Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Fukushima, Masahiro; Ando, Masaki; Nagaya, Yasunobu
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 199(6), p.1029 - 1043, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Watanabe, Tomoaki; Tada, Kenichi; Endo, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 16 Pages, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study investigated the impact of nuclear data updates from JENDL-4.0 (J4) to JENDL-5 (J5) on the light-water reactor fuel burnup calculations. Burnup calculations were conducted with J4 and J5 for PWR pin-cell and BWR fuel assembly geometries. The calculation results revealed significant burnup-dependent differences in the neutron multiplication factor (k ). Across the burnup range of 0-50 GWd/t, k
). Across the burnup range of 0-50 GWd/t, k values of J5 were consistently smaller than those of J4 and the difference gradually increased as burnup progressed. Direct sensitivity calculations, in which each nuclide data was replaced from J4 to J5, indicated that updates to the cross-sections of
values of J5 were consistently smaller than those of J4 and the difference gradually increased as burnup progressed. Direct sensitivity calculations, in which each nuclide data was replaced from J4 to J5, indicated that updates to the cross-sections of  U,
U,  U, and
U, and  Pu and the thermal scattering law data of H in H
Pu and the thermal scattering law data of H in H O notably impacted the k
O notably impacted the k differences. For the BWR assembly geometry containing Gd fuels, large k
differences. For the BWR assembly geometry containing Gd fuels, large k differences were observed in the burnup range of 10-15 GWd/t. This difference was primarily attributed to updates in the
differences were observed in the burnup range of 10-15 GWd/t. This difference was primarily attributed to updates in the  U,
U,  Gd, and
Gd, and  Gd cross-sections, and thermal scattering law data of H in H
Gd cross-sections, and thermal scattering law data of H in H O. Furthermore, we investigated how the nuclear data updates affected the k
O. Furthermore, we investigated how the nuclear data updates affected the k differences by examining nuclide number densities, the energy-dependent sensitivities, and the neutron spectra.
differences by examining nuclide number densities, the energy-dependent sensitivities, and the neutron spectra.
Fukushima, Masahiro; Ando, Masaki; Nagaya, Yasunobu
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 199(1), p.18 - 41, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)A series of integral experiments were conducted at FCA of JAEA, simulating LWR cores with a tight lattice cell of highly enriched MOX fuel containing more than 15% fissile plutonium. The three experimental configurations were constructed using foamed polystyrene with different void fractions to clarify the prediction accuracy of neutronic calculation codes and nuclear data among various neutron spectra. The nuclear characteristics measured in the experiments were criticality, moderator void reactivity worths, and sample reactivity worths. The preliminary analyses on experiments were conducted using a deterministic calculation code conventionally used for fast reactors with JENDL-4.0. Most reactivity worth calculations correlated well with the experimental values. Specifically for the softer neutron spectra configurations, the treatment of ultrafine energy groups obviously improved the prediction accuracy of the deterministic calculations. Furthermore, reference calculations were performed with MVP3 code by modeling the experimental setup in detail, confirming the validity of the deterministic calculations.
Suzuki, Motomu*; Nagaya, Yasunobu
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(2), p.177 - 191, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:23.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)With the release of the latest Japanese evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-5, the prediction accuracy of JENDL-5 for neutronics parameters of the BEAVRS benchmark for the hot zero power condition was evaluated in this study. The criticality, control rod bank worth (CRW), isothermal temperature coefficient (ITC), and in-core detector signals were calculated and compared with the measured data for evaluation. For the criticality, the calculation-to-experimental (C/E) values varied between 1.0001 and 1.0045. Sensitivity analysis by replacing cross section data from the JENDL-4.0u1 with JENDL-5 revealed that 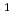 H,
H,  U,
U,  U, and
U, and  O significantly affected the criticality. The individual CRW agreed within 50 pcm, and total CRW also agreed within 100 pcm from the measured values. The ITC results calculated with a temperature deviation of 5.56 K case were negatively overestimated comparing with the measured values; whereas those of with 2.78 K were improved and agree with the measured values within a standard deviation. The axial detector signals indicated a maximum relative error of 4.46% and the root mean squared error (RMSE) of 2.13%. The differences between the previous version of JENDL-4.0u1 and JENDL-5 were also investigated.
