Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Konno, Chikara; Kochiyama, Mami; Hayashi, Hirokazu
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 11(2), p.23-00386_1 - 23-00386_11, 2024/04
Activation cross-section libraries for the ORIGEN and ORIGEN-S codes have been generated from JENDL-5 and JENDL/AD-2017. The ORIGEN activation cross-section libraries of the 200 and 48 group structures were generated with the AMPX-6 code, while the ORIGEN-S activation cross-section libraries with a MAXS format of the 199 group structure were done with the PREPO2018 code. Activation calculations for JPDR were carried out in order to validate the produced ORIGEN and ORIGEN-S activation cross-section libraries. The following comparisons were performed: the ORIGEN calculation results with the produced activation cross-section libraries and bundled ones, the 200 group and 48 group ORIGEN calculations, the ORIGEN and ORIGEN-S calculations with the JENDL-5 activation cross-section libraries, etc. Most of the differences of the calculation results were less than 20%, which demonstrated that the libraries were produced adequately.
Konno, Chikara
JAEA-Conf 2023-001, p.143 - 146, 2024/02
I modified NJOY2016.67 to produce photonuclear ACE files which can be used in MCNP6.2 and PHITS3.27 and produced the ACE file of the JENDL-5 photonuclear sub-library. Simple test calculations with the produced ACE file supported that the produced ACE file had no serious problems.
Watanabe, Tomoaki; Suyama, Kenya; Tada, Kenichi; Ferrer, R. M.*; Hykes, J.*; Wemple, C. A.*
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 10 Pages, 2024/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.08(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new nuclear data library for the advanced lattice physics code CASMO5 has been prepared based on JENDL-5. In JENDL-5, many essential nuclides for conventional LWR analysis have also been modified based on state-of-the-art evaluations. The new JENDL-5-based CASMO5 library was prepared by replacing as much of the nuclear data of the current CASMO5 ENDF/B-VII.1-based library as possible with JENDL-5. This study verified and validated the new library. Verifications were performed based on the OECD/NEA burnup credit criticality safety benchmark phase III-C, and the calculated k and fuel compositions of the BWR fuel assembly were compared with reported benchmark results. Comparison with the MCNP6.2 result was also performed using the same benchmark model. In addition, the TCA critical experiment and Takahama-3 post-irradiation experiment were used for validation. The results indicate that the new library performs well and is comparable to the ENDF/B-VII.1-based library in predictions of reactivity and fuel compositions for LWR systems.
and fuel compositions of the BWR fuel assembly were compared with reported benchmark results. Comparison with the MCNP6.2 result was also performed using the same benchmark model. In addition, the TCA critical experiment and Takahama-3 post-irradiation experiment were used for validation. The results indicate that the new library performs well and is comparable to the ENDF/B-VII.1-based library in predictions of reactivity and fuel compositions for LWR systems.
Nakayama, Shinsuke
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(12), p.1447 - 1453, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The d+Be neutron source is a candidate for transportable neutron source for on-site nondestructive inspection of infrastructure facilities such as bridges, tunnels and so on. The applicability of the d+Be neutron source to a transportable fast neutron source is explored by Monte Carlo particle transport simulations with PHITS and JENDL-5. The simulation results show that by increasing the shielding thickness by about 1.5 times, it is possible to realize the d+Be neutron source with the comparable performance to another candidate, the 2.5-MeV p+Li neutron source, at lower beam energy.
Watanabe, Tomoaki; Tada, Kenichi; Endo, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1386 - 1396, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:94.27(Nuclear Science & Technology)The burnup calculations for estimating the nuclide composition of the spent fuel are highly dependent on nuclear data. Many nuclides in the latest version of the Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library JENDL-5 were modified from JENDL-4.0 and the modification affects the burnup calculations. This study confirmed the validity of JENDL-5 in the burnup calculations. The PIE data of Takahama-3 was used for the validation. The effect of modifications of the parameters, e.g., cross sections and fission yields, from JENDL-4.0 to JENDL-5 on the nuclide compositions was quantitatively investigated. The calculation results showed that JENDL-5 has a similar performance to JENDL-4.0. The calculation results also revealed that the modifications of the cross sections of actinide nuclides, fission yields, and thermal scattering low data of hydrogen in H O affected the nuclide compositions of PWR spent fuels.
O affected the nuclide compositions of PWR spent fuels.
Fukahori, Tokio
INDC(JPN)-210 (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/10
The  U(n,f) cross section values were not correctly compiled in the ENDF format, and wrong values are disseminated in the JENDL/HE-2007 file. The high energy part of the
U(n,f) cross section values were not correctly compiled in the ENDF format, and wrong values are disseminated in the JENDL/HE-2007 file. The high energy part of the  U(n,f) cross section for the JENDL/HE-2007 library was evaluated by using the results of the FISCAL code. The correct
U(n,f) cross section for the JENDL/HE-2007 library was evaluated by using the results of the FISCAL code. The correct  U(n,f) cross section values of the JENDL/HE-2007 library above 200 MeV is given in this report.
