Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 U accumulations in
U accumulations in 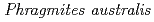 naturally growing at the mill tailings pond; Iron plaque formation possibly related to root-endophytic bacteria producing siderophores
naturally growing at the mill tailings pond; Iron plaque formation possibly related to root-endophytic bacteria producing siderophoresNakamoto, Yukihiro*; Doyama, Kohei*; Haruma, Toshikatsu*; Lu, X.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kozai, Naofumi; Fukuyama, Kenjin; Fukushima, Shigeru; Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Yamaji, Keiko*
Minerals (Internet), 11(12), p.1337_1 - 1337_17, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:35.78(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Mine drainage is a vital water problem in the mining industry worldwide because of the heavy metal elements and low pH. Rhizofiltration using wetland plants is an appropriate method to remove heavy metals from the water via accumulation in the rhizosphere. 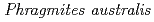 is one of the candidate plants for this method because of metal accumulation, forming iron plaque around the roots. At the study site, which was the mill tailings pond in the Ningyo-toge uranium mine,
is one of the candidate plants for this method because of metal accumulation, forming iron plaque around the roots. At the study site, which was the mill tailings pond in the Ningyo-toge uranium mine,  has been naturally growing since 1998. The results showed that
has been naturally growing since 1998. The results showed that  accumulated Fe, Mn, and
accumulated Fe, Mn, and  U in the nodal roots without/with iron plaque compared with other plant tissues. Among the 837 bacterial colonies isolated from nodal roots, 88.6% showed siderophore production activities. Considering iron plaque formation around
U in the nodal roots without/with iron plaque compared with other plant tissues. Among the 837 bacterial colonies isolated from nodal roots, 88.6% showed siderophore production activities. Considering iron plaque formation around  roots, we hypothesized that microbial siderophores might influence iron plaque formation because bacterial siderophores have catechol-like functional groups. The complex of catechol or other phenolics with Fe was precipitated due to the networks between Fe and phenolic derivatives. The experiment using bacterial products of root endophytes, such as
roots, we hypothesized that microbial siderophores might influence iron plaque formation because bacterial siderophores have catechol-like functional groups. The complex of catechol or other phenolics with Fe was precipitated due to the networks between Fe and phenolic derivatives. The experiment using bacterial products of root endophytes, such as 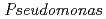 spp. and
spp. and 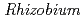 spp., showed precipitation with Fe ions, and we confirmed that several
spp., showed precipitation with Fe ions, and we confirmed that several 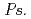 spp. and
spp. and 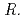 spp. produced unidentified phenolic compounds. In conclusion, root-endophytic bacteria such as
spp. produced unidentified phenolic compounds. In conclusion, root-endophytic bacteria such as 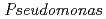 spp. and
spp. and 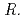 spp., isolated from metal-accumulating roots of
spp., isolated from metal-accumulating roots of  , might influence iron plaque formation as the metal accumulation site. Iron plaque formation is related to tolerance in
, might influence iron plaque formation as the metal accumulation site. Iron plaque formation is related to tolerance in  , and
, and 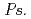 spp. and
spp. and 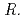 spp. might indirectly contribute to tolerance.
spp. might indirectly contribute to tolerance.
 Sr
Sr MnO
MnO studied by resonant inelastic X-ray scattering
studied by resonant inelastic X-ray scatteringIshii, Kenji; Inami, Toshiya; Owada, Kenji; Kuzushita, Kaori; Mizuki, Junichiro; Murakami, Yoichi; Ishihara, Sumio*; Endo, Yasuo*; Maekawa, Sadamichi*; Hirota, Kazuma*; et al.