O significantly affected the criticality. The individual CRW agreed within 50 pcm, and total CRW also agreed within 100 pcm from the measured values. The ITC results calculated with a temperature deviation of 5.56 K case were negatively overestimated comparing with the measured values; whereas those of with 2.78 K were improved and agree with the measured values within a standard deviation. The axial detector signals indicated a maximum relative error of 4.46% and the root mean squared error (RMSE) of 2.13%. The differences between the previous version of JENDL-4.0u1 and JENDL-5 were also investigated.
Konno, Chikara
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(1), p.121 - 126, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:23.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)The JENDL-4.0/HE neutron and proton ACE files were produced in 2017 and those of 22 nuclei for neutron and 25 nuclei for proton were bundled in the PHITS code. Recently it was found that the following five data in the JENDL-4.0/HE neutron and proton ACE files had any problems; ACE files for  N and
N and  O, heating numbers, damage energy production cross sections, secondary neutron multiplicities and fission cross sections. Thus new JENDL-4.0/HE neutron and proton ACE files were produced with the problems fixed. This paper describes the problems and how to produce the new neutron and proton ACE files in detail.
O, heating numbers, damage energy production cross sections, secondary neutron multiplicities and fission cross sections. Thus new JENDL-4.0/HE neutron and proton ACE files were produced with the problems fixed. This paper describes the problems and how to produce the new neutron and proton ACE files in detail.
Watanabe, Tomoaki; Tada, Kenichi; Endo, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1386 - 1396, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:71.02(Nuclear Science & Technology)The burnup calculations for estimating the nuclide composition of the spent fuel are highly dependent on nuclear data. Many nuclides in the latest version of the Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library JENDL-5 were modified from JENDL-4.0 and the modification affects the burnup calculations. This study confirmed the validity of JENDL-5 in the burnup calculations. The PIE data of Takahama-3 was used for the validation. The effect of modifications of the parameters, e.g., cross sections and fission yields, from JENDL-4.0 to JENDL-5 on the nuclide compositions was quantitatively investigated. The calculation results showed that JENDL-5 has a similar performance to JENDL-4.0. The calculation results also revealed that the modifications of the cross sections of actinide nuclides, fission yields, and thermal scattering low data of hydrogen in H O affected the nuclide compositions of PWR spent fuels.
O affected the nuclide compositions of PWR spent fuels.
Yanagisawa, Hiroshi; Umeda, Miki; Motome, Yuiko; Murao, Hiroyuki
JAEA-Technology 2022-030, 80 Pages, 2023/02
Nuclear criticality benchmark analyses were carried out for TRIGA-type reactor systems in which uranium-zirconium hydride fuel rods are loaded by using the continuous-energy Monte Carlo code MVP with the evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-5. The analyses cover two sorts of benchmark data, the IEU-COMP-THERM-003 and IEU-COMP-THERM-013 in the International Criticality Safety Benchmark Evaluation Project (ICSBEP) Handbook, and effective neutron multiplication factors, reactivity worths for control rods etc. were calculated by JENDL-5 in comparison with those by the previous version of JENDL. As the results, it was confirmed that the effective neutron multiplication factors obtained by JENDL-5 were 0.4 to 0.6% greater than those by JENDL-4.0, and that there were no significant differences in the calculated reactivity worths by between JENDL-5 and JENDL-4.0. Those results are considered to be helpful for the confirmation of calculation accuracy in the analyses on NSRR control rod worths, which are planned in the future.
Kochiyama, Mami
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (133), p.76 - 81, 2022/10
The outline of the presentation at the joint session of Research Committee for Nuclear Data and Subcommittee on Nuclear Data in the Atomic Energy Society of Japan 2022 Autumn Meeting was contributed to Nuclear Data News. As part of the study on the near surface disposal of waste from research facilities, we are studying a method for evaluating the radioactivity inventory of waste generated by the dismantling of research reactors. In the radioactivity evaluation of the research reactor, we have investigated the method of calculating the neutron transport in the reactor and using the obtained neutron spectrum to calculate the activation of the internal structure by the ORIGEN-S code. In recent years, we have introduced and evaluated libraries created based on JENDL-4.0 and JENDL/AD-2017, and we will introduce the status of their examination. And we will introduce how to apply the results obtained by the radioactivity evaluation calculation to burial disposal.
