Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Mn
Mn N and Fe
N and Fe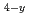 Co
Co N films
N filmsYin, W.*; Ito, Keita*; Tsubowa, Yusuke*; Tsujikawa, Masahito*; Shirai, Masafumi*; Umetsu, Rie*; Takanashi, Koki
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 628, p.173157_1 - 173157_8, 2025/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction studyYamashita, Takayuki*; Koga, Norimitsu*; Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.; Fujii, Hidetoshi*; Umezawa, Osamu*
Materials Science and Engineering A, 941, p.148602_1 - 148602_11, 2025/09
Times Cited Count:0Gu, G. H.*; Jeong, S. G.*; Heo, Y.-U.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Cho, J.*; Kim, H. S.*; 4 of others*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 223, p.308 - 324, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Gao, S.*; Ito, Tatsuya; Yamashita, Takayuki*; Harjo, S.; Zhao, L.*; Wang, Q.*
Scripta Materialia, 264, p.116726_1 - 116726_6, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Yoshida, Kazuo; Hiyama, Mina*; Tamaki, Hitoshi
JAEA-Research 2025-003, 24 Pages, 2025/06
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high-level radioactive liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (RuO ) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into the atmosphere. Accurate quantitative estimation of released Ru is one of the important issues for risk assessment of those facilities. RuO
) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into the atmosphere. Accurate quantitative estimation of released Ru is one of the important issues for risk assessment of those facilities. RuO is expected to be absorbed chemically into water dissolving nitrous acid. Condensation of mixed vapor plays an important role for Ru transporting behavior in the facility building. The thermal-hydraulic behavior in the facility building is simulated with MELCOR code. The latent heat, which is a governing factor for vapor condensing behavior, has almost same value for nitric acid and water at the temperature range under 120 centigrade. Considering this thermal characteristic, it is assumed that the amount of nitric acid is substituted with mole-equivalent water in MELCOR simulation. Compensating modeling induced deviation by this assumption have been assembled with control function features of MELCOR. The comparison results have been described conducted between original simulation and modified simulation with compensating model in this report. It has been revealed that the total amount of pool water in the facility was as same as both simulations.
is expected to be absorbed chemically into water dissolving nitrous acid. Condensation of mixed vapor plays an important role for Ru transporting behavior in the facility building. The thermal-hydraulic behavior in the facility building is simulated with MELCOR code. The latent heat, which is a governing factor for vapor condensing behavior, has almost same value for nitric acid and water at the temperature range under 120 centigrade. Considering this thermal characteristic, it is assumed that the amount of nitric acid is substituted with mole-equivalent water in MELCOR simulation. Compensating modeling induced deviation by this assumption have been assembled with control function features of MELCOR. The comparison results have been described conducted between original simulation and modified simulation with compensating model in this report. It has been revealed that the total amount of pool water in the facility was as same as both simulations.
Yanagisawa, Hiroshi; Motome, Yuiko
JAEA-Research 2025-001, 99 Pages, 2025/06
The detailed computational models for nuclear criticality analyses on the first startup cores of NSRR (Nuclear Safety Research Reactor), which is categorized as a TRIGA-ACPR (Annular Core Pulse Reactor), were created for the purposes of deeper understandings of safety inspection data on the neutron absorber rod worths of reactivity and improvement of determination technique of the reactivity worths. The uncertainties in effective neutron multiplication factor (k ) propagated from errors in the geometry, material, and operation data for the present models were evaluated in detail by using the MVP version 3 code with the latest Japanese nuclear data library, JENDL-5, and the previous versions of JENDL libraries. As a result, the overall uncertainties in k
) propagated from errors in the geometry, material, and operation data for the present models were evaluated in detail by using the MVP version 3 code with the latest Japanese nuclear data library, JENDL-5, and the previous versions of JENDL libraries. As a result, the overall uncertainties in k for the present models were evaluated to be in the range of 0.0027 to 0.0029
for the present models were evaluated to be in the range of 0.0027 to 0.0029  k
k . It is expected that the present models will be utilized as the benchmark on k
. It is expected that the present models will be utilized as the benchmark on k for TRIGA-ACPR. Moreover, it is confirmed that the overall uncertainties were sufficiently smaller than the values of absorber rod worths determined in NSRR. Thus, it is also considered that the present models are applicable to further analyses on the absorber rod worths in NSRR.
for TRIGA-ACPR. Moreover, it is confirmed that the overall uncertainties were sufficiently smaller than the values of absorber rod worths determined in NSRR. Thus, it is also considered that the present models are applicable to further analyses on the absorber rod worths in NSRR.
