, the test equipment, etc., and the proposed layout of the facility.
 La and evaluation of resonance parameters
La and evaluation of resonance parametersEndo, Shunsuke; Kawamura, Shiori*; Okudaira, Takuya*; Yoshikawa, Hiromoto*; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki
European Physical Journal A, 59(12), p.288_1 - 288_12, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
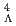 H hypernucleus using in-flight
H hypernucleus using in-flight  He
He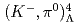 H reaction
H reactionAkaishi, Takaya; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Tanida, Kiyoshi; 35 of others*
Physics Letters B, 845, p.138128_1 - 138128_4, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:59.27(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Nakanishi, Takumi*; Hori, Yuta*; Shigeta, Yasuteru*; Sato, Hiroyasu*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Munakata, Koji*; Ohara, Takashi; Okazawa, Atsushi*; Shimada, Rintaro*; Sakamoto, Akira*; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 145(35), p.19177 - 19181, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:39.98(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) Gd and
Gd and  Gd in the thermal energy region with the Li-glass detectors and NaI(Tl) spectrometer installed in J-PARC
Gd in the thermal energy region with the Li-glass detectors and NaI(Tl) spectrometer installed in J-PARC MLF
MLF ANNRI
ANNRIKimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Harada, Hideo; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Terada, Kazushi*; Hori, Junichi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(6), p.678 - 696, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:48.47(Nuclear Science & Technology)Oigawa, Hiroyuki
Shiki, 59, P. 1, 2023/06
There are the world's leading neutron science research facilities, J-PARC and JRR-3, in Tokai-mura. In order to convey the value created by these facilities to the public, it is important for users to appeal their achievements.
Endo, Shunsuke; Okudaira, Takuya*
Hamon, 33(2), p.68 - 72, 2023/05
no abstracts in English
Hashimoto, Shunsuke*; Yamaguchi, Satoshi*; Harada, Masashi*; Nakajima, Kenji; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Oishi, Kazuki*
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 638, p.475 - 486, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:55.84(Chemistry, Physical)Recently, it has been reported that anomalous improvement in the thermal conductivity of nanofluid composed of base liquids and dispersed solid nanoparticles, compared to the theoretically predicted value calculated from the particle fraction. Generally, the thermal conductivity values of gases and liquids are dominated by the mean free path of the molecules during translational motion. Herein, we present solid evidence showing the possible contribution of the vibrational behavior of liquid molecules around nanoparticles to increasing these thermal conductivities.
Nakanishi, Takumi*; Hori, Yuta*; Shigeta, Yasuteru*; Sato, Hiroyasu*; Wu, S.-Q.*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Munakata, Koji*; Ohara, Takashi; Sato, Osamu*
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 25(17), p.12394 - 12400, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:44.88(Chemistry, Physical) particles generated by residual gas stripping in the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex linac
particles generated by residual gas stripping in the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex linacTamura, Jun; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Liu, Y.*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Morishita, Takatoshi; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Okabe, Kota; Yoshimoto, Masahiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1049, p.168033_1 - 168033_7, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:63.33(Instruments & Instrumentation)The Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) linac is a high-intensity accelerator in which beam loss is a critical issue. In the J-PARC linac, H beams are accelerated to 191~MeV by a separated drift tube linac (SDTL) and subsequently to 400~MeV by an annular-ring coupled structure (ACS). Because there are more beam loss mechanisms in H
beams are accelerated to 191~MeV by a separated drift tube linac (SDTL) and subsequently to 400~MeV by an annular-ring coupled structure (ACS). Because there are more beam loss mechanisms in H linacs than in proton linacs, it is imperative to investigate the beam loss circumstances for beam loss mitigation. Electron-stripping phenomena, which generate uncontrollable H
linacs than in proton linacs, it is imperative to investigate the beam loss circumstances for beam loss mitigation. Electron-stripping phenomena, which generate uncontrollable H particles, are characteristic beam loss factors of H
particles, are characteristic beam loss factors of H linacs. To clarify the beam loss causes in the J-PARC linac, a new diagnostic line was installed in the beam transport between the SDTL and ACS. In this diagnostic line, H
linacs. To clarify the beam loss causes in the J-PARC linac, a new diagnostic line was installed in the beam transport between the SDTL and ACS. In this diagnostic line, H particles were separated from the H
particles were separated from the H beam, and the intensity profiles of the H
beam, and the intensity profiles of the H particles were successfully measured by horizontally scanning a graphite plate in the range where H
particles were successfully measured by horizontally scanning a graphite plate in the range where H particles were distributed. By examining the intensity variation of the H
particles were distributed. By examining the intensity variation of the H particles with different residual pressure levels, we proved that half of the H
particles with different residual pressure levels, we proved that half of the H particles in the SDTL section are generated by the residual gas stripping in the nominal beam operation of the J-PARC linac.
particles in the SDTL section are generated by the residual gas stripping in the nominal beam operation of the J-PARC linac.