 I(n,
I(n,  ) using fast neutron source in the "YAYOI" reactor
) using fast neutron source in the "YAYOI" reactorNakamura, Shoji; Toh, Yosuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Hatsukawa, Yuichi*; Harada, Hideo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(7), p.851 - 865, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)The present study performed integral experiments of  I using a fast-neutron source reactor "YAYOI" of the University of Tokyo to validate evaluated nuclear data libraries. The iodine-129 sample and flux monitors were irradiated by fast neutrons in the Glory hole of the YAYOI reactor. Reaction rates of
I using a fast-neutron source reactor "YAYOI" of the University of Tokyo to validate evaluated nuclear data libraries. The iodine-129 sample and flux monitors were irradiated by fast neutrons in the Glory hole of the YAYOI reactor. Reaction rates of  I were obtained by measurement of decay gamma-rays emitted from
I were obtained by measurement of decay gamma-rays emitted from  I. The validity of the fast-neutron flux spectrum in the Glory hole was confirmed by the
I. The validity of the fast-neutron flux spectrum in the Glory hole was confirmed by the 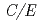 ratios of the reaction rates of flux monitors. The experimental reaction rate of
ratios of the reaction rates of flux monitors. The experimental reaction rate of  I was compared with that calculated with both the fast-neutron flux spectrum and evaluated nuclear data libraries. The present study revealed that the evaluated nuclear data of
I was compared with that calculated with both the fast-neutron flux spectrum and evaluated nuclear data libraries. The present study revealed that the evaluated nuclear data of  I cited in JENDL-4.0 should be reduced as much as 18% in neutron energies ranging from 10 keV to 3 MeV, and supported the reported data by Noguere
I cited in JENDL-4.0 should be reduced as much as 18% in neutron energies ranging from 10 keV to 3 MeV, and supported the reported data by Noguere  below 100 keV.
below 100 keV.
Kochiyama, Mami; Sakai, Akihiro
JAEA-Technology 2022-009, 56 Pages, 2022/06
It is necessary to evaluate radioactivity inventory in wastes before disposal of low-level radioactive wastes generated from dismantling research reactors. It is efficient for owners of each research reactor to use a common radioactive evaluation method in order to comply with the license application for disposal facility. In this report, neutron transport and activation calculations were carried out for the Rikkyo University research reactor in order to examine a common radioactivity evaluation method for burial disposal of radioactive wastes generated by dismantling. We adopted the neutron transport codes DORT and MCNP and the activation code ORIGEN-S with cross-section libraries based on JENDL-4.0 and JENDL/AD-2017. The radioactivity concentrations obtained by the radiochemical analysis and both calculation codes were in agreement by 0.4 to 3 times. Therefore, by appropriately considering this difference, the radioactivity evaluation method by DORT, MCNP and ORIGEN-S can be applied to the radioactivity evaluation for buried disposal. In order to classify wastes from dismantling by clearance or buried disposal method according to their radioactivity levels, we also created radioactivity concentration distributions in the concrete area and graphite thermal column area.
