Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -treated column study of Hanford 300 area sediment using a simple ion exchange and immobile domain model
-treated column study of Hanford 300 area sediment using a simple ion exchange and immobile domain modelSaito, Tatsuo; Sato, Kazuhiko; Yamazawa, Hiromi*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 237, p.106708_1 - 106708_9, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.14(Environmental Sciences)We succeeded at numerical reproduction of dissolved U concentrations from column experiments with PO -treated Hanford 300 Area sediment. The time-series curves of dissolved U concentrations under various Darcy flow rate conditions were reproduced by the numerical model in the present study through optimization of the following parameters:(i) the mass of U in mobile domain (on surface soil connected to the stream) and the rest of the total U left as precipitation in immobile domain (isolated in deep soil);(ii) the mixing ratio between immobile and mobile domains, to fit the final recovering curve of concentration; and (iii) the cation exchange capacity (CEC
-treated Hanford 300 Area sediment. The time-series curves of dissolved U concentrations under various Darcy flow rate conditions were reproduced by the numerical model in the present study through optimization of the following parameters:(i) the mass of U in mobile domain (on surface soil connected to the stream) and the rest of the total U left as precipitation in immobile domain (isolated in deep soil);(ii) the mixing ratio between immobile and mobile domains, to fit the final recovering curve of concentration; and (iii) the cation exchange capacity (CEC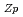 ) and equilibrium constant (k
) and equilibrium constant (k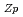 ) of the exchange reaction of UO
) of the exchange reaction of UO
 and H
and H on simulated soil surface (
on simulated soil surface (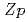 ), to fit the transient equilibrium concentration, forming the bed of the bathtub curve.
), to fit the transient equilibrium concentration, forming the bed of the bathtub curve.
Haga, Katsuhiro; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Wakui, Takashi; Naoe, Takashi; Takada, Hiroshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(2), p.160 - 168, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:45.24(Nuclear Science & Technology)The mercury target vessel used for the spallation neutron source in J-PARC has multi-walled structure made of stainless steel type 316L, which comprises a mercury vessel and a water shroud. In 2015, water leak incidents from the water shroud occurred while the mercury target was operated with a proton beam power of 500 kW. Several investigations were conducted to identify the cause of failure. The results of the visual inspections, mockup tests, and analytical evaluations suggested that the water leak was caused by the combination of two factors. One was the diffusion bonding failure due to the large thermal stress induced by welding of the bolt head, which fixes the mercury vessel and the water shroud, during the fabrication process. The other was the thermal fatigue failure of the seal weld due to the repetitive beam trip during the operating period. These target failures point to the importance of eliminating initial defects from welding lines and to secure the rigidity and reliability of welded structures. The next mercury target was fabricated with an improved design which adopted parts of monolithic structure machined by wire EDM to reduce welding lines, and intensified inspections to eliminate the initial defects. The operation with the improved target is planned to be started in October 2017.
Yamada, Fumiaki; Imaizumi, Yuya; Nishimura, Masahiro; Fukano, Yoshitaka; Arikawa, Mitsuhiro*
Proceedings of 25th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-25) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2017/07
The loss-of-reactor-level (LORL) is one of the loss-of-heat-removal-system (LOHRS) of beyond-DBA (BDBA) severe accident. An evaluation method for the LORL which is caused by the coolant leakage in two positions of the primary heat transport system (PHTS) was developed for prototype JSFR which is loop-type sodium-cooled fast reactor. The secondary leakage in cold standby which occurred in different loop from that of the first leakage in rated power operation can lead LORL by excessive declining of the sodium level. Therefore, the sodium level behavior in RV was studied in a representative accident sequence by considering the sodium pumping up into RV, siphon-breaking to stop pumping out from RV and maintain the sodium level, and calculation programs for the transient sodium level in RV. The representative sequence with lowest sodium level was selected by considering combinations of possible leakage positions. As a result of the evaluation considering the countermeasures above, it was revealed that the LOHRS can be prevented by maintaining the sodium level for the operation of decay heat removal system, even in the leakages in two positions of PHTS which corresponds to BDBA.
