Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Kubo, Kenya*; Inagaki, Makoto*; Yoshida, Go*; Takeshita, Soshi*; Tampo, Motonobu*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Strasser, P.*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 333(7), p.3445 - 3450, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.66(Chemistry, Analytical)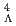 H hypernucleus using in-flight
H hypernucleus using in-flight  He
He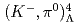 H reaction
H reactionAkaishi, Takaya; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Tanida, Kiyoshi; 35 of others*
Physics Letters B, 845, p.138128_1 - 138128_4, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:25.07(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Yamamoto, Masanobu; Furusawa, Masashi*; Hara, Keigo*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Nomura, Masahiro; Omori, Chihiro*; Shimada, Taihei; Sugiyama, Yasuyuki*; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yoshii, Masahito*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011022_1 - 011022_6, 2021/03
A Tetrode vacuum tubes (Thales TH589) are used in the J-PARC ring rf system. The operation has started in 2007, and the total operation time is more than 50,000 hours. There is no tube which reaches the end of life except an initial failure in the 3 GeV synchrotron. TH589 has a thoriated tungsten filament and it is carburized to suppress an evaporation of the thorium. The resistance of the filament decreases through the decarburization process after the filament operation has started. The tube constructor suggests that reduced filament voltage up to 10% compared with the rated value is effective to suppress the decarburization. However, the filament current increases even though the voltage is kept constant due to the resistance reduction, and it is observed that an increment of the power dissipation promotes the decarburization. This means that keeping the filament voltage constant is not enough; keeping the power dissipation constant is necessary to prolong the tube life time, and we employ a procedure to decrease the current regularly.
 rays from
rays from  LiF tile as an inner wall of a neutron-decay detector
LiF tile as an inner wall of a neutron-decay detectorKoga, Jun*; Kimura, Atsushi; Okudaira, Takuya*; 12 of others*
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 16(2), p.P02001_1 - P02001_13, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.49(Instruments & Instrumentation)Sukegawa, Atsuhiko; Murakami, Haruyuki; Matsunaga, Go; Sakurai, Shinji; Takechi, Manabu; Yoshida, Kiyoshi; Ikeda, Yoshitaka
Fusion Engineering and Design, 98-99, p.2076 - 2079, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.43(Nuclear Science & Technology)The JT-60SA project is a EU - JA satellite tokamak under Broader Approach in support of the ITER project. In-vessel coils are designed and assembled by JA. The resin-insulator is required to have a heat resistance against the baking temperature of vacuum vessel of  200
200 C (40000 hour). Thus the assessment of the heat load is fundamental for the design of the coils. However, the estimation of the lifetime of resin-insulator under the high-temperature region has not been examined. In the present study, the estimation of the lifetime of seven candidate resin-insulators such as epoxy resin and cyanate-ester resin under the
C (40000 hour). Thus the assessment of the heat load is fundamental for the design of the coils. However, the estimation of the lifetime of resin-insulator under the high-temperature region has not been examined. In the present study, the estimation of the lifetime of seven candidate resin-insulators such as epoxy resin and cyanate-ester resin under the  220
220 C temperature region have been performed for the current coils design. Weight reduction of the seven candidate insulators was measured at different heating times under 180
C temperature region have been performed for the current coils design. Weight reduction of the seven candidate insulators was measured at different heating times under 180 C, 200
C, 200 C and 220
C and 220 C environment using three thermostatic ovens, respectively. The reduction of the insulators has been used as input for Weibull-analysis towards Arrhenius-plot. Lifetime of the resins has been estimated for the first time at the high temperature region by the plot. Lifetime of the resin-insulators have been evaluated and discussed as well as the available temperature of the in-vessel coils.
C environment using three thermostatic ovens, respectively. The reduction of the insulators has been used as input for Weibull-analysis towards Arrhenius-plot. Lifetime of the resins has been estimated for the first time at the high temperature region by the plot. Lifetime of the resin-insulators have been evaluated and discussed as well as the available temperature of the in-vessel coils.
