Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Mn
Mn N and Fe
N and Fe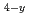 Co
Co N films
N filmsYin, W.*; Ito, Keita*; Tsubowa, Yusuke*; Tsujikawa, Masahito*; Shirai, Masafumi*; Umetsu, Rie*; Takanashi, Koki
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 628, p.173157_1 - 173157_8, 2025/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)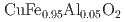
Tamatsukuri, Hiromu; Uchihara, Takeru*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*; Ishii, Yuta*; Nakao, Hironori*; Takehana, Kanji*; Imanaka, Yasutaka*
Physical Review B, 111(13), p.134403_1 - 134403_9, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) GeTe
GeTe to hydrostatic pressure
to hydrostatic pressureWang, Y.*; Zeng, X.-T.*; Li, B.*; Su, C.*; Hattori, Takanori; Sheng, X.-L.*; Jin, W.*
Chinese Physics B, 34(4), p.046203_1 - 046203_6, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Two-dimensional van der Waals ferromagnet Fe GeTe
GeTe (FGT) holds a great potential for applications in spintronic devices, due to its high Curie temperature, easy tunability, and excellent structural stability in air. In this study, we have performed high-pressure neutron powder diffraction (NPD) up to 5 GPa, to investigate the evolution of its structural and magnetic properties with hydrostatic pressure. The NPD data clearly reveal the robustness of the ferromagnetism in FGT, despite of an apparent suppression by hydrostatic pressure. As the pressure increases from 0 to 5 GPa, the Curie temperature is found to decrease monotonically from 225(5) K to 175(5) K, together with a dramatically suppressed ordered moment of Fe, which is well supported by the first-principles calculations. Although no pressure-driven structural phase transition is observed up to 5 GPa, quantitative analysis on the changes of bond lengths and bond angles indicate a significant modification of the exchange interactions, which accounts for the pressure-induced suppression of the ferromagnetism in FGT.
(FGT) holds a great potential for applications in spintronic devices, due to its high Curie temperature, easy tunability, and excellent structural stability in air. In this study, we have performed high-pressure neutron powder diffraction (NPD) up to 5 GPa, to investigate the evolution of its structural and magnetic properties with hydrostatic pressure. The NPD data clearly reveal the robustness of the ferromagnetism in FGT, despite of an apparent suppression by hydrostatic pressure. As the pressure increases from 0 to 5 GPa, the Curie temperature is found to decrease monotonically from 225(5) K to 175(5) K, together with a dramatically suppressed ordered moment of Fe, which is well supported by the first-principles calculations. Although no pressure-driven structural phase transition is observed up to 5 GPa, quantitative analysis on the changes of bond lengths and bond angles indicate a significant modification of the exchange interactions, which accounts for the pressure-induced suppression of the ferromagnetism in FGT.
Scaria, J.*; P drot, M.*; Fablet, L.*; Yomogida, Takumi; Nguyen, T. T.*; Sivry, Y.*; Catrouillet, C.*; Pradas del Real, A. E.*; Choueikani, F.*; Vantelon, D.*; et al.
drot, M.*; Fablet, L.*; Yomogida, Takumi; Nguyen, T. T.*; Sivry, Y.*; Catrouillet, C.*; Pradas del Real, A. E.*; Choueikani, F.*; Vantelon, D.*; et al.
Environmental Science & Technology, 59(11), p.5747 - 5755, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Environmental)Understanding and predicting the interaction mechanisms between chromium and magnetite is of particular interest to elucidate the biogeochemical behavior of Cr in the environment and to develop optimal soil remediation and water treatment strategies. However, while the elimination of the most toxic form of (Cr(VI)) by its reduction to Cr(III) has widely been documented, elucidating the exact mechanism involved in Cr(III) sorption to magnetite has attracted less attention. This study examined the interaction of Cr(III) solution with 10 nm-sized magnetites, whose stoichiometries were carefully defined and preserved in anaerobic conditions. This study reveals the joint effects of pH and magnetite stoichiometry on Cr(III) sorption mechanism, and that Cr(III)-(hydr)oxide precipitation is not necessarily the driving process of Cr(III) elimination from solutions. These results will help predict the fate and transport of chromium, as well as developing magnetite-based chromium remediation processes.

Chung, J.-H.*; Kwangwoo, S.*; Yokoo, Tetsuya R.; Ueta, Daichi*; Imai, Masaki; Kim, H.-S.; Kiem, D. H.; Han, M. J.*; Shamoto, Shinichi
Scientific Reports (Internet), 15, p.5978_1 - 5978_10, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Maeda, Mizuho*; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Haga, Yoshinori; Shirasaki, Kenji*; Kimura, Noriaki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(2), p.024707_1 - 024707_6, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Idomura, Yasuhiro
Physics of Plasmas, 31(10), p.102504_1 - 102504_10, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Hydrogen isotope mixing phenomena in tokamak plasmas are analyzed using global full-f gyrokinetic simulations. Model plasma parameters are chosen based on the hydrogen isotope pellet experiments on JET, in which hydrogen isotope mixing in the time scale of the energy confinement time occurred after injecting deuterium (D) pellets into hydrogen (H) plasmas. Two numerical experiments are conducted using plasma profiles before and after the D pellet injection. In both cases, turbulent fluctuations in the plasma core are characterized by ion temperature gradient driven turbulence, while in the latter case, trapped electron mode turbulence also exists in the outer region. In the former case, the density profile of bulk H ions is kept in a quasi-steady state, and the particle confinement time of bulk H ions is an order of magnitude longer than the energy confinement time. In the latter case, the density profiles of bulk H ions and pellet D ions show transient relaxation in the time scale of the energy confinement time, indicating the fast hydrogen isotope mixing. In the toroidal angular momentum balance, it is found that the hydrogen isotope mixing is driven by the toroidal field stress.