U(n,f) cross section values of the JENDL/HE-2007 library above 200 MeV is given in this report.
Okita, Shoichiro; Goto, Minoru
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/10
Kawaguchi, Maho*; Shiba, Shigeki*; Iwahashi, Daiki*; Okawa, Tsuyoshi*; Gunji, Satoshi; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/10
The Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA) has been working on an experimental approach for evaluating the criticality of fuel debris produced by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNP) accident since 2014, collaborating with the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). As part of the approach, JAEA has modified the STAtic experiment Critical facilitY (STACY) for critical experiments to evaluate characteriscs of pseudo-fuel debris. As the preliminary analyses, we verified critical characteristics with major nuclear data libraries for the proposed core configuration patterns. The three-dimensional continuous-energy Monte Carlo neutron and photon transport code, SERPENT-V2.2.0 was used with the latest JENDL, JENDL-5. As a result, larger multiplication factors of JENDL-5 across the modified STACY core configuration patterns were evaluated in comparison to the other libraries. And,  H scattering and
H scattering and  U fission sensitivity coefficients of JENDL-5 were different from those of the other libraries. Comparing among analyses with those libraries, the updated S(
U fission sensitivity coefficients of JENDL-5 were different from those of the other libraries. Comparing among analyses with those libraries, the updated S( ,
,  ) of JENDL-5 might affect the result of critical characteristics in the critical analyses for the modified STACY core configuration.
) of JENDL-5 might affect the result of critical characteristics in the critical analyses for the modified STACY core configuration.
Konno, Chikara; Ota, Masayuki*; Kwon, Saerom*; Onishi, Seiki*; Yamano, Naoki*; Sato, Satoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(9), p.1046 - 1069, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:97.05(Nuclear Science & Technology)JENDL-5 was validated from a viewpoint of shielding applications under the Shielding Integral Test Working Group of the JENDL Committee. The following benchmark experiments were selected: JAEA/FNS in-situ experiments, Osaka Univ./OKTAVIAN TOF experiments, ORNL/JASPER sodium experiments, NIST iron experiment and QST/TIARA experiments. These experiments were analyzed with MCNP and nuclear data libraries (JENDL-5, JENDL-4.0 or JENDL-4.0/HE, ENDF/B-VIII.0 and JEFF-3.3). The analysis results demonstrate that JENDL-5 is comparable to or better than JENDL-4.0 or JENDL-4.0/HE, ENDF/B-VIII.0 and JEFF-3.3.
Sugawara, Takanori; Kunieda, Satoshi
Proceedings of International Conference on Mathematics and Computational Methods Applied to Nuclear Science and Engineering (M&C 2023) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2023/08
This study investigates the impact of the change from JENDL-4 to JENDL-5 on neutronics analysis of transmutation systems. As the transmutation systems, the following two systems are targeted: JAEA-ADS, a lead-bismuth cooled accelerator-driven system, and MARDS, a molten salt chloride accelerator-driven system. For the JAEA-ADS, the k-eff value increased 189 pcm from JENDL-4 to JENDL-5. It was found that the revisions of various nuclides affected to this difference. For example, the revision of  N indicated an increase of 200 pcm from the JENDL-4 result. For the MARDS, it was found that the major revision of
N indicated an increase of 200 pcm from the JENDL-4 result. For the MARDS, it was found that the major revision of  Cl and
Cl and  Cl cross sections was the main cause of the k-eff differences. This study confirmed that the difference in the nuclear data libraries still indicated differences in calculation results for the transmutation systems.
Cl cross sections was the main cause of the k-eff differences. This study confirmed that the difference in the nuclear data libraries still indicated differences in calculation results for the transmutation systems.
Suyama, Kenya; Ueki, Taro; Gunji, Satoshi; Watanabe, Tomoaki; Araki, Shohei; Fukuda, Kodai
Proceedings of 20th International Symposium on the Packaging and Transportation of Radioactive Materials (PATRAM22) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/06
Since the 1990s, the importance of the handbook has changed significantly, as the computational power has improved and continuous energy Monte Carlo codes have become widely used, which enables highly accurate criticality calculations, when necessary, irrespective of the complexity of the system. Because the value of performing a large number of calculations in advance and summarizing the data has decreased, since the second edition was published publicly in 1999, there has been no revision of criticality safety handbooks in Japan for nearly a quarter of a century. In Japan, where the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident occurred in 2011, it became necessary to deal with criticality safety issues in the transport and storage of the fuel debris which contains complex constituent elements, and the summary the criticality safety management for such material is an urgent issue. In the area of burnup credit, the transport and storage of fuel assemblies with low achieved burnups due to the consequences of accidents might be the problem. In addition, nuclear data, which is the input for the continuous energy Monte Carlo code, has been improved several times, now JENDL-5 is available from the end of 2021, and its incorporation becomes a need in the field. This report provides an overview of the latest criticality safety research in Japan and the planned revision of the Criticality Safety Handbook, which could be applied to the transport and storage sectors.
