Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Shibahara, Yuji*
KURNS Progress Report 2024, P. 31, 2025/06
no abstracts in English
 Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe
FeNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(3), p.300 - 307, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Fujita, Tatsuya; Yamamoto, Akio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(2), p.179 - 196, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study newly established a direct coupling code system consisting of the nuclear data processing code FRENDY version 2, and the three-dimensional heterogeneous transport code GENESIS (FRENDY-V2/GENESIS) for easy implementation of the random-sampling-based uncertainty quantification considering the implicit effect due to nuclear cross-section (XS) perturbations. The multi-group macroscopic XSs prepared for GENESIS were generated by FRENDY version 2, where the Dancoff factor was calculated by the neutron current method. Then the background XSs were evaluated based on the Carlvik two-term rational approximation. The infinite multiplication factor (k-infinity) and the fission reaction rate distribution in UO and MOX lattice geometries were compared with MVP3 to verify the calculation accuracy of FRENDY-V2/GENESIS. The sensitivity analyses on the discretization conditions such as the ray tracing of the method of characteristics were also carried out. Through several comparisons between FRENDY-V2/GENESIS and MVP3, FRENDY-V2/GENESIS with the SHEM 361-group structure calculates the k-infinity within approximately 50 pcm and the fission reaction rate distribution within approximately 0.1% by the root mean square, respectively. Consequently, the applicability of FRENDY-V2/GENESIS was verified, and FRENDY-V2/GENESIS can be used to discuss the implicit effect due to multi-group XS perturbations.
and MOX lattice geometries were compared with MVP3 to verify the calculation accuracy of FRENDY-V2/GENESIS. The sensitivity analyses on the discretization conditions such as the ray tracing of the method of characteristics were also carried out. Through several comparisons between FRENDY-V2/GENESIS and MVP3, FRENDY-V2/GENESIS with the SHEM 361-group structure calculates the k-infinity within approximately 50 pcm and the fission reaction rate distribution within approximately 0.1% by the root mean square, respectively. Consequently, the applicability of FRENDY-V2/GENESIS was verified, and FRENDY-V2/GENESIS can be used to discuss the implicit effect due to multi-group XS perturbations.
 Er(n,
Er(n, )
)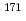 Er and
Er and  Hf(n,
Hf(n, )
) Hf reactions
Hf reactionsNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 14 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Konno, Chikara
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(1), p.121 - 126, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:25.62(Nuclear Science & Technology)The JENDL-4.0/HE neutron and proton ACE files were produced in 2017 and those of 22 nuclei for neutron and 25 nuclei for proton were bundled in the PHITS code. Recently it was found that the following five data in the JENDL-4.0/HE neutron and proton ACE files had any problems; ACE files for  N and
N and  O, heating numbers, damage energy production cross sections, secondary neutron multiplicities and fission cross sections. Thus new JENDL-4.0/HE neutron and proton ACE files were produced with the problems fixed. This paper describes the problems and how to produce the new neutron and proton ACE files in detail.
O, heating numbers, damage energy production cross sections, secondary neutron multiplicities and fission cross sections. Thus new JENDL-4.0/HE neutron and proton ACE files were produced with the problems fixed. This paper describes the problems and how to produce the new neutron and proton ACE files in detail.
