Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 SO
SO and HF
and HFSasaki, Yuji; Kaneko, Masashi; Matsumiya, Masahiko*
Chemistry Letters, 53(9), p.upae164_1 - upae164_4, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Ion-pair extractions enable to recover the anionic metal ions, such as TcO
 and ReO
and ReO
 , using cationic extractant. Recently the noble metals in hydrochloric acid are extracted by extractants having secondary and tertiary amino N atoms in their structures. Following this, extractions of Zr, Hf, Nb and Ta, metal anions present in sulfonic and hydrofluoric acids, are examined using this technique. Zr and Hf in H
, using cationic extractant. Recently the noble metals in hydrochloric acid are extracted by extractants having secondary and tertiary amino N atoms in their structures. Following this, extractions of Zr, Hf, Nb and Ta, metal anions present in sulfonic and hydrofluoric acids, are examined using this technique. Zr and Hf in H SO
SO , and Zr, Hf, Nb and Ta in HF can be extracted by NTAamide, MIDOA and TOA, and a basic information on their extraction behavior is obtained in this work.
, and Zr, Hf, Nb and Ta in HF can be extracted by NTAamide, MIDOA and TOA, and a basic information on their extraction behavior is obtained in this work.
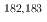 Bi isotopes
Bi isotopesHuang, H.*; Andreyev, A. N.; 37 of others*
Physical Review C, 110(1), p.014326_1 - 014326_8, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:74.11(Physics, Nuclear)Suzuki, Satoshi*; Yuguchi, Takashi*; Ishiguro, Keito*; Endo, Kyoka*; Kato, Asuka*; Yokoyama, Kosuke*; Ogita, Yasuhiro; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Sakata, Shuhei*; Ono, Takeshi*; et al.
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences (Internet), 119(1), p.230807_1 - 230807_18, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:45.39(Mineralogy)Understanding the crustal evolutionary dynamics of island arc-trench systems requires a thorough evaluation of magma chamber processes, and especially of shallow crustal granitic magma intrusion and emplacement processes. To address this, we studied the petrography and geochronology of the Kuki granite, Kitakami Mountains, northeast Japan, as an example of a non-adakitic granite at the magmatic flare-up stage. Granitic borehole samples reflect vertical variation within a magma chamber. Whole-rock chemical composition and mode data reveal a vertical transition from felsic to mafic composition with increasing depth, potentially due to gravitational fractionation of crystals in the magma chamber. The pressure and temperature history of the Kuki granite indicates no change in the magma depth with cooling from 800 to 730 C, and geobarometric calculations indicate the emplacement of magma at a depth of approximately10 km. Simultaneous determination of the zircon U Pb age, Ti concentration, and Th/U yields 1) the time temperature history of granitic magma before its solidification, and 2) the correlation between temperature and Th/U in the magma. The magma chamber cooled from ca. 900 to 700
C, and geobarometric calculations indicate the emplacement of magma at a depth of approximately10 km. Simultaneous determination of the zircon U Pb age, Ti concentration, and Th/U yields 1) the time temperature history of granitic magma before its solidification, and 2) the correlation between temperature and Th/U in the magma. The magma chamber cooled from ca. 900 to 700 C at approximately 125 Ma. The change in Th/U with temperature indicates greater fractional crystallization in the magma chamber at temperatures above 800
C at approximately 125 Ma. The change in Th/U with temperature indicates greater fractional crystallization in the magma chamber at temperatures above 800 C than below 800
C than below 800 C. Samples from different depth exhibit common tendencies in terms of the relationship between Th/U and temperature, indicating the same system of fractional crystallization throughout the cooling magma chamber.
C. Samples from different depth exhibit common tendencies in terms of the relationship between Th/U and temperature, indicating the same system of fractional crystallization throughout the cooling magma chamber.
Maruyama, Shuhei; Endo, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1372 - 1385, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:23.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)Meigo, Shinichiro; Nakano, Keita*; Matsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Yoshida, Makoto*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.05001_1 - 05001_4, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:68.83(Nuclear Science & Technology)In high-intensity proton accelerator facilities such as Accelerator Driven System (ADS) and the spallation neutron source, it is crucial to evaluate the damage of beam-interception materials and accelerator components, such as a magnet coil. The displacement per atom (dpa) is used as a damage index, which is derived by integrating the particle flux and the displacement cross section based on the NRT model. Although the dpa is employed as the standard, the experimental data of displacement cross section are scarce for a proton in the energy region above 20 MeV. To obtain the data for superconducting materials for high-intensity accelerators and magnets, the displacement cross section of Nb for proton irradiation with a kinetic energy range between 0.4 and 3 GeV was measured. For sustaining damage in the sample, the Nb sample was cooled at a cryogenic temperature ( 8 K), where the recombination of Frenkel pairs due to thermal motion was well suppressed with maintaining the normal conductivity to maintain Matthiessen's rule. The displacement cross section of Nb was calculated using the PHITS code, and was compared with the present experimental results. It was found that the widely utilized NRT model overestimates the cross section by a factor of 2, as suggested by the previous works. It was also found that the calculation with a recently proposed athermal recombination corrected (arc) model based on Molecular Dynamics (MD) shows good agreement with the present data.