Li, H.; Maekawa, Masaki; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Tanimura, Naoki*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 27(24), p.246001_1 - 246001_5, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:29.96(Physics, Condensed Matter)Miyake, Keiko*; Yasuda, Tomonari*; Kato, Masashi*; Ichimura, Masaya*; Hatayama, Tomoaki*; Oshima, Takeshi
Materials Science Forum, 778-780, p.503 - 506, 2014/02
Soyama, Hitoshi*; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Homma, Kana*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 343(1-3), p.116 - 122, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:55.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In order to estimate life time of the mercury target vessel of spallation neutron source which will be subjected to cavitation impacts, prediction methods of pitting damage induced by the cavitation impact were proposed. It is very important to estimate incubation time, in which plastic deformation occurs without mass loss, because the thickness of vessel is very thin. In the present paper, two estimation methods were proposed. One of them is estimatiion from erosion test of severely damaged specimen by plotting the mass loss as a function of exposure time to cavitation on the logarithmic scales. Another method is the observation method of plastic deformation pits on damaged surface at very early period in incubation stage.
 Pb
Pb intermetallic compound
intermetallic compoundOno, Masao; Huang, X. S.*; Shibata, Yasuhiro*; Iguchi, Yusuke*; Sakai, Seiji; Maekawa, Masaki; Chen, Z. Q.*; Osakabe, Toyotaka; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 1st International Conference on Diffusion in Solids and Liquids (DSL 2005), p.531 - 533, 2005/07
Recently, we formed atomic-scale graded structures in some miscible alloys and observed the decomposition in Bi Pb
Pb intermetallic compound by sedimentation of atoms under strong gravitational field. In this study, we measured positron lifetime of centrifuged Bi
intermetallic compound by sedimentation of atoms under strong gravitational field. In this study, we measured positron lifetime of centrifuged Bi Pb
Pb , to which the composition change was very small as it was treated at low temperature. It was found that the positron lifetime became longer than that of starting state. This indicated that the point defects (vacancy or divacancy) increased in the sample by centrifugal treatment. We are now investigating the relationship between increase in point defects and sedimentation of atoms.
, to which the composition change was very small as it was treated at low temperature. It was found that the positron lifetime became longer than that of starting state. This indicated that the point defects (vacancy or divacancy) increased in the sample by centrifugal treatment. We are now investigating the relationship between increase in point defects and sedimentation of atoms.
Ishikura, Shuichi*; Shiga, Akio*; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Sato, Hiroshi; Haga, Katsuhiro; Ikeda, Yujiro
JAERI-Tech 2005-026, 65 Pages, 2005/03
Failure probability analysis was carried out to estimate the lifetime of the mercury target which will be installed into the JSNS (Japan spallation neutron source) in J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex). The lifetime was estimated as taking loading condition and materials degradation into account. Considered loads imposed on the target vessel were the static stresses due to thermal expansion and static pre-pressure on He-gas and mercury and the dynamic stresses due to the thermally shocked pressure waves generated repeatedly at 25 Hz. Materials used in target vessel will be degraded by the fatigue, neutron and proton irradiation, mercury immersion and pitting damages, etc. The imposed stresses were evaluated through static and dynamic structural analyses. The material-degradations were deduced based on published experimental data. As results, it was quantitatively confirmed that the failure probability for the lifetime expected in the design is very much lower, 10 in the safety hull, meaning that it will be hardly failed during the design lifetime. On the other hand, the beam window of mercury vessel suffered with high-pressure waves exhibits the failure probability of 12%. It was concluded, therefore, that the leaked mercury from the failed area at the beam window is adequately kept in the space between the safety hull and the mercury vessel to detect mercury-leakage sensors.
in the safety hull, meaning that it will be hardly failed during the design lifetime. On the other hand, the beam window of mercury vessel suffered with high-pressure waves exhibits the failure probability of 12%. It was concluded, therefore, that the leaked mercury from the failed area at the beam window is adequately kept in the space between the safety hull and the mercury vessel to detect mercury-leakage sensors.