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 66(12), p.2157 - 2162, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We have studied electronic excitations of hole-doped manganese oxides La Sr
Sr MnO
MnO (
(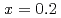 and
and 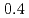 ) by resonant inelastic X-ray scattering at Mn K absorption edge. We observed in the excitation spectra that the Mott gap of La
) by resonant inelastic X-ray scattering at Mn K absorption edge. We observed in the excitation spectra that the Mott gap of La Sr
Sr MnO
MnO was filled by hole-doping. In La
was filled by hole-doping. In La Sr
Sr MnO
MnO , which shows a metal-insulator transition, we found that temperature dependence of scattering intensity is different between two scattering vectors. It may reflects a anisotropic electronic structure which originates from the orbital degrees of freedom in manganese oxides.
, which shows a metal-insulator transition, we found that temperature dependence of scattering intensity is different between two scattering vectors. It may reflects a anisotropic electronic structure which originates from the orbital degrees of freedom in manganese oxides.
 Sr
Sr MnO
MnO (
(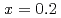 ,
, 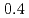 )
)Ishii, Kenji; Inami, Toshiya; Owada, Kenji; Kuzushita, Kaori; Mizuki, Junichiro; Murakami, Yoichi; Ishihara, Sumio*; Endo, Yasuo*; Maekawa, Sadamichi*; Hirota, Kazuma*; et al.
Physical Review B, 70(22), p.224437_1 - 224437_6, 2004/12
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:67.44(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Electronic excitations in the hole doped manganese oxides (La Sr
Sr MnO
MnO ,
, 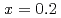 and
and 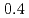 ) have been elucidated by using the resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) method. A doping effect in the strongly correlated electron systems has been observed for the first time. The scattering spectra show that a salient peak appears in low energies indicating the persistence of the Mott gap. At the same time, the energy gap is partly filled by doping holes and the spectral weight energy shifts toward lower energies. The excitation spectra show little change in the momentum space as is in undoped LaMnO
) have been elucidated by using the resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) method. A doping effect in the strongly correlated electron systems has been observed for the first time. The scattering spectra show that a salient peak appears in low energies indicating the persistence of the Mott gap. At the same time, the energy gap is partly filled by doping holes and the spectral weight energy shifts toward lower energies. The excitation spectra show little change in the momentum space as is in undoped LaMnO . On the other hand, the scattering intensities in the low energy excitations of
. On the other hand, the scattering intensities in the low energy excitations of 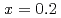 are anisotropic in temperature dependence, which indicates an anisotropy of magnetic interaction and underlying effect of the orbital.
are anisotropic in temperature dependence, which indicates an anisotropy of magnetic interaction and underlying effect of the orbital.
 Sn heat treatment
Sn heat treatmentNakajima, Hideo; Hamada, Kazuya; Takano, Katsutoshi*; Okuno, Kiyoshi; Fujitsuna, Nobuyuki*
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 14(2), p.1145 - 1148, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:78.21(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)In ITER, the conductor for the Central Solenoid (CS) uses Incoloy 908, which requires special environment control to prevent cracks caused by Stress Accelerated Grain Boundary Oxidation (SAGBO) during Nb3Sn heat treatment. Use of a stainless steel jacket can simplify the design and fabrication because the special caution is not required for SAGBO. JAERI has already developed high manganese, JK2, whose thermal contraction from 300K to 4 K is almost the same as that of Incoloy: thus no change in the mechanical design of the CS is necessary. However, during the heat treatment, phosphorus enhances embrittlement of JK2. Carbon reduction and boron addition was considered to be a possible solution to mitigate the phosphorus effect. Jackets of low carbon and boron added JK2(JK2LB) were produced and tensile properties, fracture toughness, and crack propagation rate were measured at 4K. Elongation and fracture toughness at 4K after the heat treatment are 33% and 91 MPam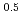 for the final jacket, which satisfy the ITER targets. JK2LB can be applied to the ITER CS.
for the final jacket, which satisfy the ITER targets. JK2LB can be applied to the ITER CS.