Ding, H.*; Ito, Keita*; Endo, Yasushi*; Takanashi, Koki; Seki, Takeshi*
Journal of Physics D; Applied Physics, 57(38), p.385002_1 - 385002_10, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:57.35(Physics, Applied)Zhu, L.*; He, H.*; Naeem, M.*; Sun, X.*; Qi, J.*; Liu, P.*; Harjo, S.; Nakajima, Kenji; Li, B.*; Wang, X.-L.*
Physical Review Letters, 133(12), p.126701_1 - 126701_6, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:43.84(Physics, Multidisciplinary)
Vali ka, M.*; Haidamak, T.*; Cabala, A.*; Posp
ka, M.*; Haidamak, T.*; Cabala, A.*; Posp
 il, J.*; Bastien, G.*; Sechovsk
il, J.*; Bastien, G.*; Sechovsk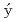 , V.*; Prokle
, V.*; Prokle ka, J.*; Yanagisawa, Tatsuya*; Opletal, P.; Sakai, Hironori; et al.
ka, J.*; Yanagisawa, Tatsuya*; Opletal, P.; Sakai, Hironori; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 8(9), p.094415_1 - 094415_9, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:51.02(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Takanashi, Koki; Seki, Takeshi*
Magune, 19(3), p.100 - 106, 2024/06
Perpendicular magnetic anisotropy of thin films currently plays an important role in spintronics as well as magnetic recording. Regarding perpendicular magnetic anisotropy, in this article, the fundamentals, the research history, and the recent research trends are reviewed, showing specific examples with perpendicular magnetization such as magnetic multilayers, ordered alloy films, rare earth-transition metal amorphous alloy films, and inhomogeneous or granular films. The physical origins for perpendicular magnetic anisotropy, including interface anisotropy due to structural symmetry breaking, magnetoelastic anisotropy due to strain, bulk-type magnetocrystalline anisotropy, and directional pair ordering of atoms, are discussed in each example.
funabiki, Yuta*; Iyota, Muneyoshi*; Shobu, Takahisa; Matsuda, Tomoki*; Hayashi, Yujiro*; Sano, Tomokazu*; 8 of others*
Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 115, p.40 - 55, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:78.76(Engineering, Manufacturing)
Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Honda, Fuminori*; Aoki, Dai*; Haga, Yoshinori; Kida, Takanori*; Narumi, Yasuo*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Kindo, Koichi*; Karube, Kosuke*; Harima, Hisatomo*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(4), p.044708_1 - 044708_10, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary) -FeNi films with island structures on LaAlO
-FeNi films with island structures on LaAlO (110) substrates by nitrogen insertion and topotactic extraction
(110) substrates by nitrogen insertion and topotactic extractionNishio, Takahiro*; Ito, Keita*; Kura, Hiroaki*; Takanashi, Koki; Yanagihara, Hideto*
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 976, p.172992_1 - 172992_8, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:34.67(Chemistry, Physical) CoSi
CoSiYamauchi, Hiroki; Sari, D. P.*; Yasui, Yukio*; Sakakura, Terutoshi*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Nakao, Akiko*; Ohara, Takashi; Honda, Takashi*; Kodama, Katsuaki; Igawa, Naoki; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(1), p.013144_1 - 013144_9, 2024/02

Suetsugu, Shota*; Sakai, Hironori; Opletal, P.; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Haga, Yoshinori; 12 of others*
Science Advances (Internet), 10(6), p.eadk3772_1 - eadk3772_6, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:95.83(Multidisciplinary Sciences) Fe
Fe Mn
Mn Si heusler alloy thin films
Si heusler alloy thin filmsNabialek, A.*; Chumak, O.*; Seki, Takeshi*; Takanashi, Koki; Baczewski, L. T.*; Szymczak, H.*
IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 59(11), p.2501405_1 - 2501405_5, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:28.34(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Tei, C.; Otaka, Masahiko; Kuwahara, Daisuke*
Chemical Physics Letters, 829, p.140755_1 - 140755_6, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.83(Chemistry, Physical)We were able to detect the nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) signal of a liquid sodium clinging to the interface of solid metal particles for the first time. In this study, we confirmed the difference in the relaxation times due to the difference in the interactions between liquid sodium and metal particles suspended in the liquid sodium. It was found that the surface of the micro titanium particles and liquid metallic sodium interact physically, not chemically.
Hirohata, Atsufumi*; Lloyd, D. C.*; Kubota, Takahide*; Seki, Takeshi*; Takanashi, Koki; Sukegawa, Hiroaki*; Wen, Z.*; Mitani, Seiji*; Koizumi, Hiroki*
IEEE Access, 11, p.117443 - 117459, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:20.14(Computer Science, Information Systems) Fe
Fe Mn
Mn Si Heusler alloys
Si Heusler alloysNabialek, A.*; Chumak, O. M.*; Aleshkevych, P.*; Domagala, J. Z.*; Pacewicz, A.*; Salski, B.*; Krupka, J.*; Seki, Takeshi*; Takanashi, Koki; Baczewski, L. T.*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 13, p.17016_1 - 170169, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:47.87(Multidisciplinary Sciences)