Kojima, Kensuke; Okumura, Keisuke; Kosako, Kazuaki*; Torii, Kazutaka*
JAEA-Research 2015-019, 90 Pages, 2016/01
At the decommissioning of light water reactors (LWRs), it is important to evaluate an amount of radioactivity in the ex-core structures such as a reactor containment vessel, radiation shieldings, and so on. It is thought that the leakage neutron spectra in these radioactivation regions, which strongly affect the induced radioactivity, would be changed by different reactor core configurations such as fuel assembly loading pattern and fuel burnups. This study was intended to evaluate these effects. For the purpose, firstly, partial neutron currents on the core surfaces were calculated for some core configurations. Then, the leakage neutron flux spectra in major radioactivation regions were calculated based on the provided currents. Finally, influence of the core configurations upon the neutron flux spectra was evaluated. As a result, it has been found that the influence is small on the spectrum shapes of neutron fluxes. However, it is necessary to pay attention to the facts that intensities of the leakage neutron fluxes are changed by the configurations and that intensities and spectrum shapes of the leakage neutron fluxes are changed depending on the angular direction around the core.
Takeda, Takeshi; Otsu, Iwao
Journal of Energy and Power Sources, 2(7), p.274 - 290, 2015/07
Yoshida, Hajime; Kosaku, Yasuo*; Enoeda, Mikio; Abe, Tetsuya; Akiba, Masato
JAERI-Research 2005-003, 13 Pages, 2005/03
Hydrogen permeation fluxes of the reduced activation ferritic steel F82H were quantitatively measured by a newly proposed method, vacuum thermo-balance method, for a precise estimation of tritium leakage in a fusion reactor. We prepared sample capsules made of F82H, which enclosed hydrogen gas. The hydrogen in the capsules permeated through the capsule wall, and subsequently desorbed from the capsule surface during isothermal heating. The vacuum thermo-balance method allows simultaneous measurement of the hydrogen permeation flux by two independent methods, namely, the net weight reduction of the sample capsule and exhaust gas analysis. Thus the simultaneous measurements by two independent methods increase the reliability of the permeability measurement. The ratio of the hydrogen permeation fluxes obtained by the net weight reduction to that measured by the exhaust gas analysis was in the range from 1/4 to 1/1 in this experiment. It has been demonstrated that the vacuum thermo-balance method is effective for the measurement of hydrogen permeation rate of F82H.
Sakaba, Nariaki; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Kondo, Masaaki; Emori, Koichi
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 233(1-3), p.135 - 145, 2004/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:35.12(Nuclear Science & Technology)The containment structures of the HTTR consist of the reactor containment vessel, the service area, and the emergency air purification system, which minimise the release of fission products in postulated accidents which lead to fission product release from the reactor facilities. The reactor containment vessel is designed to withstand the temperature and pressure transients and to be leak-tight in the case of a rupture of the primary concentric hot gas duct, etc. The pressure inside the service area is maintained at a negative pressure by the emergency air purification system. The emergency air purification system will also remove airborne radio-activity and will maintain a correct pressure in the service area. The leak-tightness characteristics of the containment structures are described in this paper. The measured leakage rates of the reactor containment vessel were enough less than the specified leakage limit of 0.1%/d confirmed during the commissioning tests and annual inspections. The service area was kept the design pressure well below its allowable limitation by the emergency air purification system which filter efficiency of particle removal and iodine removal were well over the limited values. The obtained data demonstrates that the reactor containment structures were fabricated to minimise the release of fission products in the postulated accidents with fission product release from the reactor facilities.
Ito, Haruhiko; Homma, Kenzo; Itabashi, Yukio; Tabata, Toshio; Akashi, Kazutomo; Inaba, Yukio; Kumahara, Hajime; Takahashi, Kunihiro; Kitajima, Toshio; Yokouchi, Iichiro
JAERI-Review 2003-024, 76 Pages, 2003/10
no abstracts in English
Hanawa, Satoshi; Tachibana, Yukio; Iyoku, Tatsuo; Ishihara, Masahiro; Ito, Haruhiko
JAERI-Tech 2003-064, 25 Pages, 2003/07
On the 147cycle operation, the water leakage was found at the pressure instrumentation pipe which is attached to the exit pipe of No.1 charge pump of the purification system of primary cooling system at JMTR in the Oarai establishment, JAERI. Then JMTR was shutted down manually on December 10th. It was predicted that the crack on the pressure instrumentation pipe was initiated and propagated by the cyclic load which was caused by the charge pump. Therefore, vibration and stress analyses of pressure instrumentation pipe were performed. From the vibration analysis, the natural frequency of the pressure instrumentation pipe of No.1 charge pump is between 53 58Hz, which is close to the resonance frequency of 50Hz. From the stress analysis results, total stress generated on the pressure instrumentation pipe is 112.2MPa at the natural frequency of 53Hz and 74.2Mpa at 58Hz. It was found that the stress of 112.2MPa is close to the fatigue limit of used materials.