 Nb by activation method and half-life of
Nb by activation method and half-life of  Nb by mass analysis
Nb by mass analysisNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1361 - 1371, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:62.75(Nuclear Science & Technology)The thermal-neutron capture cross section (
 ) and resonance integral (I
) and resonance integral (I ) for
) for  Nb among nuclides for decommissioning were measured by an activation method and the half-life of
Nb among nuclides for decommissioning were measured by an activation method and the half-life of  Nb by mass analysis. Niobium-93 samples were irradiated with a hydraulic conveyer installed in the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Gold-aluminum, cobalt-aluminum alloy wires were used to monitor thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indexes at an irradiation position. A 25-
Nb by mass analysis. Niobium-93 samples were irradiated with a hydraulic conveyer installed in the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Gold-aluminum, cobalt-aluminum alloy wires were used to monitor thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indexes at an irradiation position. A 25- m-thick gadolinium foil was used to sort out reactions ascribe to thermal-and epi-thermal neutrons. Its thickness provided a cut-off energy of 0.133 eV. In order to attenuate radioactivity of
m-thick gadolinium foil was used to sort out reactions ascribe to thermal-and epi-thermal neutrons. Its thickness provided a cut-off energy of 0.133 eV. In order to attenuate radioactivity of 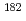 Ta due to impurities, the Nb samples were cooled for nearly 2 years. The induced radio activity in the monitors and Nb samples were measured by
Ta due to impurities, the Nb samples were cooled for nearly 2 years. The induced radio activity in the monitors and Nb samples were measured by  -ray spectroscopy. In analysis based on Westcott's convention, the
-ray spectroscopy. In analysis based on Westcott's convention, the 
 and I
and I values were derived as 1.11
values were derived as 1.11 0.04 barn and 10.5
0.04 barn and 10.5 0.6 barn, respectively. After the
0.6 barn, respectively. After the  -ray measurements, mass analysis was applied to the Nb sample to obtain the reaction rate. By combining data obtained by both
-ray measurements, mass analysis was applied to the Nb sample to obtain the reaction rate. By combining data obtained by both  -ray spectroscopy and mass analysis, the half-life of
-ray spectroscopy and mass analysis, the half-life of  Nb was derived as (2.00
Nb was derived as (2.00 0.15)
0.15) 10
10 years.
years.
 Se(n,
Se(n, ) cross section up to 200 keV at the n_TOF facility at CERN
) cross section up to 200 keV at the n_TOF facility at CERNSosnin, N. V.*; Harada, Hideo; Kimura, Atsushi; 128 of others*
Physical Review C, 107(6), p.065805_1 - 065805_9, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)Nakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(11), p.1388 - 1398, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:14.76(Nuclear Science & Technology)The present study selected  Np among radioactive nuclides and aimed to measure the thermal-neutron capture cross-section for
Np among radioactive nuclides and aimed to measure the thermal-neutron capture cross-section for  Np in a well-thermalized neutron field by an activation method. A
Np in a well-thermalized neutron field by an activation method. A  Np standard solution was used for irradiation samples. A thermal-neutron flux at an irradiation position was measured with neutron flux monitors:
Np standard solution was used for irradiation samples. A thermal-neutron flux at an irradiation position was measured with neutron flux monitors:  Sc,
Sc,  Co,
Co,  Mo,
Mo,  Ta and
Ta and  Au. The
Au. The  Np sample and flux monitors were irradiated together for 30 minutes in the graphite thermal column equipped with the Kyoto University Research Reactor. The similar irradiation was carried out twice. After the irradiations, the
Np sample and flux monitors were irradiated together for 30 minutes in the graphite thermal column equipped with the Kyoto University Research Reactor. The similar irradiation was carried out twice. After the irradiations, the  Np samples were quantified using 312-keV gamma ray emitted from
Np samples were quantified using 312-keV gamma ray emitted from  Pa in a radiation equilibrium with
Pa in a radiation equilibrium with  Np. The reaction rates of
Np. The reaction rates of  Np were obtained from gamma-ray peak net counts given by
Np were obtained from gamma-ray peak net counts given by  Np, and then the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of
Np, and then the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of  Np was found to be 173.8
Np was found to be 173.8 4.4 barn by averaging the results obtained by the two irradiations. The present result was in agreement with the reported data given by a time-of-flight method within the limit of uncertainty.
4.4 barn by averaging the results obtained by the two irradiations. The present result was in agreement with the reported data given by a time-of-flight method within the limit of uncertainty.