Nakayama, Shinsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Sublet, J.-Ch.*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.14011_1 - 14011_4, 2023/05
JENDL-5, the latest version of the Japanese evaluated nuclear data library, includes several sub-libraries to contribute to various applications. In this paper, we outline the evaluation and validation of the deuteron reaction sub-library developed mainly for the design of accelerator-based neutron sources and the alpha-particle reaction sub-library developed mainly for use in the back-end field. As for the deuteron sub-library, the data for 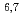 Li,
Li,  Be, and
Be, and 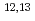 C from JENDL/DEU-2020 were partially modified and adopted. The data up to 200 MeV for
C from JENDL/DEU-2020 were partially modified and adopted. The data up to 200 MeV for  Al,
Al, 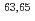 Cu, and
Cu, and  Nb, which are important as accelerator structural materials, were newly evaluated based on the calculations with the DEURACS code. As for the alpha-particle sub-library, the data up to 15 MeV for 18 light nuclides from Li to Si isotopes were evaluated based on the calculations with the CCONE code, and then only the neutron production cross sections were replaced with the data of JENDL/AN-2005. Validation on neutron yield by Monte Carlo transport simulations was performed for both sub-libraries. As a result, it was confirmed that the simulations based on the sub-libraries showed good agreement with experimental data.
Nb, which are important as accelerator structural materials, were newly evaluated based on the calculations with the DEURACS code. As for the alpha-particle sub-library, the data up to 15 MeV for 18 light nuclides from Li to Si isotopes were evaluated based on the calculations with the CCONE code, and then only the neutron production cross sections were replaced with the data of JENDL/AN-2005. Validation on neutron yield by Monte Carlo transport simulations was performed for both sub-libraries. As a result, it was confirmed that the simulations based on the sub-libraries showed good agreement with experimental data.
Tada, Kenichi; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Taninaka, Hiroshi; Yokoyama, Kenji; Okita, Shoichiro; Oizumi, Akito; Fukushima, Masahiro; Nakayama, Shinsuke
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 21 Pages, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:99.12(Nuclear Science & Technology)The new version of the Japanese evaluated nuclear data library, JENDL-5, was released in December 2021. This paper demonstrates the validation of JENDL-5 for fission reactor applications. Benchmark calculations are performed with the continuous-energy Monte Carlo codes MVP and MCNP and the deterministic code system MARBLE. The benchmark calculation results indicate that the performance of JENDL-5 for fission reactor applications is better than that of the former library JENDL-4.0.
Yokoyama, Kenji
EPJ Web of Conferences, 281, p.00004_1 - 00004_10, 2023/03
In Japan, development of adjusted nuclear data library for fast rector application based on the cross-section adjustment method has been conducted since the early 1990s. The adjusted library is called the unified cross-section set. The first version was developed in 1991 and is called ADJ91. Recently, the integral experimental data were further expanded to improve the design prediction accuracy of the core loaded with minor actinoids and/or degraded Pu. Using the additional integral experimental data, development of ADJ2017 was started in 2017. In 2022, the latest unified cross-section set AJD2017R was developed based on JENDL-4.0 by using 619 integral experimental data. An overview of the latest version with a review of previous ones will be shown. On the other hand, JENDL-5 was released in 2021. In the development of JENDL-5, some of the integral experimental data used in ADJ2017R were explicitly utilized in the nuclear data evaluation. However, this is not reflected in the covariance data. This situation needs to be considered when developing a unified cross-section set based on JENDL-5. Preliminary adjustment calculation based on JENDL-5 is performed using C/E (calculation/experiment) values simply evaluated by a sensitivity analysis. The preliminary results will be also discussed.
Yanagisawa, Hiroshi; Umeda, Miki; Motome, Yuiko; Murao, Hiroyuki
JAEA-Technology 2022-030, 80 Pages, 2023/02
Nuclear criticality benchmark analyses were carried out for TRIGA-type reactor systems in which uranium-zirconium hydride fuel rods are loaded by using the continuous-energy Monte Carlo code MVP with the evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-5. The analyses cover two sorts of benchmark data, the IEU-COMP-THERM-003 and IEU-COMP-THERM-013 in the International Criticality Safety Benchmark Evaluation Project (ICSBEP) Handbook, and effective neutron multiplication factors, reactivity worths for control rods etc. were calculated by JENDL-5 in comparison with those by the previous version of JENDL. As the results, it was confirmed that the effective neutron multiplication factors obtained by JENDL-5 were 0.4 to 0.6% greater than those by JENDL-4.0, and that there were no significant differences in the calculated reactivity worths by between JENDL-5 and JENDL-4.0. Those results are considered to be helpful for the confirmation of calculation accuracy in the analyses on NSRR control rod worths, which are planned in the future.