Takeda, Takeshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2025-005, 106 Pages, 2025/06
JAEA has been creating input data for pressurized water reactor (PWR) analysis with RELAP5/MOD3.3 code, mainly based on design information for the four-loop PWR's Tsuruga Power Station Unit-2 as the reference reactor of the Large Scale Test Facility (LSTF). The cold leg large-break loss-of-coolant accident (LBLOCA) calculation in the flamework of the BEMUSE program is cited as a representative OECD/NEA activity related to the PWR analysis. The new regulatory requirements for PWRs in Japan include the event of loss of recirculation functions from emergency core cooling system (ECCS) in the cold leg LBLOCA. This event should be evaluated the effectiveness of measures against severe core damage. The input data for this study were made preparations to analyze the PWR LBLOCA, which is one of the design basis accidents that should be postulated in the safety design. This report describes the main features of the input data for the PWR LBLOCA analysis. The PWR model comprised a reactor vessel, pressurizer (PZR), hot legs, steam generators (SGs), SG secondary-side system, crossover legs, cold legs, and ECCS. A four-loop PWR was simulated by two loops in the LBLOCA calculation. Specifically, loop-A attached with the PZR corresponded to three loops, and loop-B mounted with the break was equal to one loop. The nodalization schemes of the PWR components were referred to those of the LSTF components. Moreover, interpretations were added to the main input data for the PWR LBLOCA analysis, and further information such as the basis for determining the input data was provided. In addition, transient analysis was performed employing the prepared input data for the loss of ECCS recirculation functions event. The present transient analysis was confirmed to be appropriate generally by comparing with the calculation in the previous study using the RELAP5/MOD3.3 code. Furthermore, sensitivity analyses were executed exploiting the RELAP5/MOD3.3 code to clarify the effects of a discharge coefficient through the break and water injection flow rate of the alternative recirculation on the fuel rod cladding surface temperature. This report explains the results of the sensitivity analyses within the defined ranges, which complement some of the content of the previous study's calculation for the loss of ECCS recirculation functions event.
Iwasawa, Yuzuru; Matsumoto, Toshinori; Moriyama, Kiyofumi*
JAEA-Data/Code 2025-001, 199 Pages, 2025/06
A steam explosion is defined as a phenomenon that occurs when a hot liquid comes into contact with a low-temperature cold liquid with volatile properties. The rapid transfer of heat from the hot liquid to the cold liquid results in a chain reaction of the explosive vaporization of the cold liquid and fine fragmentation of the hot liquid. The explosive vaporization of the cold liquid initiates the propagation of shock waves in the cold liquid. The expansion of the hot and cold liquid mixture exerts mechanical forces on the surrounding structures. In severe accidents of light water reactors, the molten core (melt) is displaced into the coolant water, resulting in fuel-coolant interactions (FCIs). The explosive FCI, referred to as a steam explosion, has been identified as a significant safety assessment issue as it can compromise the integrity of the primary containment vessel. The JASMINE code is an analytical tool developed to evaluate the mechanical forces imposed by steam explosions in nuclear reactors. It performs numerical simulations of steam explosions in a mechanistic manner. The present report describes modeling concepts, basic equations, numerical solutions, and example simulations, as well as instructions for input preparation, code execution, and the use of supporting tools for practical purpose. The present report is the updated version of the "Steam Explosion Simulation Code JASMINE v.3 User's Guide, JAEA-Data/ Code 2008-014". The present report was compiled and updated based on the latest version of the code, JASMINE 3.3c, with corrections for minor errors of the distributed code JASMINE 3.3b, and conformance to recently widely used compilers on UNIX-like environments such as the GNU compiler. The numerical simulations described in the present report were obtained using the latest version JASMINE 3.3c. The latest parameter adjustment method for a model parameter proposed by the previous study is employed to conduct the numerical simulations.
Park, M.-H.*; Shibata, Akinobu*; Harjo, S.; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Acta Materialia, 292, p.121061_1 - 121061_13, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:84.88(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Sugita, Yutaka; Ono, Hirokazu; Beese, S.*; Pan, P.*; Kim, M.*; Lee, C.*; Jove-Colon, C.*; Lopez, C. M.*; Liang, S.-Y.*
Geomechanics for Energy and the Environment, 42, p.100668_1 - 100668_21, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Energy & Fuels)The international cooperative project DECOVALEX 2023 focused on the Horonobe EBS experiment in the Task D, which was undertaken to study, using numerical analyses, the thermo-hydro-mechanical (or thermo-hydro) interactions in bentonite based engineered barriers. One full-scale in-situ experiment and four laboratory experiments, largely complementary, were selected for modelling. The Horonobe EBS experiment is a temperature-controlled non-isothermal experiment combined with artificial groundwater injection. The Horonobe EBS experiment consists of the heating and cooling phases. Six research teams performed the THM or TH (depended on research team approach) numerical analyses using a variety of computer codes, formulations and constitutive laws.