 Np(n,
Np(n,  ) reaction with TC-Pn in KUR
) reaction with TC-Pn in KURNakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Shibahara, Yuji*
KURNS Progress Report 2021, P. 93, 2022/07
In terms of nuclear transmutation studies of minor actinides in nuclear wastes, the present work selected  Np among them and aimed to measure the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of
Np among them and aimed to measure the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of  Np using a well-thermalized neutron field by a neutron activation method because there have been discrepancies among reported cross-section data. A
Np using a well-thermalized neutron field by a neutron activation method because there have been discrepancies among reported cross-section data. A  Np standard solution was used for irradiation samples. The thermal-neutron flux at an irradiation position was measured with flux monitors:
Np standard solution was used for irradiation samples. The thermal-neutron flux at an irradiation position was measured with flux monitors:  Sc,
Sc,  Co,
Co,  Mo,
Mo,  Ta and
Ta and  Au. The
Au. The  Np sample was irradiated together with the flux monitors for 30 minutes in the graphite thermal column equipped in the Kyoto University Research Reactor. The similar irradiation was repeated once more to confirm the reproducibility of the results. After irradiation, the
Np sample was irradiated together with the flux monitors for 30 minutes in the graphite thermal column equipped in the Kyoto University Research Reactor. The similar irradiation was repeated once more to confirm the reproducibility of the results. After irradiation, the  Np samples were quantified using 312-keV gamma-ray emitted from
Np samples were quantified using 312-keV gamma-ray emitted from  Pa in radiation equilibrium with
Pa in radiation equilibrium with  Np. The reaction rates of
Np. The reaction rates of  Np were obtained from the peak net counts of gamma-rays emitted from generated
Np were obtained from the peak net counts of gamma-rays emitted from generated  Np, and then the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of
Np, and then the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of  Np was found to be 173.8
Np was found to be 173.8 4.7 barn by averaging the results obtained by the two irradiations. The present result was in agreement with the reported data given by a time-of-flight method within a limit of uncertainty.
4.7 barn by averaging the results obtained by the two irradiations. The present result was in agreement with the reported data given by a time-of-flight method within a limit of uncertainty.
Yokoyama, Kenji; Maruyama, Shuhei; Taninaka, Hiroshi; Oki, Shigeo
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-019, 115 Pages, 2022/03
In JAEA, several versions of unified cross-section set for fast reactors have been developed so far; we have developed a new unified cross-section set ADJ2017R, which is an improved version of the unified cross-section setADJ2017 for fast reactors. The unified cross-section set is used for reflecting information of C/E values (analysis / experiment values) obtained by integral experiment analyses in reactor core design via the cross-section adjustment methodology; the values are stored in the standard database for FBR core design. In the methodology, the cross-section set is adjusted by integrating the information such as uncertainty (covariance) of nuclear data, uncertainty of integral experiment / analysis, sensitivity of integral experiment with respect to nuclear data. ADJ2017R basically has the same performance as ADJ2017, but we conducted an additional investigation on ADJ2017 and revised the following two points. The first is to unify the evaluation method of the correlation coefficient of uncertainty caused by experiments (hereinafter referred to as the experimental correlation coefficient). Because it was found that the common uncertainty used in the evaluation of the experimental correlation coefficient was evaluated by two different methods, the experimental correlation coefficients were revised for all experimental data, and the evaluation method was unified. The second is the review of the integral experiment data used for the cross-section adjustment calculation. It was found that one of the experimental values of composition ratio after irradiation of the Am-243 sample has a problem in uncertainty evaluation because its experimental uncertainty is extremely small compared to the others. The cross-section adjustment calculation was, therefore, redone by excluding the experimental value. In the creation of ADJ2017, a total of 719 data sets were analyzed and evaluated, and eventually adopted 620 integral experimental data sets. In contrast, a total of 61
Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Terada, Kazushi*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Toh, Yosuke; Segawa, Mariko; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(3), p.318 - 333, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:67.14(Nuclear Science & Technology) Np
NpRovira Leveroni, G.; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Tosaka, Kenichi*; Matsuura, Shota*; Kodama, Yu*; Nakano, Hideto*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(1), p.110 - 122, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:49.08(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(10), p.1061 - 1070, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:71.62(Nuclear Science & Technology)In a well-thermalized neutron field, it is principally possible to drive a thermal-neutron capture cross-section without considering an epithermal neutron component. This was demonstrated by a neutron activation method using the graphite thermal column (TC-Pn) of the Kyoto University Research Reactor. First, in order to confirm that the graphite thermal column was a well-thermalized neutron field, neutron irradiation was performed with neutron flux monitors:  Au,
Au,  Co,
Co,  Sc,
Sc,  Cu, and
Cu, and  Mo. The TC-Pn was confirmed to be extremely thermalized on the basis of Westcott's convention, because the thermal-neutron flux component took a constant value regardless of the sensitivity of each flux monitor to epithermal neutrons. Next, as a demonstration, the thermal-neutron capture cross section of
Mo. The TC-Pn was confirmed to be extremely thermalized on the basis of Westcott's convention, because the thermal-neutron flux component took a constant value regardless of the sensitivity of each flux monitor to epithermal neutrons. Next, as a demonstration, the thermal-neutron capture cross section of  Ta(n,
Ta(n, )
)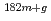 Ta reaction was measured using the graphite thermal column, and then derived to be 20.5
Ta reaction was measured using the graphite thermal column, and then derived to be 20.5 0.4 barn, which supported the evaluated value of 20.4
0.4 barn, which supported the evaluated value of 20.4 0.3 barn. The
0.3 barn. The  Ta nuclide could be useful as a flux monitor that complements the sensitivity between
Ta nuclide could be useful as a flux monitor that complements the sensitivity between  Au and
Au and  Mo monitors.