Yokoyama, Kenji; Maruyama, Shuhei; Taninaka, Hiroshi; Oki, Shigeo
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-019, 115 Pages, 2022/03
In JAEA, several versions of unified cross-section set for fast reactors have been developed so far; we have developed a new unified cross-section set ADJ2017R, which is an improved version of the unified cross-section setADJ2017 for fast reactors. The unified cross-section set is used for reflecting information of C/E values (analysis / experiment values) obtained by integral experiment analyses in reactor core design via the cross-section adjustment methodology; the values are stored in the standard database for FBR core design. In the methodology, the cross-section set is adjusted by integrating the information such as uncertainty (covariance) of nuclear data, uncertainty of integral experiment / analysis, sensitivity of integral experiment with respect to nuclear data. ADJ2017R basically has the same performance as ADJ2017, but we conducted an additional investigation on ADJ2017 and revised the following two points. The first is to unify the evaluation method of the correlation coefficient of uncertainty caused by experiments (hereinafter referred to as the experimental correlation coefficient). Because it was found that the common uncertainty used in the evaluation of the experimental correlation coefficient was evaluated by two different methods, the experimental correlation coefficients were revised for all experimental data, and the evaluation method was unified. The second is the review of the integral experiment data used for the cross-section adjustment calculation. It was found that one of the experimental values of composition ratio after irradiation of the Am-243 sample has a problem in uncertainty evaluation because its experimental uncertainty is extremely small compared to the others. The cross-section adjustment calculation was, therefore, redone by excluding the experimental value. In the creation of ADJ2017, a total of 719 data sets were analyzed and evaluated, and eventually adopted 620 integral experimental data sets. In contrast, a total of 61
Yanagisawa, Hiroshi
JAEA-Technology 2021-023, 190 Pages, 2021/11
Computational analyses on nuclear criticality characteristics were carried out for heterogeneous lattice systems composed of water moderator and fuel rods utilized in low-power research and test reactors, in which the depletion of fuel due to burnup is relatively small, by using the continuous-energy Monte Carlo code MVP Version 2 with the evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-4.0. In the analyses, the minimum critical number of fuel rods was evaluated using calculated neutron multiplication factors for the heterogeneous systems of the uranium dioxide fuel rod in the Static Experiments Critical Facility (STACY) and the Tank-type Critical Assembly (TCA), and the uranium-zirconium hydride fuel rod in the Nuclear Safety Research Reactor (NSRR). In addition, six sorts of the ratio of reaction rates, which are components of neutron multiplication factors, were calculated in the analyses to explain the variation of neutron multiplication factors with the ratio of water moderator to fuel volume in a unit fuel rod cell. Those results of analyses are considered to be useful for the confirmation of reasonableness and validity of criticality safety measures as data showing criticality characteristics for water-moderated heterogeneous lattice systems composed of the existing fuel rods in research and test reactors, of which criticality data are not sufficiently provided by the Criticality Safety Handbook.
Sugino, Kazuteru; Numata, Kazuyuki*; Ishikawa, Makoto; Takeda, Toshikazu*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 130, p.118 - 123, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)In MA sample irradiation test data calculations, the neutron fluence during irradiation period is generally scaled by using dosimetry data in order to improve calculation accuracy. In such a case, appropriate correction is required to burnup sensitivity coefficients obtained by the conventional generalized perturbation theory because some cancellations occur in the burnup sensitivity coefficients. Therefore, a new formula for the burnup sensitivity coefficient has been derived with the consideration of the neutron fluence scaling effect (NFS). In addition, the cross-section-induced uncertainty is evaluated by using the obtained burnup sensitivity coefficients and the covariance data based on the JENDL-4.0.
Yokoyama, Kenji; Sugino, Kazuteru; Ishikawa, Makoto; Maruyama, Shuhei; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Numata, Kazuyuki*; Jin, Tomoyuki*
JAEA-Research 2018-011, 556 Pages, 2019/03
We have developed a new unified cross-section set ADJ2017, which is an improved version of the unified cross-section set ADJ2010 for fast reactors. The unified cross-section set is used for reflecting information of C/E values (analysis / experiment values) obtained by integral experiment analyses; the values are stored in the standard database for FBR core design via the cross-section adjustment methodology, which integrates with the information such as uncertainty (covariance) of nuclear data, uncertainty of integral experiment / analysis, sensitivity of integral experiment with respect to nuclear data. The ADJ2017 is based on Japan's latest nuclear data library JENDL-4.0 as in the previous version of ADJ2010, and it incorporates more information on integral experimental data sets related to minor actinides (MAs) and degraded plutonium (Pu). In the creation of ADJ2010, a total of 643 integral experimental data sets were analyzed and evaluated, and 488 of the integral experimental data sets were finally selected to be used for the cross-section adjustment. In contrast, we have evaluated a total of 719 data sets, and eventually adopted 620 integral experimental data sets to create ADJ2017. ADJ2017 shows almost the same performance as ADJ2010 for the main neutronic characteristics of conventional sodium-cooled MOX-fuel fast reactors. In addition, for the neutronic characteristics related to MA and degraded Pu, ADJ2017 improves the C/E values of the integral experimental data sets, and reduces the uncertainty induced by the nuclear data. ADJ2017 is expected to be widely used in the analysis and design research of fast reactors. Moreover, it is expected that the integral experimental data sets used for ADJ2017 can be utilized as a standard database of FBR core design.
