Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
麓 耕二*; 大久保 建斗*; 大島 章太朗*; 畑本 明彩未*; 栗田 圭輔; 原山 勲; 飯倉 寛
Journal of Visualization, 12 Pages, 2025/11
Self-heating in electronic devices and machinery poses a critical challenge for thermal management. To address this issue, we developed a Meander-Shaped Low-Fill Heat Pipe (MLFHP) as a novel cooling solution. The MLFHP, fabricated from aluminum alloy and filled with water as the working fluid, features a serpentine microchannel structure that enables effective heat transport even at a filling ratio as low as 10 vol.%. Although previous studies have demonstrated its superior thermal performance compared to conventional cooling systems, including pulsating heat pipes (PHPs), the internal flow and heat transfer mechanisms remain unclear. In this study, we employed neutron radiography to non-invasively visualize the working fluid behavior inside the MLFHP during operation. This paper presents the results of the visualization experiments and offers new insights into the unique thermal transport mechanism of the MLFHP.
 Ta
Ta静間 俊行*; Omer, M.; 羽島 良一*; 小泉 光生
Physical Review C, 109(5), p.054320_1 - 054320_8, 2024/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)Low-lying levels in the odd-mass nucleus  Ta have been populated via nuclear resonance fluorescence using a quasi-monoenergetic, linearly polarized photon beam at the High Intensity
Ta have been populated via nuclear resonance fluorescence using a quasi-monoenergetic, linearly polarized photon beam at the High Intensity  -ray Source (HI
-ray Source (HI S) facility at Duke University. The spin and parity of the levels were determined from the azimuthal intensity asymmetry of resonantly scattered
S) facility at Duke University. The spin and parity of the levels were determined from the azimuthal intensity asymmetry of resonantly scattered  -rays with respect to the polarization plane of the incident photon beam. The electric and magnetic dipole strengths were obtained for excitation energies from 2.2 to 3.2 MeV. The results are discussed in terms of the nuclear scissors mode. This work is a contribution of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) under the agreement of the coordinated research program (CRP), J02015 (Facilitation of Safe and Secure Trade Using Nuclear Detection Technology - Detection of RN and Other Contraband). This work was a part of a study of the nuclear resonance fluorescence aiming at nuclear security and safeguards applications, being supported by the subsidiary for "promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like" of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
-rays with respect to the polarization plane of the incident photon beam. The electric and magnetic dipole strengths were obtained for excitation energies from 2.2 to 3.2 MeV. The results are discussed in terms of the nuclear scissors mode. This work is a contribution of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) under the agreement of the coordinated research program (CRP), J02015 (Facilitation of Safe and Secure Trade Using Nuclear Detection Technology - Detection of RN and Other Contraband). This work was a part of a study of the nuclear resonance fluorescence aiming at nuclear security and safeguards applications, being supported by the subsidiary for "promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like" of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
 Ni
Ni静間 俊行*; Omer, M.; 早川 岳人*; 湊 太志*; 松葉 俊哉*; 宮本 修治*; 清水 則孝*; 宇都野 穣
Physical Review C, 109(1), p.014302_1 - 014302_7, 2024/01
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:82.73(Physics, Nuclear)Low-lying dipole states in the singly closed-shell nucleus  Ni were studied via nuclear resonance fluorescence experiments using a quasi-monoenergetic, linearly polarized photon beam. The parity quantum numbers of the dipole states were determined by the intensity asymmetry of resonantly scattered
Ni were studied via nuclear resonance fluorescence experiments using a quasi-monoenergetic, linearly polarized photon beam. The parity quantum numbers of the dipole states were determined by the intensity asymmetry of resonantly scattered  -rays with respect to the polarization plane of the incident photon beam. The electric and magnetic dipole (E1 and M1) strengths at excitation energies between 5.9 and 9.8 MeV were obtained based on dipole strengths taken from literature. The E1 and M1 strength distributions were compared with large-scale shell-model predictions in the
-rays with respect to the polarization plane of the incident photon beam. The electric and magnetic dipole (E1 and M1) strengths at excitation energies between 5.9 and 9.8 MeV were obtained based on dipole strengths taken from literature. The E1 and M1 strength distributions were compared with large-scale shell-model predictions in the 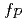 -shell using the SDPFSDG-MU interaction.
