Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
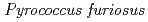 by BIX-3, a single-crystal diffractometer for biomacromolecules
by BIX-3, a single-crystal diffractometer for biomacromoleculesKurihara, Kazuo; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Chatake, Toshiyuki*; Adams, M. W. W.*; Jenney, F. E. Jr.*; Moiseeva, N.*; Bau, R.*; Niimura, Nobuo
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101(31), p.11215 - 11220, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:60.16(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The structure of a rubredoxin (Rd) from 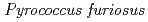 , an organism that grows optimally at 100
, an organism that grows optimally at 100  C, was determined using the neutron single-crystal diffractometer for biological macromolecules (BIX-3) at the JRR-3 reactor of JAERI. Data were collected at room temperature up to a resolution of 1.5
C, was determined using the neutron single-crystal diffractometer for biological macromolecules (BIX-3) at the JRR-3 reactor of JAERI. Data were collected at room temperature up to a resolution of 1.5  , and the completeness of the data set was 81.9 %. The model contains 306 H atoms and 50 D atoms. A total of 37 hydration water molecules were identified. The model has been refined to final agreement factors of
, and the completeness of the data set was 81.9 %. The model contains 306 H atoms and 50 D atoms. A total of 37 hydration water molecules were identified. The model has been refined to final agreement factors of  = 18.6 % and
= 18.6 % and 
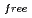 = 21.7 %. Several orientations of the O-D bonds of side chains, whose assignments from X-ray data were previously ambiguous, were clearly visible in the neutron structure. While most backbone N-H bonds had undergone some degree of H/D exchange throughout the molecule, five H atom positions still had distinctly negative (H) peaks. The neutron Fourier maps clearly showed the details of an extensive set of H bonds involving the ND
= 21.7 %. Several orientations of the O-D bonds of side chains, whose assignments from X-ray data were previously ambiguous, were clearly visible in the neutron structure. While most backbone N-H bonds had undergone some degree of H/D exchange throughout the molecule, five H atom positions still had distinctly negative (H) peaks. The neutron Fourier maps clearly showed the details of an extensive set of H bonds involving the ND
 terminus that may contribute to the unusual thermostability of this molecule.
terminus that may contribute to the unusual thermostability of this molecule.
Kurihara, Kazuo; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Niimura, Nobuo
Nihon Kessho Gakkai-Shi, 46(3), p.193 - 200, 2004/05
Neutron diffraction provides an experimental method of directly locating hydrogen atoms in proteins and nucleic acids, and the development of the neutron imaging plate (NIP) became a breakthrough event in neutron protein crystallography. A high-resolution neutron diffractometers dedicated to biological macromolecules (BIX-3, BIX-4) with the NIP have been constructed at Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute. The detailed structure of the diffractometer and the systematic procedure of the neutron diffraction experiment from the crystallization of a large single crystal to the data collection and the data processing, and the future prospect of the neutron diffractometry in proteins will be presented.
Niimura, Nobuo; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tanaka, Ichiro
Kagaku, 59(2), p.46 - 47, 2004/02
no abstracts in English
Tanaka, Ichiro; Kurihara, Kazuo; Chatake, Toshiyuki; Niimura, Nobuo
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 35(Part1), p.34 - 40, 2002/02
A high performance neutron diffractometer for biological crystallography (BIX-3) has been constructed at JRR-3M in Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) in order to determine the hydrogen positions in biological macromolecules. It uses several recent technical innovations, such as a neutron imaging plate and an elastically bent silicon monochromator developed by the authors. These have made it possible to realize a compact vertical arrangement of the diffractometer. Diffraction data have been collected from the proteins rubredoxin and myoglobin in about one month, to a resolution of 1.5 , good enough to identify the hydrogen atoms with high accuracy. By adopting a crystal-step scan method for measuring Bragg diffraction intensities, the signal to noise ratio was much better than that of the Laue method. This shows that BIX-3 is one of the best-performing machines for neutron protein crystallography in the world currently.
, good enough to identify the hydrogen atoms with high accuracy. By adopting a crystal-step scan method for measuring Bragg diffraction intensities, the signal to noise ratio was much better than that of the Laue method. This shows that BIX-3 is one of the best-performing machines for neutron protein crystallography in the world currently.
Niimura, Nobuo
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 70(Suppl.A), p.396 - 399, 2001/05
no abstracts in English
JAERI-M 85-112, 67 Pages, 1985/08
no abstracts in English
; ;
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 17(SUPPL.B-2), p.354 - 358, 1962/00
no abstracts in English
Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Mao, W.; Ito, Tatsuya; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Mao, W.; Ito, Tatsuya
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Ohara, Takashi; Hosoya, Takaaki; Sakasai, Kaoru
no journal, ,
Detector performances of large area two-dimensional neutron detectors produced for upgrade of SENJU diffractometer at Materials and Life science experimental Facility at J-PARC have been evaluated. The detectors are developed based on a  Li:ZnS(Ag) scintillator and wavelength-shifting fiber technology. The prototype detector has a neutron-sensitive area of 512
Li:ZnS(Ag) scintillator and wavelength-shifting fiber technology. The prototype detector has a neutron-sensitive area of 512  768 mm, which is six-fold of the original detector installed in the SENJU. The prototype detector exhibited a detection efficiency of 40-50% for 2-
768 mm, which is six-fold of the original detector installed in the SENJU. The prototype detector exhibited a detection efficiency of 40-50% for 2- space neutrons and
space neutrons and  Co gamma-ray sensitivity of ~10
Co gamma-ray sensitivity of ~10 . 9 detector modules have been produced for the planned SENJU upgrade. The produced detectors exhibited similar detector efficiencies and gamma-ray sensitivities to that of the prototype detector. Neutron counts of these detectors with a
. 9 detector modules have been produced for the planned SENJU upgrade. The produced detectors exhibited similar detector efficiencies and gamma-ray sensitivities to that of the prototype detector. Neutron counts of these detectors with a  Cf source varied within 5% to the average. The experimental results of the prototype and the produced beamline detectors are presented.
Cf source varied within 5% to the average. The experimental results of the prototype and the produced beamline detectors are presented.
Kurihara, Kazuo*; Tamura, Itaru; Hirano, Yu*; Hiromoto, Takeshi*; Kono, Fumiaki*; Tamada, Taro*
no journal, ,