Matsuda, Norihiro; Kunieda, Satoshi; Okamoto, Tsutomu*; Tada, Kenichi; Konno, Chikara
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 6, p.225 - 229, 2019/01
 for MYRRHA using a Monte Carlo technique
for MYRRHA using a Monte Carlo techniqueIwamoto, Hiroki; Stankovskiy, A.*; Fiorito, L.*; Van den Eynde, G.*
EPJ Nuclear Sciences & Technologies (Internet), 4, p.42_1 - 42_7, 2018/11
This paper presents a nuclear data sensitivity and uncertainty analysis of the effective delayed neutron fraction  for critical and subcritical cores of the MYRRHA reactor using the continuous-energy Monte Carlo transport code MCNP. The
for critical and subcritical cores of the MYRRHA reactor using the continuous-energy Monte Carlo transport code MCNP. The  sensitivities are calculated by the modified
sensitivities are calculated by the modified  -ratio method proposed by Chiba. Comparing the
-ratio method proposed by Chiba. Comparing the  sensitivities obtained with different scaling factors
sensitivities obtained with different scaling factors  introduced by Chiba shows that a value of
introduced by Chiba shows that a value of 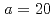 is the most suitable for the uncertainty quantification of
is the most suitable for the uncertainty quantification of  . Using the calculated
. Using the calculated  sensitivities and the JENDL-4.0u covariance data, the
sensitivities and the JENDL-4.0u covariance data, the  uncertainties for the critical and subcritical cores are determined to be 2.2
uncertainties for the critical and subcritical cores are determined to be 2.2  0.2% and 2.0
0.2% and 2.0  0.2%, respectively, which are dominated by delayed neutron yield of
0.2%, respectively, which are dominated by delayed neutron yield of  Pu and
Pu and  U.
U.
Usami, Shin; Kishimoto, Yasufumi*; Taninaka, Hiroshi; Maeda, Shigetaka
JAEA-Technology 2018-003, 97 Pages, 2018/07
The decay heat used for effectiveness evaluation of the prevention measures against severe accidents in the prototype fast breeder reactor Monju was evaluated by applying the updated nuclear data libraries based on JENDL-4.0, reflecting the realistic core operation pattern, and setting the rational extent of uncertainty. The decay heats of fission products, the actinide nuclides such as Cm-242, and radioactive structural materials were calculated by FPGS code. The decay heat of U-239 and Np-239 was evaluated based on ANSI/ANS-5.1-1994. The calculation uncertainty of each decay heat was evaluated based on summation of uncertainty factors, C/E values of reaction rates obtained in Monju system startup test, and so on. Furthermore, the decay heat evaluation method based on the FPGS90 was verified by the comparison of the results of the decay heat measurement of the two spent MOX fuel subassemblies in the experimental fast reactor Joyo MK-II core.
Fukushima, Masahiro; Goda, J.*; Bounds, J.*; Cutler, T.*; Grove, T.*; Hutchinson, J.*; James, M.*; McKenzie, G.*; Sanchez, R.*; Oizumi, Akito; et al.