-shell using the SDPFSDG-MU interaction.
Omer, M.; 静間 俊行*; 小泉 光生; 平 義隆*; Zen, H.*; 大垣 英明*; 羽島 良一
UVSOR-50, P. 37, 2023/08
核共鳴蛍光(NRF)を用いた非破壊分析において、試料温度によるドップラー効果による影響を調べることを目的とした研究を開始した。今回は、波長1980nmのファイバーレーザーを加速エネルギー746MeVの電子ビームと衝突させて生成した最大エネルギー5.54MeVのレーザーコンプトンガンマ線を Pb標的に照射し、共鳴散乱ガンマ線を3台の高純度ゲルマニウム検出器を用いて測定した。その結果、レーザーコンプトンガンマ線最大エネルギーよりも高いエネルギーで、複数のガンマ線ピークが観測された。これらのガンマ線は、実験室内の制動放射線によって発生した中性子が測定装置の周囲の物質と反応した後に放出された中性子捕獲即発ガンマ線であると考えられる。そのため、バックグラウンドガンマ線の低減のため、ゲルマニウム検出器の周囲を厚さ10cmの鉛を用いて遮蔽した。その結果、即発ガンマ線のバックグラウンドは抑制され、
Pb標的に照射し、共鳴散乱ガンマ線を3台の高純度ゲルマニウム検出器を用いて測定した。その結果、レーザーコンプトンガンマ線最大エネルギーよりも高いエネルギーで、複数のガンマ線ピークが観測された。これらのガンマ線は、実験室内の制動放射線によって発生した中性子が測定装置の周囲の物質と反応した後に放出された中性子捕獲即発ガンマ線であると考えられる。そのため、バックグラウンドガンマ線の低減のため、ゲルマニウム検出器の周囲を厚さ10cmの鉛を用いて遮蔽した。その結果、即発ガンマ線のバックグラウンドは抑制され、 Pbの共鳴散乱ガンマ線を観測することができた。
Pbの共鳴散乱ガンマ線を観測することができた。
Omer, M.; 静間 俊行*; 羽島 良一*; 小泉 光生
日本核物質管理学会第40回年次大会プロシーディングス集, p.59 - 62, 2019/11
Nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) is a phenomenon that a nuclide-specific  -ray is resonantly absorbed and re-emitted. This method is considered useful for the nondestructive detection of nuclear materials. In order to demonstrate how accurate the NRF method is able to measure the isotopic abundance, we performed NRF experiments on natural tungsten as a surrogate of nuclear materials at the High Intensity
-ray is resonantly absorbed and re-emitted. This method is considered useful for the nondestructive detection of nuclear materials. In order to demonstrate how accurate the NRF method is able to measure the isotopic abundance, we performed NRF experiments on natural tungsten as a surrogate of nuclear materials at the High Intensity  -ray Source (HI
-ray Source (HI S) facility, Duke University. Our results show that the relative deviations between the reference and measured abundances are less than
S) facility, Duke University. Our results show that the relative deviations between the reference and measured abundances are less than  4%. This work was supported by the subsidiary for promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
4%. This work was supported by the subsidiary for promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
瀬谷 道夫; 羽島 良一*; 呉田 昌俊
Proceedings of INMM 58th Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2017/07