Mo monitors.
Harada, Hideo
Applied Sciences (Internet), 11(14), p.6558_1 - 6558_20, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)For accuracy improvement of neutron activation analysis and neutron capture cross section, bias effects are investigated on g- and s-factors in the Westcott convention. As origins of biases, a joining function shape, neutron temperature and sample temperature, have been investigated. Biases are quantitatively deduced for two 1/v isotopes ( Au,
Au,  Co) and six non-1/v isotopes (
Co) and six non-1/v isotopes ( Am,
Am,  Eu,
Eu, 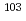 Rh,
Rh,  In,
In,  Hf,
Hf,  Ra). The s-factor calculated with a joining function deduced recently by a detailed Monte Carlo simulation is compared to s-factors calculated with traditional joining functions by Westcott. The results show the bias induced by sample temperature is small as the order of 0.1% for g-factor and the order of 1% for s-factor. On the other hand, biases induced by a joining function shape for s-factor depend significantly on both isotopes and neutron temperature. As the result, reaction rates are also affected significantly as well. The bias size on reaction rate is given in the case of epithermal neutron index r = 0.1, for the eight isotopes.
Ra). The s-factor calculated with a joining function deduced recently by a detailed Monte Carlo simulation is compared to s-factors calculated with traditional joining functions by Westcott. The results show the bias induced by sample temperature is small as the order of 0.1% for g-factor and the order of 1% for s-factor. On the other hand, biases induced by a joining function shape for s-factor depend significantly on both isotopes and neutron temperature. As the result, reaction rates are also affected significantly as well. The bias size on reaction rate is given in the case of epithermal neutron index r = 0.1, for the eight isotopes.
Kawase, Shoichiro*; Kimura, Atsushi; Harada, Hideo; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Iwamoto, Osamu; Nakamura, Shoji; Segawa, Mariko; Toh, Yosuke
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(7), p.764 - 786, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:40.86(Nuclear Science & Technology) Ce(n,
Ce(n, )
)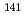 Ce cross-section measurement at n_TOF
Ce cross-section measurement at n_TOFAmaducci, S.*; Harada, Hideo; Kimura, Atsushi; 127 of others*
Universe (Internet), 7(6), p.200_1 - 200_11, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.21(Astronomy & Astrophysics) Am(n,
Am(n, )
)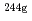 Am and
Am and  Am(n,
Am(n, )
)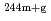 Am reactions
Am reactionsNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(3), p.259 - 277, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:43.04(Nuclear Science & Technology)Research and development were made for accuracy improvement of neutron capture cross section data on  Am among minor actinides. First, the emission probabilities of decay
Am among minor actinides. First, the emission probabilities of decay  rays were obtained with high accuracy, and the amount of the ground state of
rays were obtained with high accuracy, and the amount of the ground state of  Am produced by reactor neutron irradiation of
Am produced by reactor neutron irradiation of  Am was examined by
Am was examined by  -ray measurement. Next, the total amount of isomer and ground states was examined by
-ray measurement. Next, the total amount of isomer and ground states was examined by  -ray measurement. Thermal-neutron capture cross sections and resonance integrals were derived both for the
-ray measurement. Thermal-neutron capture cross sections and resonance integrals were derived both for the  Am(n,
Am(n, )
)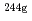 Am and for
Am and for  Am(n,
Am(n, )
)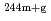 Am reactions.
Am reactions.