Okumura, Takuma*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; 40 of others*
Physical Review Letters, 130(17), p.173001_1 - 173001_7, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:83.24(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Rovira Leveroni, G.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 281, p.00012_1 - 00012_5, 2023/03
Shimomura, Koichiro*; Koda, Akihiro*; Pant, A. D.*; Natori, Hiroaki*; Fujimori, Hiroshi*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Tampo, Motonobu*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Teshima, Natsuki*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2462, p.012033_1 - 012033_5, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.21(Physics, Applied)Watanabe, Masao; Kihara, Takumi*; Nojiri, Hiroyuki*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(1), p.1_1 - 1_10, 2023/03
A pulsed magnet system has been developed as a new user-friendly sample environment equipment at the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility in Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex. It comprises a vacuum chamber, a 4 K closed-cycle refrigerator for samples, and a nitrogen bath made of a stainless-steel tube with a miniature solenoidal coil. The coil is cooled by liquid nitrogen supplied by an automatic liquid nitrogen supply system, and the sample is cooled by a refrigerator. This combination facilitates the automatic high magnetic field diffraction measurement for the user's operation. A relatively large scattering angle is up to 42 degrees, which is significantly wider than the previous setup. Neutron diffraction experiments were performed on a multiferroic TbMnO and the field dependence of the diffraction peaks was clearly observed. The new pulsed magnet system was established for a practical high magnetic field diffraction for the user program.
and the field dependence of the diffraction peaks was clearly observed. The new pulsed magnet system was established for a practical high magnetic field diffraction for the user program.
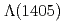 measured in
measured in 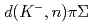 reactions
reactionsAikawa, Shu*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Tanida, Kiyoshi; 73 of others*
Physics Letters B, 837, p.137637_1 - 137637_8, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:47.44(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Oda, Kodai; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Ono, Ayato; Horino, Koki*; Ueno, Tomoaki*; Sugita, Moe; Morishita, Takatoshi; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Tokuchi, Akira*; Kamezaki, Hiroaki*; et al.
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.610 - 614, 2023/01
Kicker system is being used to kick the accelerated 3 GeV beam into the transport lines in RCS of J-PARC. The current kicker power supply applies thyratrons to discharge switches. We are developing a new kicker power supply using next-generation power semiconductors. The timing of the semiconductor switch operation is determined by the input of an external trigger signal. Large timing jitter causes unstable output pulses and beam loss due to beam orbit deviate from reference orbit. Therefore, a low jitter circuit that achieves high repeatability of 2 ns or less will be developed for the new kicker power supply. A prototype trigger generator has been fabricated, and jitter has been evaluated. The results of the evaluation test and the circuit configuration plan for reducing jitter will be reported.
Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Ono, Ayato; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Horino, Koki*; Ueno, Tomoaki*; Sugita, Moe; Yamamoto, Kazami; Oguri, Hidetomo; Kinsho, Michikazu; et al.
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.242 - 246, 2023/01
At J-PARC, semiconductor short pulse power supplies to replace kicker power supplies and semiconductor long pulse power supplies to replace klystron power supply systems are under construction. We have fabricated a 40kV/2kA/1.2 s unit power supply that employs a linear transformer drivers (LTD) system for kickers. Currently, we are working on a high voltage insulating cylinder insulator that suppresses corona discharges using only the insulator structure, without using insulating oil. In addition, the MARX system was adopted for klystron power supply system. A main circuit unit for 8kV/60A/830
s unit power supply that employs a linear transformer drivers (LTD) system for kickers. Currently, we are working on a high voltage insulating cylinder insulator that suppresses corona discharges using only the insulator structure, without using insulating oil. In addition, the MARX system was adopted for klystron power supply system. A main circuit unit for 8kV/60A/830 s rectangular pulse output and an 800V/60A correction circuit unit that improves the flat top droop from 10% to 1% were manufactured. Furthermore, a 2.2kV/2.4kW high voltage SiC inverter charger has been fabricated for this MARX power supply. The presentation will report the evaluation results of each test and prospects for semiconductor pulse power supplies.
s rectangular pulse output and an 800V/60A correction circuit unit that improves the flat top droop from 10% to 1% were manufactured. Furthermore, a 2.2kV/2.4kW high voltage SiC inverter charger has been fabricated for this MARX power supply. The presentation will report the evaluation results of each test and prospects for semiconductor pulse power supplies.