港湾で扱われる貨物コンテナは容積が大きく重量物も運べるため、核物質が隠されて持ち込まれる危険性が高い。核セキュリティを強化する上では、重遮へい物中の規制外核物質の確実な検知、及び、重遮へい物体の安全な解体により中から核物質を取出すことが不可欠である。このための対応として、確実な核物質検知システムの導入、検知物の正確な内部構造把握、及び核物質性状把握(核兵器か否か、爆発物の混入等)が要求され、これらの情報を使うことにより検知物の安全な解体と核物質の取出しが可能となる。この発表では、X線スキャン装置と単色線利用NRFベース非破壊検知装置の組合せを確実な核物質検知システム及び内部検査システムとして、また、取出された核物質部分に関する内部検査機能を持つものとして、小型中性子線源(D-T中性子源)を用いるアクティブNDA装置を提案する。
瀬谷 道夫; 羽島 良一*; 呉田 昌俊
第37回核物質管理学会日本支部年次大会論文集(CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2017/02
港湾で扱われる貨物コンテナは容積が大きく重量物も運べるため、核物質が隠されて持ち込まれる危険性が高い。核セキュリティを強化する上では、重遮へい物中の規制外核物質の確実な検知、及び、重遮へい物体の安全な解体により中から核物質を取出すことが不可欠である。このための対応として、(1)確実な核物質検知システムの導入、(2)検知物の正確な内部構造把握、及び(3)核物質性状把握(核兵器か否か、爆発物の混入等)が要求され、これらの情報を使うことにより検知物の安全な解体と核物質の取出しが可能となる。この発表では、(1)については、X線スキャン装置と単色 線利用NRFベース非破壊検知装置の組合せを提案する。後者の装置は重遮へい体に対しては、(2)及び(3)の機能も有している。また、取出された核物質部分に関する(2)及び(3)の機能を持つものとして、小型中性子線源(D-T中性子源)を用いるアクティブNDA装置を提案する。
線利用NRFベース非破壊検知装置の組合せを提案する。後者の装置は重遮へい体に対しては、(2)及び(3)の機能も有している。また、取出された核物質部分に関する(2)及び(3)の機能を持つものとして、小型中性子線源(D-T中性子源)を用いるアクティブNDA装置を提案する。
飯倉 寛; 酒井 卓郎; 松林 政仁
波紋, 25(4), p.277 - 282, 2015/11
中性子ラジオグラフィに関する入門講座として、原理の説明から、JRR-3に設置されている熱中性子ラジオグラフィ装置(TNRF)の概要や測定手法の説明、さらに実際に行われている応用研究や技術開発に関して簡潔に紹介したものである。中性子ラジオグラフィは非破壊分析技術として、学術研究だけでなく産業界への応用など、幅広い分野で利用されており、TNRFにおいては利用者の多様なニーズに対応すべく、様々な技術開発が行われてきた。本稿は、中性子利用の初心者に向けて、これらの概要をまとめたものである。
瀬谷 道夫; 小泉 光生; 富川 裕文; 直井 洋介; 呉田 昌俊; 原田 秀郎; 羽島 良一; 中村 仁宣
Proceedings of INMM 56th Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2015/07
核不拡散・核セキュリティセンターは、発足から原子力機構内の部門と連携して、以下の先進NDA技術開発を実施した。(1)PNAR-NDA装置によるふげん使用済み燃料の測定、(2)LCS 線を用いるNRF-NDAの基礎技術開発、(3)ヘリウム3代替中性子検知技術開発、(4)中性子共鳴濃度分析法開発。また、平成27年度からは以下の開発プログラムを開始したところである。(5)LCS
線を用いるNRF-NDAの基礎技術開発、(3)ヘリウム3代替中性子検知技術開発、(4)中性子共鳴濃度分析法開発。また、平成27年度からは以下の開発プログラムを開始したところである。(5)LCS 線を使うNRF非破壊検知の実証試験、(6)アクティブ中性子NDA技術開発、(7)セル内タンクの廃液モニタリング技術のフィージビリティ研究。本発表は、これまでに実施してきた技術開発の概要とこれから実施する技術開発の概要を紹介するものである。
線を使うNRF非破壊検知の実証試験、(6)アクティブ中性子NDA技術開発、(7)セル内タンクの廃液モニタリング技術のフィージビリティ研究。本発表は、これまでに実施してきた技術開発の概要とこれから実施する技術開発の概要を紹介するものである。
瀬谷 道夫; 小林 直樹; 直井 洋介; 羽島 良一; 曽山 和彦; 呉田 昌俊; 中村 仁宣; 原田 秀郎
Book of Abstracts, Presentations and Papers of Symposium on International Safeguards; Linking Strategy, Implementation and People (Internet), 8 Pages, 2015/03
原子力機構では、2011年度より次の3つのプログラムからなる先進核物質非破壊測定技術の基礎開発を実施している。(1)レーザー・コンプトン散乱 線(大強度単色
線(大強度単色 線)を使う核共鳴蛍光NDA技術開発、(2)ZnS/B
線)を使う核共鳴蛍光NDA技術開発、(2)ZnS/B O
O セラミックシンチレータによる中性子検出技術開発、(3)中性子共鳴透過分析(NRTA)及び中性子共鳴捕獲分析(NRCA)による中性子濃度分析法(NRD)技術開発。これらのプログラムは2014年度に終了する予定であり、2015年2-3月に実証試験を行う予定である。