 Am(n,
Am(n, )
)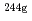 Am,
Am, 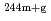 Am reactions
Am reactionsNakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Shibahara, Yuji*
KURNS Progress Report 2019, P. 132, 2020/08
Research and development were made for accuracy improvement of neutron capture cross section data on  Am among minor actinides. First, the emission probabilities of decay
Am among minor actinides. First, the emission probabilities of decay  rays were obtained with high accuracy, and the amount of the ground state of
rays were obtained with high accuracy, and the amount of the ground state of  Am produced by reactor neutron irradiation of
Am produced by reactor neutron irradiation of  Am was examinded by
Am was examinded by  -ray measurement. Next, the total amount of isomer and ground states was examoned by
-ray measurement. Next, the total amount of isomer and ground states was examoned by  -ray measurement.
-ray measurement.
 Cs
CsShibahara, Yuji*; Nakamura, Shoji; Uehara, Akihiro*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*; Fukutani, Satoshi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Iwamoto, Osamu
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 325(1), p.155 - 165, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:75.34(Chemistry, Analytical)The measurements of isotopic ratios of Cs samples by thermal ionization mass spectrometry were performed for the analysis of their samples used to evaluate nuclear data obtained for  Cs. To obtain a high intensity and stable ion beam, the effects of additive agents on the ionization of Cs were examined. The effect of silicotungstic acid on the ionization of Cs was the largest among the additive agents studied in the present study, while the silicotungstic acid also showed the largest isobaric interference of polyatomic ions. It was demonstrated that as small as 2
Cs. To obtain a high intensity and stable ion beam, the effects of additive agents on the ionization of Cs were examined. The effect of silicotungstic acid on the ionization of Cs was the largest among the additive agents studied in the present study, while the silicotungstic acid also showed the largest isobaric interference of polyatomic ions. It was demonstrated that as small as 2 10
10 g of a Cs sample was sufficient to achieve the analytical precision required to measure the
g of a Cs sample was sufficient to achieve the analytical precision required to measure the  Cs/
Cs/ Cs ratio in the case where an additive agent of TaO/glucose was employed. After examining of the analytical conditions, such as the interference effect due to Ba, the measurements of the isotopic ratios of two Cs samples used in our study using TIMS were conducted, and it was discussed how much the ratios contributed to evaluation of the neutron capture cross-section of
Cs ratio in the case where an additive agent of TaO/glucose was employed. After examining of the analytical conditions, such as the interference effect due to Ba, the measurements of the isotopic ratios of two Cs samples used in our study using TIMS were conducted, and it was discussed how much the ratios contributed to evaluation of the neutron capture cross-section of  Cs.
Cs.
Nakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Kimura, Atsushi; Iwamoto, Osamu; Uehara, Akihiro*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(4), p.388 - 400, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:26.20(Nuclear Science & Technology)The thermal-neutron capture cross-section ( ) and resonance integral(I
) and resonance integral(I ) were measured for the
) were measured for the  Cs(n,
Cs(n, )
) Cs reaction by an activation method and mass spectrometry. We used
Cs reaction by an activation method and mass spectrometry. We used  Cs contained as an impurity in a normally available
Cs contained as an impurity in a normally available  Cs standard solution. An isotope ratio of
Cs standard solution. An isotope ratio of  Cs and
Cs and  Cs in a standard
Cs in a standard  Cs solution was measured by mass spectrometry to quantify
Cs solution was measured by mass spectrometry to quantify  Cs. The analyzed
Cs. The analyzed  Cs samples were irradiated at the hydraulic conveyer of the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Wires of Co/Al and Au/Al alloys were used as neutron monitors to measure thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indices at an irradiation position. A gadolinium filter was used to measure the
Cs samples were irradiated at the hydraulic conveyer of the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Wires of Co/Al and Au/Al alloys were used as neutron monitors to measure thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indices at an irradiation position. A gadolinium filter was used to measure the  , and a value of 0.133 eV was taken as the cut-off energy. Gamma-ray spectroscopy was used to measure induced activities of
, and a value of 0.133 eV was taken as the cut-off energy. Gamma-ray spectroscopy was used to measure induced activities of  Cs,
Cs,  Cs and monitor wires. On the basis of Westcott's convention, the
Cs and monitor wires. On the basis of Westcott's convention, the  and I
and I values were derived as 8.57
values were derived as 8.57 0.25 barn, and 45.3
0.25 barn, and 45.3 3.2 barn, respectively. The
3.2 barn, respectively. The  obtained in the present study agreed within the limits of uncertainties with the past reported value of 8.3
obtained in the present study agreed within the limits of uncertainties with the past reported value of 8.3 0.3 barn.
0.3 barn.