Lis, S.*; Kimura, Takaumi; Yoshida, Zenko; But, S.*
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 380(1-2), p.173 - 176, 2004/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.24(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Oku, Tatsuo*; Ishihara, Masahiro
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 227(2), p.209 - 217, 2004/01
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:87.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)The lifetime of graphite material and/or components has been discussed individually from different concepts, and sometimes gives confusion to material researchers as well as designers. The lifetime of graphite materials is determined based on the dimensional changes due to neutron irradiation, at which they return to their original dimensions after initially contracting. On the other hand, the lifetime of graphite components for HTGRs is defined based on a margin of the specified minimum ultimate strengths of the graphite to the stresses induced in the graphite components. As an example, the stresses induced in the graphite block for the HTTR were, then, compared with the limited stress value determined from the specified minimum ultimate strength, and the lifetime of the graphite component was evaluated and compared with that defined as dimensional changes. As a result, it was found that the lifetime of graphite components for HTGRs should be determined as the shorter one in the two lifetimes defined by the stress-strength relationship and by the dimensional changes.
Futakawa, Masatoshi; Naoe, Takashi; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Tsai, C.-C.*; Ikeda, Yujiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 40(11), p.895 - 904, 2003/11
Times Cited Count:52 Percentile:93.79(Nuclear Science & Technology)A liquid-mercury target system for the MW-scale target is being developed in the world. The pitting damage induced by pressure wave propagation gets to be one of critical issues to estimate the life of the target structure with mercury and to evaluate its structural integrity. The off-line test on the pitting damage at high cycles over 10 millions was carried out using a novel device, the MIMTM which drives electromagnetically to impose pulse pressure into the mercury. It was found that from the pitting damage data obtained by the MIMTM that the pitting damage can be characterized in two steps, an incubation period that can extend to more than 106 cycles in 316SS and 107 cycles in surface hardening treated one and steady state erosion where mass loss scales with the number of cycles to approximately the 1.27 power for mercury. The length of the incubation period is primarily a function of the material and the intensity of the pressure. This observation provides a simple model for estimating lifetime for different materials and beam power.
Meigo, Shinichiro; Harada, Masahide; Teraoku, Takuji*; Maekawa, Fujio
Proceedings of ICANS-XVI, Volume 3, p.1175 - 1180, 2003/07
It is important to monitor the proton beam for the high intensity pulse spallation target. Especially for the beam halo, which may irradiate the bulk surrounding the target, it is important to be observed to prevent causing heat spot in the shielding bulk. At JSNS, a proton beam monitors are located at front of the target. These monitors are assembled with the proton beam window. Since this scheme increases the radiation on the monitor due to the beam loss at the windows, it may arise heat deposition on the monitor. Therefore, heat deposition is calculated with NMTC/JAM. It is found that the heat deposition for normal operation is less than 0.1 W/cc.
 =3 states in Al-like ions
=3 states in Al-like ionsSafronova, U. I.*; Sataka, Masao; Albritton, J. R.*; Johnson, W. R.*; Safronova, M. S.*
Atomic Data and Nuclear Data Tables, 84(1), p.1 - 83, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:87.67(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)no abstracts in English
Takeda, Takeshi; Tachibana, Yukio; Nakagawa, Shigeaki
JAERI-Tech 2002-091, 45 Pages, 2002/12
no abstracts in English
Dai, S.*; Sugiyama, Akira; Hu, L.*; Liu, Z.*; Huang, G.*; Jiang, Z.*
Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 311(2), p.138 - 144, 2002/11
Low-temperature absorption and fluorescence spectra of the Yb3+ ions were measured in phosphate glass with compositions of (60-65)P O
O -(4-8)B
-(4-8)B O
O -(5-10)Al
-(5-10)Al O
O -(10-15)K
-(10-15)K O-(5-10)BaO-(0-2)La
O-(5-10)BaO-(0-2)La O
O -(0-2)Nb
-(0-2)Nb O
O -(4-87)Yb
-(4-87)Yb O
O in mol-%. Temperature dependence of lifetime from
in mol-%. Temperature dependence of lifetime from  F
F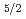 upper level of YB
upper level of YB was investigated with a cryostat. The glass laser performance pumped by 940 nm laser diode was measured at different temperature range. At 8 K, glass laser oscillation had a slope efficiency of 4% and a maximum power of 2 mW at the peak laser wavelength of 1001 nm.
was investigated with a cryostat. The glass laser performance pumped by 940 nm laser diode was measured at different temperature range. At 8 K, glass laser oscillation had a slope efficiency of 4% and a maximum power of 2 mW at the peak laser wavelength of 1001 nm.