58Hz, which is close to the resonance frequency of 50Hz. From the stress analysis results, total stress generated on the pressure instrumentation pipe is 112.2MPa at the natural frequency of 53Hz and 74.2Mpa at 58Hz. It was found that the stress of 112.2MPa is close to the fatigue limit of used materials.
Working Group for Investigation of Cause of Crack Initiation
JAERI-Tech 2003-060, 183 Pages, 2003/07
On December 10, 2002, the water leakage was found at the pressure instrumentation pipe attached to the exit pipe of No.1 charging pump of the purification system of a primary cooling system at JMTR, and the cracks were detected on the pressure instrumentation pipe by the visual observation. The Investigation Committee for Water Leakage from Instrumentation Pipe in JMTR was established and organized by specialists from inside and outside JAERI on December 16. In order to investigate the cause of crack initiation at the pressure instrumentation pipe, the Working Group was organized in the Department of JMTR. Visual inspection, fractgraphy test, metallographic observation and hardness test for the pressure instrumentation pipe and its weldment were carried out in the JMTR Hot Laboratory. This report summarized above data obtained by investigation on the cause of the crack initiation.
Sakaba, Nariaki; Nakazawa, Toshio; Kawasaki, Kozo; Urakami, Masao*; Saishu, Sadanori*
JAERI-Tech 2003-041, 106 Pages, 2003/03
In the second stage of the research and development for a high-temperature helium-leak detection system, the temperature sensor using optical fibres was studied. The sensor detects the helium leakage by the temperature inclease surrounded opitical fibre with or without heat insulator. Moreover, the applicability of high temperature equipments as the HTTR system was studied. With the sensor we detected 5.0-20.0 cm /s helium leakages within 60 minutes. Also it was possible to detect earlier when the leakage level is at 20.0 cm
/s helium leakages within 60 minutes. Also it was possible to detect earlier when the leakage level is at 20.0 cm /s.
/s.
Sakaba, Nariaki; Nakazawa, Toshio; Kawasaki, Kozo; Urakami, Masao*; Saishu, Sadanori*
JAERI-Review 2002-041, 86 Pages, 2003/03
In High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactors (HTGR), the detection of leakage of helium at an early stage is very important for the safety and stability of operations. Since helium is a colourless gas, it is generally difficult to identify the location and the amount of leakage when very little leakage has occurred. The purpose of this R&D is to develop a helium-leak detection system for the high temperature environment appropriate to the HTTR. This system can shorten the time of detection to several hours from about one week in the current detection time. In addition, it can also identify easily the leak location using the optical fibre network. As the first step in the development, this paper describes the result of surveying leakage events at nuclear facilities inside and outside Japan and current gas leakage detection technology to adapt optical fibre detection technology to HTGRs.
Sakaba, Nariaki; Nakazawa, Toshio; Kawasaki, Kozo; Urakami, Masao*; Saishu, Sadanori*
JAERI-Research 2003-006, 65 Pages, 2003/03
In the final third stage of the research and development for a high-temperature helium-leak detection system, the radiation sensor was developed in order to detect very small helium leakage. Applying the radiation sensor, we proposed not only the direct detection method which uses the detection of FP gas in helium, but also the active method which uses the difference in the radiation absorption between helium and air. From obtained data it was found that we can detect 0.2 cm /s leakage within 10 minutes by the active method.
/s leakage within 10 minutes by the active method.
Kugo, Teruhiko; Okubo, Tsutomu;
JAERI-Research 99-057, p.29 - 0, 1999/09
no abstracts in English
Teshigawara, Makoto*; Watanabe, Noboru*; Takada, Hiroshi; Nakashima, Hiroshi; ; Oyama, Yukio; Kosako, Kazuaki*
JAERI-Research 99-010, 16 Pages, 1999/02
no abstracts in English
Tachibana, Yukio; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko; Furusawa, Takayuki; Shinozaki, Masayuki; ;
JAERI-Tech 98-045, 36 Pages, 1998/10
no abstracts in English
; Maruyama, Yu; Kudo, Tamotsu; Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Ito, Hideo; ; ; Sugimoto, Jun
JAERI-Tech 98-019, 105 Pages, 1998/06
no abstracts in English
Asano, Yoshihiro
JAERI-Research 97-058, 78 Pages, 1997/09
no abstracts in English
Sugimoto, Jun; Yamano, N.; Maruyama, Yu; Kudo, Tamotsu; Soda, Kunihisa
Safety Options for Future Pressurized Water Reactors, 0, 14 Pages, 1994/00
no abstracts in English
Kinouchi, Nobuyuki; ; Ikezawa, Yoshio
Hoken Butsuri, 26, p.31 - 38, 1991/00
no abstracts in English