セラミックシンチレータによる中性子検出技術開発、(3)中性子共鳴透過分析(NRTA)及び中性子共鳴捕獲分析(NRCA)による中性子濃度分析法(NRD)技術開発。これらのプログラムは2014年度に終了する予定であり、2015年2-3月に実証試験を行う予定である。
瀬谷 道夫; 呉田 昌俊; 曽山 和彦; 中村 仁宣; 原田 秀郎; 羽島 良一
Proceedings of INMM 55th Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2014/07
原子力機構は保障措置及び核セキュリティのための、次の先進的な核物質非破壊測定の基礎技術開発プログラムを実施してきている。(1)ZnS/B O
O セラミックシンチレータによる
セラミックシンチレータによる He代替中性子検知技術、(2)中性子共鳴透過分析(NRTA)及び中性子共鳴捕獲分析(NRCA)の組み合わせによる中性子共鳴濃度分析法、(3)レーザー・コンプトン散乱
He代替中性子検知技術、(2)中性子共鳴透過分析(NRTA)及び中性子共鳴捕獲分析(NRCA)の組み合わせによる中性子共鳴濃度分析法、(3)レーザー・コンプトン散乱 線(大強度単色
線(大強度単色 線)利用核共鳴蛍光NDA(1)は、供給不足が懸念される
線)利用核共鳴蛍光NDA(1)は、供給不足が懸念される Heに代わるZnS/B
Heに代わるZnS/B O
O セラミックシンチレータ中性子検出器の開発であり、(2)は、粒子状溶融燃料などの測定対象物中の核物質同位体組成比測定NDA技術開発、(3)は、レーザー・コンプトン散乱により発生させたエネルギー可変の大強度の単色
セラミックシンチレータ中性子検出器の開発であり、(2)は、粒子状溶融燃料などの測定対象物中の核物質同位体組成比測定NDA技術開発、(3)は、レーザー・コンプトン散乱により発生させたエネルギー可変の大強度の単色 線により引き起こすPu/U同位体の核共鳴蛍光反応を利用するNDAのためのプログラムである。この論文ではこれらについて紹介する。
線により引き起こすPu/U同位体の核共鳴蛍光反応を利用するNDAのためのプログラムである。この論文ではこれらについて紹介する。
小泉 光生
no journal, ,
原子力機構が実施している核セキュリティ技術開発プロジェクトを紹介する。一つは、核共鳴蛍光非破壊分析技術開発で、この技術は、準単色な高輝度ガンマ線ビームを測定対象物に照射して、核共鳴蛍光を測定することにより内包される原子核を検出する技術である。もう一つは、広域モニターシステムの開発で、大規模イベントなどにおいて核テロを抑止するための技術として、衛星測位システムなどを組み込んだガンマ線検出器の開発や、スペクトル簡易診断のためのAIプログラムの開発、中性子源を効率よく探し出すための検出器の開発などを行っている。
静間 俊行*; Omer, M.; 羽島 良一*; 小泉 光生; Zen, H.*; 大垣 英明*; 平 義隆*
no journal, ,
レーザーコンプトン(LCS)ガンマ線を用いて、 Pbの透過型の核共鳴蛍光散乱(NRF)実験を行った。実験では吸収ターゲットの温度を室温と液体窒素温度で測定を行った。観測された
Pbの透過型の核共鳴蛍光散乱(NRF)実験を行った。実験では吸収ターゲットの温度を室温と液体窒素温度で測定を行った。観測された Pbの遷移に対して、共鳴吸収の大きさを求め、計算値との比較を行った。
Pbの遷移に対して、共鳴吸収の大きさを求め、計算値との比較を行った。
大垣 英明*; Zen, H.*; 早川 岳人*; 静間 俊行*; Omer, M.; 西本 海*
no journal, ,
UVSORのBL1Uにおいて、複数の同位体イメージング及びその定量評価に関する研究を、小径のビームでエネルギー幅を拡大したF-LCSガンマ線ビームと通常のLCSガンマ線ビームを用いて行っている。 Pbに対してUVSORのBL1Uビームラインで行っているNRF収量の定量評価に関する結果を報告する。
Pbに対してUVSORのBL1Uビームラインで行っているNRF収量の定量評価に関する結果を報告する。
松本 亮介*; 藤川 直人*; 小田 豊*; 栗田 圭輔; 飯倉 寛; 原山 勲
no journal, ,
空調機用の熱交換器として用いられている扁平管熱交換器では、伝熱面を高密度に配置でき、従来の熱交換器に比べ伝熱性能が向上している。しかし、着霜による熱交換性能の低下は依然として課題である。さらには、扁平管が水平に設置されていることから、除霜時には扁平管が融解水の排出を妨げる可能性や、熱交換器内への融解水の残留量が増加する恐れがある。発表者らは、中性子線が物体を透過する際の特性を利用して物体内部の状態を可視化することができる中性子ラジオグラフィを用いて、熱交換器への着霜分布を評価してきた。本報では、扁平管熱交換器の着霜分布、その後の除霜時の融解水の挙動を報告する。
社本 真一; 伊巻 正*; 大下 英敏*; 中谷 健; 樹神 克明; 金子 直勝*; 鈴木 裕士; 飯倉 寛; 盛合 敦; 松林 政仁; et al.
no journal, ,
銅ブロックに埋め込んだSUS430試料について、散乱イメージングをJ-PARCの高強度全散乱装置NOVAで、またJRR-3の高分解能粉末中性子回折装置HRPD、残留応力解析装置RESA、中性子ラジオグラフィー装置TNRFで行ったので、これらの結果を比較検討した。
Omer, M.; 静間 俊行*; 羽島 良一*; 小泉 光生
no journal, ,