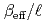 measurement on low enriched uranyl nitrate solution with single unit cores (600
measurement on low enriched uranyl nitrate solution with single unit cores (600 , 280T, 800
, 280T, 800 ) of STACY
) of STACYTonoike, Kotaro; Miyoshi, Yoshinori; Kikuchi, Tsukasa*; Yamamoto, Toshihiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(11), p.1227 - 1236, 2002/11
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:76.50(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kinetic parameter 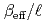 of low enriched uranyl nitrate solution was measured by the pulsed neutron source method in the STACY. This measurement was repeated systematically over several uranium concentrations from 193.7 gU/
of low enriched uranyl nitrate solution was measured by the pulsed neutron source method in the STACY. This measurement was repeated systematically over several uranium concentrations from 193.7 gU/ to 432.1 gU/
to 432.1 gU/ . Used core tanks were two cylindrical tanks whose diameters are 600 mm and 800 mm and one slab tank which has 280 mm thickness and 700 mm width. In this report, experimental data such as solution conditions, critical solution level for each solution condition, subcritical solution levels where measurements were conducted, measured decay time constants of prompt neutron and extrapolated
. Used core tanks were two cylindrical tanks whose diameters are 600 mm and 800 mm and one slab tank which has 280 mm thickness and 700 mm width. In this report, experimental data such as solution conditions, critical solution level for each solution condition, subcritical solution levels where measurements were conducted, measured decay time constants of prompt neutron and extrapolated 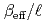 values are described as well as basic principle of the pulsed neutron source method.
values are described as well as basic principle of the pulsed neutron source method. 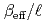 values were evaluated also by computation with the diffusion code CITATION in SRAC and the nuclear data library JENDL 3.2. Both experimental and computational
values were evaluated also by computation with the diffusion code CITATION in SRAC and the nuclear data library JENDL 3.2. Both experimental and computational 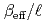 values show good agreement.
values show good agreement.
Dai, S.*; Hu, L.*; Sugiyama, Akira; Izawa, Yasukazu*; Liu, Z.*; Jiang, Z.*
Chinese Science Bulletin, 47(3), p.255 - 259, 2002/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:52.58(Multidisciplinary Sciences)A new type of ytterbium doped phosphate laser glass has been produced and studied about physical and optical properties such as thermo-mechanical properties, nonlinear properties, crystalline phase, micro defects and spectroscopic properties. In the glass forming process, newly developed OH removing technology was adopted. From the reduction of OH concentration in the glass, upper state fluorescence lifetime reached 2.2 ms. Additionally, the glass shows remarkable athermal property of 0.42 10E
10E /K, which is around one-tenth of QX/Yb glass.
/K, which is around one-tenth of QX/Yb glass.
Ioka, Ikuo; Miwa, Yukio; Tsuji, Hirokazu; Yonekawa, Minoru; Takada, Fumiki; Hoshiya, Taiji
JSME International Journal, Series A, 45(1), p.51 - 56, 2002/01
The low cycle creep-fatigue test with tensile strain hold of the austenitic stainless steel irradiated to 2dpa was carried out at 823K in vacuum. The applicability of creep-fatigue life prediction methods to the irradiated specimen was examined. The fatigue life on the irradiated specimen without tensile strain hold time was reduced by a factor of 2-5 in comparison with the unirradiated specimen. The fraction of intergranular fracture increased with increasing strain hold time. The decline in fatigue life of the irradiated specimen with tensile strain hold was almost equal to that of the unirradiated specimen. For the irradiated specimen, the time fraction damage rule trends to yield unsafe estimated lives and the ductility exhaustion damage rule trends to yield generous results. However, all of data were predicted within a factor of three on life by the linear damage rule.