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 189, p.93 - 99, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:60.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)To validate lead (Pb) nuclear cross sections, a series of integral experiments to measure lead void reactivity worths was conducted in a high-enriched uranium (HEU)/Pb system and a low enriched uranium (LEU)/Pb system using the Comet Critical Assembly at NCERC. The critical experiments were designed to provide complementary data sets having different sensitivities to scattering cross sections of lead. The larger amount of the  U present in the LEU/Pb core increases the neutron importance above 1 MeV compared with the HEU/Pb core. Since removal of lead from the core shifts the neutron spectrum to the higher energy region, positive lead void reactivity worths were observed in the LEU/Pb core while negative values were observed in the HEU/Pb core. Experimental analyses for the lead void reactivity worths were performed with the Monte Carlo calculation code MCNP6.1 together with nuclear data libraries, JENDL 4.0 and ENDF/B VII.1. The calculation values were found to overestimate the experimental ones for the HEU/Pb core while being consistent for the LEU/Pb core.
U present in the LEU/Pb core increases the neutron importance above 1 MeV compared with the HEU/Pb core. Since removal of lead from the core shifts the neutron spectrum to the higher energy region, positive lead void reactivity worths were observed in the LEU/Pb core while negative values were observed in the HEU/Pb core. Experimental analyses for the lead void reactivity worths were performed with the Monte Carlo calculation code MCNP6.1 together with nuclear data libraries, JENDL 4.0 and ENDF/B VII.1. The calculation values were found to overestimate the experimental ones for the HEU/Pb core while being consistent for the LEU/Pb core.
Fukushima, Masahiro; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi; Okajima, Shigeaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 54(7), p.795 - 805, 2017/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:72.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)A series of integral experiments was conducted in FCA assemblies with systematically changed neutron spectra covering from the intermediate to fast ones. The experiments provide systematic data of central fission rates for TRU nuclides containing minor actinides,  Np,
Np,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Am, and
Am, and  Cm. Latest major nuclear data libraries, JENDL-4.0, ENDF/B-VII.1, and JEFF-3.2, were tested using benchmark models regarding the fission rate ratios relative to
Cm. Latest major nuclear data libraries, JENDL-4.0, ENDF/B-VII.1, and JEFF-3.2, were tested using benchmark models regarding the fission rate ratios relative to  Pu. For all the libraries, the benchmark tests by a Monte Carlo calculation code show obvious overestimations particularly for the fission rate ratios of
Pu. For all the libraries, the benchmark tests by a Monte Carlo calculation code show obvious overestimations particularly for the fission rate ratios of  Cm to
Cm to  Pu. Additionally, a large discrepancy about by 20% between the libraries is revealed for the fission rate ratio of
Pu. Additionally, a large discrepancy about by 20% between the libraries is revealed for the fission rate ratio of  Pu to
Pu to  Pu measured in the intermediate neutron spectrum. The cause of discrepancy is furthermore clarified by sensitivity analyses.
Pu measured in the intermediate neutron spectrum. The cause of discrepancy is furthermore clarified by sensitivity analyses.
Kuwagaki, Kazuki*; Nagaya, Yasunobu
JAEA-Data/Code 2017-007, 27 Pages, 2017/03
The integral benchmark test of JENDL-4.0 for U-233 systems using the continuous-energy Monte Carlo code MVP was conducted. The previous benchmark test was performed only for U-233 thermal solution and fast metallic systems in the ICSBEP handbook. In this study, MVP input files were prepared for uninvestigated benchmark problems in the handbook including compound thermal systems (mainly lattice systems) and integral benchmark test was performed. The prediction accuracy of JENDL-4.0 was evaluated for effective multiplication factors (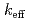 's) of the U-233 systems. As a result, a trend of underestimation was observed for all the categories of U-233 systems. In the benchmark test of ENDF/B-VII.1 for U-233 systems with the ICSBEP handbook, it is reported that a decreasing trend of calculated
's) of the U-233 systems. As a result, a trend of underestimation was observed for all the categories of U-233 systems. In the benchmark test of ENDF/B-VII.1 for U-233 systems with the ICSBEP handbook, it is reported that a decreasing trend of calculated 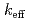 values in association with a parameter ATFF (Above-Thermal Fission Fraction) is observed. The ATFF values were also calculated in this benchmark test of JENDL-4.0 and the same trend as ENDF/B-VII.1 was observed.
values in association with a parameter ATFF (Above-Thermal Fission Fraction) is observed. The ATFF values were also calculated in this benchmark test of JENDL-4.0 and the same trend as ENDF/B-VII.1 was observed.