A quantitative isotopic analysis of the natural metallic samples of hafnium (Hf) and tungsten (W) elements is presented. Hf and W targets were exposed to quasi-monochromatic  -ray beams generated by laser Compton scattering (LCS) at the high intensity
-ray beams generated by laser Compton scattering (LCS) at the high intensity  -ray source (HI
-ray source (HI S) facility of Duke University. The
S) facility of Duke University. The  -ray beams, in the 2.4-3.2 MeV energy range, excited multiple nuclides simultaneously via the nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF). All excited transitions were employed to analyze the isotopic compositions of the targets. Particularly, the content of the even-mass naturally occurring isotopes of Hf and W was detected with high precision. The uncertainty of the measured abundances is 2.7-6.7%, while the deviation from the reference values ranges between 0.18-1.36%. This work is a contribution of the JAEA to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) under the agreement of the coordinated research program (CRP), J02015 (Facilitation of Safe and Secure Trade Using Nuclear Detection Technology - Detection of RN and Other Contraband). This work was a part of a study of the nuclear resonance fluorescence aiming at nuclear security and safeguards applications, being supported by the subsidiary for "promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like" of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
-ray beams, in the 2.4-3.2 MeV energy range, excited multiple nuclides simultaneously via the nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF). All excited transitions were employed to analyze the isotopic compositions of the targets. Particularly, the content of the even-mass naturally occurring isotopes of Hf and W was detected with high precision. The uncertainty of the measured abundances is 2.7-6.7%, while the deviation from the reference values ranges between 0.18-1.36%. This work is a contribution of the JAEA to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) under the agreement of the coordinated research program (CRP), J02015 (Facilitation of Safe and Secure Trade Using Nuclear Detection Technology - Detection of RN and Other Contraband). This work was a part of a study of the nuclear resonance fluorescence aiming at nuclear security and safeguards applications, being supported by the subsidiary for "promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like" of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