8 K), where the recombination of Frenkel pairs due to thermal motion was well suppressed with maintaining the normal conductivity to maintain Matthiessen's rule. The displacement cross section of Nb was calculated using the PHITS code, and was compared with the present experimental results. It was found that the widely utilized NRT model overestimates the cross section by a factor of 2, as suggested by the previous works. It was also found that the calculation with a recently proposed athermal recombination corrected (arc) model based on Molecular Dynamics (MD) shows good agreement with the present data.
 MnSi
MnSiShigeta, Iduru*; Oku, Shuta*; Kubota, Takahide*; Kimura, Shojiro*; Seki, Takeshi*; Shinozaki, Bunju*; Awaji, Satoshi*; Takanashi, Koki; Hiroi, Masahiko*
AIP Advances (Internet), 13(2), p.025116_1 - 025116_5, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.23(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Kadowaki, Satoshi; Nogami, Masato*; Thwe Thwe, A.; Katsumi, Toshiyuki*; Yamazaki, Wataru*; Kobayashi, Hideaki*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 85(879), p.19-00274_1 - 19-00274_13, 2019/11
We dealt with three-dimensional cellular premixed flames generated by hydrodynamic and diffusive-thermal instabilities to elucidate the effects of unburned-gas temperature and heat loss by adopting the three-dimensional compressible Navier-Stokes equation. As the unburned-gas temperature became lower and the heat loss became larger, the growth rate decreased and the unstable range narrowed. With a decrease of unburned-gas temperature, the normalized growth rate increased and the normalized unstable range widened, which was because the temperature ratio of burned and unburned gases became larger. The obtained hexagonal cellular fronts were qualitatively consistent with the experimental results. As the heat loss became larger, the burning velocity of a cellular flame normalized by that of a planar flame increased. This was because diffusive-thermal effects became stronger owing to the increase of apparent Zeldovich number caused by the decrease of flame temperature.
Irisawa, Eriko; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Kato, Chiaki; Motooka, Takafumi; Ban, Yasutoshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(4), p.337 - 344, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:58.28(Nuclear Science & Technology)Yokoyama, Kenji; Kitada, Takanori*
Proceedings of 2018 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2018) (CD-ROM), p.1221 - 1230, 2018/04
no abstracts in English
Yokoyama, Kenji; Yamamoto, Akio*; Kitada, Takanori*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(3), p.319 - 334, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:56.25(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new formulation of the cross-section adjustment methodology with the dimensionality reduction technique has been derived. This new formulation is proposed as the dimension reduced cross-section adjustment method (DRCA). Since the derivation of DRCA is based on the minimum variance unbiased estimation (MVUE), an assumption of normal distribution is not required. The result of DRCA depends on a user-defined matrix that determines the dimension reduced feature subspace. We have examine three variations of DRCA, namely DRCA1, DRCA2, and DRCA3. Mathematical investigation and numerical verification have revealed that DRCA2 is equivalent to the currently widely used cross-section adjustment method. Moreover, DRCA3 is found to be identical to the cross-section adjustment method based on MVUE, which has been proposed in the previous study.
Sugaya, Toshikatsu; Nakatani, Takayoshi; Sakai, Akihiro
JAEA-Technology 2017-032, 21 Pages, 2018/01
[The article has been found to have a problem about reliability of the corrosion data acquisition, and thus it is unavailable to download the full text in accordance with authors' intentions to retract the report.] For the purpose of the setting of the rate of nuclide elution necessary to safety assessment, we planned the gas-accumulating type corrosion test on Zr-2.5wt%Nb alloy in order to obtain long-term corrosion rate under low temperature, low oxygen and alkaline conditions assuming the disposal environment. A corrosion rate over a testing period of 5 years is acquired with the aim to grasp a long-term corrosion rate behavior in this report. This corrosion rate is compared with the same data that was previously acquired over a testing period of 2 years. As a result, it is confirmed that an evaluation method that is proportional to the minus cubic root of corrosion time squared can be applicable to the corrosion rate behavior acquired this time over a testing period of 5 years, which is the same result in evaluating the corrosion rate behavior acquired over a testing period of 2 years.