Tada, Kenichi; Yamamoto, Akio*; Kunieda, Satoshi; Nagaya, Yasunobu
JAEA-Data/Code 2022-009, 208 Pages, 2023/02
The nuclear data processing code has an important role to connect evaluated nuclear data libraries and neutronics calculation codes. Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has developed the nuclear data processing code FRENDY since 2013 to generate cross section files from evaluated nuclear data libraries, such as JENDL, ENDF/B, JEFF, and TENDL. The first version of FRENDY was released in 2019. FRENDY version 1 generates ACE files which are used for continuous energy Monte Carlo codes such as PHITS, Serpent, and MCNP. FRENDY version 2 generates multi-group neutron cross-section files from ACE files. The other major improvements are as follows: (1) uncertainty quantification for the probability tables of the unresolved resonance cross-section; (2) perturbation of the ACE file for the uncertainty quantification using a continuous Monte Carlo code; (3) modification of the ENDF-6 formatted nuclear data file. This report describes an overview of the nuclear data processing methods and input instructions for FRENDY.
Fukushima, Masahiro; Okajima, Shigeaki*; Mukaiyama, Takehiko*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 20 Pages, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)A series of integral experiments was conducted to evaluate the fission and the capture cross- sections of transuranic (TRU) nuclides at the fast critical facility FCA of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The experiments were carried out using seven uranium-fueled assemblies of the FCA. The neutron energy spectra of the core regions were adjusted so as to change from an intermediate neutron spectrum to a fast neutron spectrum on an assembly-by-assembly basis. The integral data measured with these experimental configurations provide some neutron energy characteristics: 1) fission rate ratios (FRRs) of  Np,
Np,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Am, and
Am, and  Cm relative to
Cm relative to  Pu by using absolutely calibrated fission chambers, 2) small sample reactivity worths (SRWs) of
Pu by using absolutely calibrated fission chambers, 2) small sample reactivity worths (SRWs) of  Np,
Np,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am, and
Am, and  Am where oxide powders of around 15 to 20 grams were used, 3) criticalities, and 4) spectral indices such as fission rate ratios of
Am where oxide powders of around 15 to 20 grams were used, 3) criticalities, and 4) spectral indices such as fission rate ratios of  U relative to
U relative to  U. In this paper, details of the SRW measurements are reported, and the latest Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library JENDL-5 is tested by using the integral data obtained in systematically varied neutron energy spectra.
U. In this paper, details of the SRW measurements are reported, and the latest Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library JENDL-5 is tested by using the integral data obtained in systematically varied neutron energy spectra.
Konno, Chikara
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 6 Pages, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:68.31(Nuclear Science & Technology)The JENDL-4.0/HE neutron and proton ACE files were produced in 2017 and those of 22 nuclei for neutron and 25 nuclei for proton were bundled in the PHITS code. Recently it was found that the following five data in the JENDL-4.0/HE neutron and proton ACE files had any problems; ACE files for  N and
N and  O, heating numbers, damage energy production cross sections, secondary neutron multiplicities and fission cross sections. Thus new JENDL-4.0/HE neutron and proton ACE files were produced with the problems fixed. This paper describes the problems and how to produce the new neutron and proton ACE files in detail.
O, heating numbers, damage energy production cross sections, secondary neutron multiplicities and fission cross sections. Thus new JENDL-4.0/HE neutron and proton ACE files were produced with the problems fixed. This paper describes the problems and how to produce the new neutron and proton ACE files in detail.
Kochiyama, Mami
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (133), p.76 - 81, 2022/10
The outline of the presentation at the joint session of Research Committee for Nuclear Data and Subcommittee on Nuclear Data in the Atomic Energy Society of Japan 2022 Autumn Meeting was contributed to Nuclear Data News. As part of the study on the near surface disposal of waste from research facilities, we are studying a method for evaluating the radioactivity inventory of waste generated by the dismantling of research reactors. In the radioactivity evaluation of the research reactor, we have investigated the method of calculating the neutron transport in the reactor and using the obtained neutron spectrum to calculate the activation of the internal structure by the ORIGEN-S code. In recent years, we have introduced and evaluated libraries created based on JENDL-4.0 and JENDL/AD-2017, and we will introduce the status of their examination. And we will introduce how to apply the results obtained by the radioactivity evaluation calculation to burial disposal.