静間 俊行*; Omer, M.; 羽島 良一*; 小泉 光生; Zen, H.*; 大垣 英明*; 平 義隆*
no journal, ,
Nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) is a process in which atomic nuclei absorb and emit gamma rays. Because the emitted gamma rays have energies specific to each nuclide, it is possible to identify the nuclide by measuring the energy of emitted NRF gamma rays. In transmission NRF, a gamma-ray beam that passes through an absorption target is irradiated to another target (called witness plate, WP) which consists of the same nuclide as the absorption target, and NRF gamma rays emitted from the WP target are measured. The absorption amount of gamma rays in transmission NRF depends on the temperature of absorption and WP targets due to the Doppler broadening of resonant width. Therefore, the temperature of the absorption or WP targets may affect the time and sensitivity of the measurement. To study the temperature dependence of the self-absorption, we irradiated Pb-206 samples at room or LN2 temperatures with a laser Compton scattering (LCS) gamma-ray beam at the ultraviolet synchrotron orbital radiation (UVSOR)-III facility, National Institutes of Natural Sciences Institute for Molecular Science. We will present the experimental technique of transmission NRF and the results of the measurements. This work is a contribution to the International Atomic Energy Agency under the coordinated research program, J02015 (Facilitation of Safe and Secure Trade Using Nuclear Detection Technology - Detection of RN and Other Contraband).
小泉 光生
no journal, ,
原子力機構では、セキュリティ強化推進事業費補助金の下、アクティブ法を用いた非破壊分析技術開発を進めてきた。本会合では、核共鳴蛍光分析(NRF)技術と中性子共鳴分析(NRA)の2つの技術開発について紹介を行う。NRFは、レーザーコンプトン散乱によって発生させた準単色ガンマ線ビームを試料に照射し、試料中の特定の核種を検知する技術である。本発表では、兵庫県立大学で行ったNRFによる非破壊検知実証試験を紹介する。NRAは、パルス中性子ビームを試料に照射し、飛行時間法で分析し、中性子エネルギーに依存した核反応を調べることによって、試料中を分析する技術である。本発表では、透過中性子を測定する中性子共鳴透過分析(NRTA)と、中性子で誘起された核分裂中性子を測定する中性子共鳴核分裂中性子分析(NRFNA)の技術開発を紹介する。
菖蒲 敬久; 向井 智久*; 有木 克良*; Choe, H.*; 山本 慎*; Han, B.*; 諸岡 聡; 栗田 圭輔; 飯倉 寛
no journal, ,
本研究では、耐震改修工事に利用される技術として一般的であり、増改築などのリニューアル工事等にも広く適用可能範囲が拡大されることが期待されているあと施工アンカーの長期付着特性評価を今後JRR-3からの中性子ビームを利用していくための基礎研究を実施した。実験は、JRR-3,熱中性子ラジオグラフィ装置(TNRF)及び中性子残留応力測定装置(RESA)を用いた。CT画像再構成後のコンクリートの中央付近の断面像では、内径60mm程度鉄缶内部のコンクリートに人工的に作成した複数の穴がきれいに撮影されおり、実測と画像で寸法を比較した結果、ほぼ同じ値を示すことが確認され、穴の先端まで精度よく観察できた。