 Zr,
Zr,  Nb, and
Nb, and  Mo in radioactive contaminated water generated at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station
Mo in radioactive contaminated water generated at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power StationShimada, Asako; Kameo, Yutaka
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 310(3), p.1317 - 1323, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:50.73(Chemistry, Analytical)Kojima, Atsushi; Hanada, Masaya; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Nishikiori, Ryo; Hiratsuka, Junichi; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Umeda, Naotaka; Yoshida, Masafumi; Ichikawa, Masahiro; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 87(2), p.02B304_1 - 02B304_5, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:50.60(Instruments & Instrumentation)Optimization techniques of the vacuum insulation design have been developed in order to realize a reliable voltage holding capability of Multi-Aperture Multi-Grid accelerators for giant negative ion sources for nuclear fusion. In this method, the nested multilayer configuration of each acceleration stage in the MAMuG accelerator can be uniquely designed to satisfy the target voltage within given boundary conditions. The evaluation of the voltage holding capabilities of each acceleration stages were based on the past experimental results of the area effect and the multi-aperture effect on the voltage holding capability. Moreover, total voltage holding capability of multi-stage was estimated by taking the multi-stage effect into account, which was experimentally obtained in this time. In this experiment, the multi-stage effect appeared as the superposition of breakdown probabilities in each acceleration stage, which suggested that multi-stage effect can be considered as the voltage holding capability of the single acceleration gap having the total area and aperture. The analysis on the MAMuG accelerator for JT-60SA agreed with the past gap-scan experiments with an accuracy of less than 10% variation.
Oi, Motoki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Akutsu, Atsushi*; Kawasaki, Tomoyuki; Nishikawa, Masaaki*; Fukuda, Shimpei
Proceedings of 12th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Applications of Accelerators (AccApp '15), p.89 - 96, 2016/00
At J-PARC, 3 GeV proton beam with power of 1MW is delivered to the spallation neutron source (JSNS) through beam transport line called 3NBT. At the high power accelerator facilities even a small abnormal event has a possibility to be critical so that the beam control system is crucial. In order to find tiny anomaly, rapid data analysis system is required. We developed control and data analysis system based on the Experimental Physics and Industrial Control System (EPICS) and Control System Studio (CSS). To carry out beam tuning efficiently, the beam control system based on the Strategic Accelerator Design (SAD) code has been developed. With the several shots of beam and by the one click of operational panel of the screen, required magnet field can be calculated and set automatically. Also we developed automated e-mail system to announce the abnormal event to the experts persons. With these systems, we can reduce both beam tuning time and down time.
Liu, W.; Podowski, M. Z.*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Netsu Kogaku Konfuarensu 2015 Koen Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 2 Pages, 2015/10
This paper gives prediction to the transient heat transfer at Departure of Nucleate Boiling (DNB) point for subcooled flow boiling. The prediction is carried out by solving the heat conduction equations in cylindrical coordinates with convective boundary condition, which changes with the change of the heat transfer mode on the heated surface. DNB is assumed to happen at the complete dryout of liquid sublayer trapped between the heated wall and an elongated vapor clot, during the passing time of the vapor clot. Important parameters including initial thickness of the liquid sublayer, vapor clot length, vapor clot velocity and void fraction etc., are calculated from the Liu - Nariai model. The initial heater surface temperature is derived from the Jens-Lottes correlation. The transient changes of liquid sublayer thickness, surface temperature at DNB are reported. No obvious temperature jumping is observed at DNB. To predict temperate excursion at Critical Heat Flux (CHF), more simulations to the transient boiling and film boiling processes are needed.