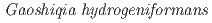 sp. nov., a novel hydrogen-producing bacterium isolated from a deep diatomaceous shale formation
sp. nov., a novel hydrogen-producing bacterium isolated from a deep diatomaceous shale formationUeno, Akio*; Sato, Kiyoshi*; Tamamura, Shuji*; Murakami, Takuma*; Inomata, Hidenori*; Tamazawa, Satoshi*; Amano, Yuki; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Naganuma, Takeshi*; Igarashi, Toshifumi*
International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 75(6), p.006802_1 - 006802_11, 2025/06
no abstracts in English
Ohashi, Tomonori*; Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Steinle-Neumann, G.*; Hattori, Takanori; Yuan, L.*; Suzuki, Akio*
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences (Internet), 120(1), p.240926a_1 - 240926a_13, 2025/06
We explore the structures of dry and hydrated (H O and D
O and D O) Na
O) Na Si
Si O
O melt at 0-6 GPa and 1000-1300 K and glasses recovered from high pressure and temperatures by in-situ neutron and X-ray diffraction. The structures of the melts at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K are also investigated by ab-initio molecular dynamics simulation. In-situ neutron experiments revealed that the D-O distance increases with compression due to the formation of -O-D-O- bridging species, which is reproduced by the molecular dynamics simulations. The pressure-induced -O-D-O- formation reflects a more rigid incorporation of hydrogen, which acts as a mechanism for the experimentally observed higher solubility of water in silicate melts. Together with shrinking modifier domains, this process dominates the compression behavior of hydrous Na
melt at 0-6 GPa and 1000-1300 K and glasses recovered from high pressure and temperatures by in-situ neutron and X-ray diffraction. The structures of the melts at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K are also investigated by ab-initio molecular dynamics simulation. In-situ neutron experiments revealed that the D-O distance increases with compression due to the formation of -O-D-O- bridging species, which is reproduced by the molecular dynamics simulations. The pressure-induced -O-D-O- formation reflects a more rigid incorporation of hydrogen, which acts as a mechanism for the experimentally observed higher solubility of water in silicate melts. Together with shrinking modifier domains, this process dominates the compression behavior of hydrous Na Si
Si O
O melt, whereas the compression of dry Na
melt, whereas the compression of dry Na Si
Si O
O at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K is governed largely by bending of the Si-O-Si angle. The molecular dynamics simulations on hydrous Na
at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K is governed largely by bending of the Si-O-Si angle. The molecular dynamics simulations on hydrous Na Si
Si O
O melts further suggest that the sodium ions are scavenged from its network-modifying role via 2(
melts further suggest that the sodium ions are scavenged from its network-modifying role via 2(![$$^{[4]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZULV4SI.gif) Si-O
Si-O + Na
+ Na )
) 
![$$^{[4]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZULV4SI.gif) Si-(O-
Si-(O-![$$^{[5]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZVLV4SI.gif) Si-O)
Si-O) + 2Na
+ 2Na and Si-O
and Si-O + Na
+ Na + Si-OH
+ Si-OH  Si-(O-H-O-Si)
Si-(O-H-O-Si) + Na
+ Na with increasing pressure.
with increasing pressure.
Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Shibahara, Yuji*
KURNS Progress Report 2024, P. 31, 2025/06
no abstracts in English
Go, G.*; Goli, D. P.*; Esaki, Nanse; Tserkovnyak, Y.*; Kim, S. K.*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 7(2), p.L022066_1 - L022066_7, 2025/06
Auh, Y. H.*; Neal, N. N.*; Arole, K.*; Regis, N. A.*; Nguyen, T.*; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Radovic, M.*; Green, M. J.*; et al.
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 17(21), p.31392 - 31402, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Li, X.; Yamaji, Akifumi*; Sato, Ikken*; Yamashita, Takuya
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 214, p.111217_1 - 111217_13, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Aoyama, Takahito; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Sato, Tomonori; Kato, Chiaki; Sano, Naruto; Yamashita, Naoki; Otani, Kyohei; Igarashi, Takahiro
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 214, p.111229_1 - 111229_6, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Mori, Airi; Johansen, M. P.*; McGinnity, P.*; Takahara, Shogo
Communications Earth & Environment (Internet), 6, p.356_1 - 356_11, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)Fablet, L.*; P drot, M.*; Choueikani, F.*; Kieffer, I.*; Proux, O.*; Pierson-Wickmann, A.-C.*; Cagniart, V.*; Yomogida, Takumi; Marsac, R.*
drot, M.*; Choueikani, F.*; Kieffer, I.*; Proux, O.*; Pierson-Wickmann, A.-C.*; Cagniart, V.*; Yomogida, Takumi; Marsac, R.*
Environmental Science; Nano, 12(5), p.2815 - 2827, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Nickel is an omnipresent trace element in the environment. Due to its high affinity for iron oxide nanoparticles, its elimination from soils and water by these nanoparticles represents an interesting strategy, specially by magnetites, which is naturally present in the environment. However, the interactions between Ni and magnetite are poorly understood, because of the difficulty to control the stoichiometry (Fe(II)-to-Fe(III) ratio) of magnetite. The behavior of Ni in the presence of magnetite nanoparticles with different stoichiometries, in aqueous solution and inert atmosphere, are probed by adsorption experiments and X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy. This study helps predicting the interactions between Ni and magnetite in environmental conditions, which can be used for the development of efficient remediation strategies.
Tomota, Yo*; Harjo, S.; Xu, P. G.; Morooka, Satoshi; Gong, W.; Wang, Y.*
Metals, 15(6), p.610_1 - 610_19, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0