Ugajin, Mitsuhiro; Ito, Akinori; Akabori, Mitsuo; Ooka, Norikazu;
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 254(1), p.78 - 83, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:88.89(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Kato, Teruo; Maeta, Hiroshi
Teion Kogaku, 30(3), p.143 - 149, 1995/00
no abstracts in English
Nagao, Seiya;
Marine Geology, 109, p.83 - 94, 1992/00
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:79.45(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English

 Co and
Co and 
 Mn in Graphite Material of Irradiated HTGR Fuel Assemblies
Mn in Graphite Material of Irradiated HTGR Fuel Assemblies; ; ; Minato, Kazuo; ; Ikawa, Katsuichi; Iwamoto, K.
JAERI-M 84-088, 24 Pages, 1984/05
no abstracts in English
 )
) }
} MnCl
MnCl }
}; Ozawa, K.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 53(2), p.627 - 634, 1984/00
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:87.74(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 -and
-and  -manganese
-manganese; ; ;
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 31-34, p.41 - 42, 1983/00
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:35.50(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 )
) }
} MnBr
MnBr
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 52(8), p.2931 - 2935, 1983/00
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:88.57(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Talanta, 24(8), p.503 - 507, 1977/08
Times Cited Count:18no abstracts in English
Akatsu, Eiko;
Anal.Chim.Acta, 62, p.325 - 335, 1972/00
Times Cited Count:7no abstracts in English
; ; ;
Journal of Radiation Research, 6, p.3 - 4, 1966/00
no abstracts in English
;
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 2(1), p.13 - 17, 1965/00
Times Cited Count:9no abstracts in English
; ; Anzai, Shuichiro*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 18(5), p.744 - 744, 1963/00
Times Cited Count:7no abstracts in English
; ;
Anal. Chem., 34(4), p.571 - 575, 1962/00
Times Cited Count:21no abstracts in English
Jiang, L.*; Wang, H. H.*; Xu, P. G.; Su, Y. H.; Shinohara, Takenao; Wang, Y. W.*
no journal, ,
High manganese austenitic steels as a cryogenic structural material are widely applied in the pressurized storage infrastructures for storing and transporting liquefied natural gas (LNG), liquefied hydrogen (LH). Considering that cryogenic impact toughness is important in predicting the service performance of high manganese austenitic steel, it is critical for analyzing residual strain and plastic deformation evolution in impacted fractures and for deeply understanding the deformation and fracture mechanisms. Here, the strain and plastic deformation evolution of impacted fractures in high manganese steel (24Mn-4Cr-0.4C-0.3Cu) were comparably investigated by neutron Bragg-edge transmission (BET) imaging and electron back scattering diffraction (EBSD) at various cryogenic temperatures. The BET results show that the residual strain  111 is negative and
111 is negative and  200 is positive in the region with large plastic deformation near the fracture. However,
200 is positive in the region with large plastic deformation near the fracture. However,  111 and
111 and  200 in the region far away from the fracture show similar distribution in the V-notched impact sample at the same temperature. With the decrease of impact temperature, the high broadening area of Bragg-edge width near the fracture gradually decreased, revealing that the local plastic strain during cryogenic impact deformation in the corresponding area decreased, which is primarily consistent in the change trend of impact toughness value obtained at various temperatures. EBSD results show evident difference in the local distribution density of
200 in the region far away from the fracture show similar distribution in the V-notched impact sample at the same temperature. With the decrease of impact temperature, the high broadening area of Bragg-edge width near the fracture gradually decreased, revealing that the local plastic strain during cryogenic impact deformation in the corresponding area decreased, which is primarily consistent in the change trend of impact toughness value obtained at various temperatures. EBSD results show evident difference in the local distribution density of  111
111 and
and  200
200 -oriented grains in the region near the fracture after cryogenic impacting. It is suggested that the steel texture is a primary reason for clarifying the different distribution features of
-oriented grains in the region near the fracture after cryogenic impacting. It is suggested that the steel texture is a primary reason for clarifying the different distribution features of  111 and
111 and  200 in the region near the cryogenic impact fracture.
200 in the region near the cryogenic impact fracture.