 Sn strand at cryogenic temperature
Sn strand at cryogenic temperatureHarjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Hemmi, Tsutomu; Ito, Takayoshi*; Nakamoto, Tatsushi*; Aizawa, Kazuya
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.031001_1 - 031001_5, 2015/09
 ion beam for ITER
ion beam for ITERUmeda, Naotaka; Kojima, Atsushi; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Hiratsuka, Junichi; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Dairaku, Masayuki; Yamanaka, Haruhiko; Hanada, Masaya
AIP Conference Proceedings 1655, p.050001_1 - 050001_10, 2015/04
For ITER neutral beam system, negative deuterium ion beam of 1 MeV, 40 A (current density of 200 A/m ) is required for 3600 s. To demonstrate ITER relevant negative ion beam acceleration, beam acceleration test has been carried out at MeV test facility in JAEA. The present target is H
) is required for 3600 s. To demonstrate ITER relevant negative ion beam acceleration, beam acceleration test has been carried out at MeV test facility in JAEA. The present target is H ion beam acceleration up to 1 MeV with 200 A/m
ion beam acceleration up to 1 MeV with 200 A/m for 60 s, which beam energy and pulse length are the present facility limit. To extend pulse duration time up to facility limit at high power density beam, new extraction grid has been developed with high cooling capability, which electron suppression magnet is placed under cooling channel. In addition, the aperture size of the electron suppression grid is enlarged from 14 mm to 16 mm and the aperture displacement is modified to reduce collision of negative ion beam on the grid. By these modifications, total grid power loading has reduced from 14% to 11%. As a result, beam acceleration up to 60 s which is the facility limit, has achieved at 700 kV, 100 A/m
for 60 s, which beam energy and pulse length are the present facility limit. To extend pulse duration time up to facility limit at high power density beam, new extraction grid has been developed with high cooling capability, which electron suppression magnet is placed under cooling channel. In addition, the aperture size of the electron suppression grid is enlarged from 14 mm to 16 mm and the aperture displacement is modified to reduce collision of negative ion beam on the grid. By these modifications, total grid power loading has reduced from 14% to 11%. As a result, beam acceleration up to 60 s which is the facility limit, has achieved at 700 kV, 100 A/m of negative ion beam without breakdown.
of negative ion beam without breakdown.
Akino, Noboru; Endo, Yasuei; Hanada, Masaya; Kawai, Mikito*; Kazawa, Minoru; Kikuchi, Katsumi*; Kojima, Atsushi; Komata, Masao; Mogaki, Kazuhiko; Nemoto, Shuji; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2014-042, 73 Pages, 2015/02
According to the project plan of JT-60 Super Advanced that is implemented as an international project between Japan and Europe, the neutral beam (NB) injectors have been disassembled. The disassembly of the NB injectors started in November, 2009 and finished in January, 2012 without any serious problems as scheduled. This reports the disassembly activities of the NB injectors.
Inoue, Takashi
Kyoka Purasuchikkusu, 60(7), p.269 - 270, 2014/07
In ITER as a thermonuclear fusion experimental reactor being conducted by an international project, a large bore insulator ring of about 1.8 m in diameter is required for generation of 1 MeV, 40 A ion beam for plasma heating by Neutral Beam Injector. At JAEA, R&D has been carried out for development of such large bore insulator ring made of ceramics, and in parallel, ion beam experiments have been carried out with insulator rings made of FRP. The experiments have troubled with frequent high voltage breakdowns after outgas from FRP. Finding melt epoxy traces at triple junction (interface of vacuum, metal and FRP as dielectric material), local stress at the triple junction has been mitigated by mounting a large metal structure, so called stress ring. As a result, acceleration of 0.98 MeV, 185 A/m hydrogen negative ion beam has successfully achieved in short pulses, where the requirement by ITER is 1 MeV and 200 A/m
hydrogen negative ion beam has successfully achieved in short pulses, where the requirement by ITER is 1 MeV and 200 A/m .
.
Ikeda, Yoshitaka; NBI Heating Group; NCT Design Team
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 49, p.S43 - S47, 2006/12
There are two type of NBI systems on JT-60U. One is the positive ion-based NBI (P-NBI) to inject the beam energy of 80-85 kV. The other is the negative ion-based NBI (N-NBI) at the beam energy more than 350 keV. Recently the pulse duration of NBI system was required to extend up to 30 sec so as to study long pulse plasmas. The four P-NBI units, which tangentially inject neutral beam to plasma, were modified to extend the pulse duration up to 30 sec with 2 MW/unit at  85 keV. The seven P-NBI units, each of which perpendicularly injects for 10 sec, were conducted to operate in series for the total pulse duration of 30 sec. The ion source of the N-NBI unit was also modified to reduce the heat load of the grid for 30 sec operation. The pulse duration was extended up to 25 sec,
85 keV. The seven P-NBI units, each of which perpendicularly injects for 10 sec, were conducted to operate in series for the total pulse duration of 30 sec. The ion source of the N-NBI unit was also modified to reduce the heat load of the grid for 30 sec operation. The pulse duration was extended up to 25 sec,  1 MW at the beam energy of 350keV. In the next step, further pulse extension of NBI up to 100 sec is planned for the modified JT-60U with superconducting coils (so called NCT). This paper reports the recent progress of the NBI system on JT-60U and the design study of the upgraded NBI system for NCT.
1 MW at the beam energy of 350keV. In the next step, further pulse extension of NBI up to 100 sec is planned for the modified JT-60U with superconducting coils (so called NCT). This paper reports the recent progress of the NBI system on JT-60U and the design study of the upgraded NBI system for NCT.