Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Teshigawara, Makoto; Ikeda, Yujiro*; Muramatsu, Kazuo*; Sutani, Koichi*; Fukuzumi, Masafumi*; Noda, Yohei*; Koizumi, Satoshi*; Saruta, Koichi; Otake, Yoshie*
Journal of Neutron Research, 26(2-3), p.69 - 74, 2024/09
Slow neutrons, such as cold neutrons, are important non-destructive probes not only for basic physics but also for the structural genomics advancements in the life sciences and the battery technology advancements needed for the transition to a hydrogen society. Neutron-based science is also known as high-neutron-intensity-dependent science. A new unique method focusing on nanosized particle aggregation has been proposed to increase neutron intensity in that energy region. The method is based on intensity enhancement by multiple coherent scatterings with nanosized particle aggregation. The aggregation of nanosized particles matches the wavelength of below cold neutrons, causing a similar effect to coherent scattering, so-called Bragg scattering, leading to neutron intensity enhancement by several orders of magnitude. Nanodiamonds and magnesium hydride have recently been studied numerically and experimentally. The major challenge with nanodiamonds in practical applications is the molding method. Another carbon structure, graphene is focused on to find a solution to this problem. It is hypothesized that nanosized graphene could aid coherent neutron scattering under particle size conditions similar to nanodiamonds. We report the potential of nanosized graphene as a reflector material below cold neutrons, together with experimental results.
 -odd/
-odd/ -odd interactions on the 0.75 eV
-odd interactions on the 0.75 eV  -wave resonance in
-wave resonance in 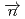 +
+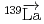 forward transmission determined using a pulsed neutron beam
forward transmission determined using a pulsed neutron beamNakabe, Rintaro*; Auton, C. J.*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Gudkov, V.*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ide, Ikuo*; Ino, Takashi*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Kambara, Wataru*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(4), p.L041602_1 - L041602_4, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.37(Physics, Nuclear) -wave resonance of
-wave resonance of 
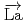 +
+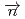
Okudaira, Takuya*; Nakabe, Rintaro*; Auton, C. J.*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Gudkov, V.*; Ide, Ikuo*; Ino, Takashi*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Kambara, Wataru*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(4), p.044606_1 - 044606_9, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:58.98(Physics, Nuclear)Rodriguez, D. C.; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Rossi, F.; Takahashi, Tone
Proceedings of 2022 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium, Medical Imaging Conference and Room Temperature Semiconductor Detector Conference (2022 IEEE NSS MIC RTSD) (Internet), 3 Pages, 2022/12
 Cf irradiator for delayed gamma-ray spectroscopy applications
Cf irradiator for delayed gamma-ray spectroscopy applicationsTohamy, M.*; Abbas, K.*; Nonneman, S.*; Rodriguez, D. C.; Rossi, F.
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 173, p.109694_1 - 109694_7, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:44.62(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Rodriguez, D. C.; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Rossi, F.; Seya, Michio; Takahashi, Tone; Bogucarska, T.*; Crochemore, J.-M.*; Pedersen, B.*; Takamine, Jun
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(8), p.975 - 988, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.75(Nuclear Science & Technology)Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Kyushu University*
JAEA-Review 2019-039, 104 Pages, 2020/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Center of World Intelligence Project for Nuclear Science/Technology and Human Resource Development (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2018. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Research and Development of Transparent Materials for Radiation Shield using Nanoparticles". The present study aims to reduce radiation exposure of workers in debris retrieval/analysis and reduce deterioration of optical and electronic systems in remote cameras. For these purposes, we develop transparent radiation shield by making the shield materials into nanoparticles, and dispersing/solidifying them in epoxy resin. By making B C and W into nanoparticles, we will also develop a radiation shield that shields both neutrons and gamma-rays, and also suppresses secondary gamma-rays produced from neutrons.
C and W into nanoparticles, we will also develop a radiation shield that shields both neutrons and gamma-rays, and also suppresses secondary gamma-rays produced from neutrons.
Katano, Ryota; Yamanaka, Masao*; Pyeon, C. H.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(2), p.169 - 176, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.79(Nuclear Science & Technology)We proposed the linear combination method as a subcriticality measurement method which estimates the prompt neutron decay constant ( ) correlated with the subcriticality using measurement results obtained at multiple detector positions. In the previous study, we confirmed applicability of the linear combination method through the pulsed neutron experiment with DT neutron source at Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA). In this study, we conduct the pulsed neutron source experiment with spallation neutrons at KUCA and confirm the robustness of the linear combination to neutron sources.
) correlated with the subcriticality using measurement results obtained at multiple detector positions. In the previous study, we confirmed applicability of the linear combination method through the pulsed neutron experiment with DT neutron source at Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA). In this study, we conduct the pulsed neutron source experiment with spallation neutrons at KUCA and confirm the robustness of the linear combination to neutron sources.
Pyeon, C. H.*; Talamo, A.*; Fukushima, Masahiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(2), p.133 - 135, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:96.05(Nuclear Science & Technology)Hayashi, Koichi*; Oyama, Kenji*; Happo, Naohisa*; Matsushita, Tomohiro*; Hosokawa, Shinya*; Harada, Masahide; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Shishido, Toetsu*; Yubuta, Kunio*
Science Advances (Internet), 3(8), p.e1700294_1 - e1700294_7, 2017/08
Faenov, A.*; Matsubayashi, Masahito; Pikuz, T.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Kando, Masaki; Yasuda, Ryo; Iikura, Hiroshi; Nojima, Takehiro; Sakai, Takuro; Shiozawa, Masahiro*; et al.
High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 3, p.e27_1 - e27_9, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:46.12(Optics) Tc from molten
Tc from molten  MoO
MoO samples by repeated milking tests
samples by repeated milking testsNagai, Yasuki; Kawabata, Masako; Sato, Nozomi; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Saeki, Hideya; Motoishi, Shoji*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 83(8), p.083201_1 - 083201_4, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:59.90(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Np,
Np,  Am and
Am and  Am
AmNakagawa, Tsuneo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 42(11), p.984 - 993, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:51.41(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Saegusa, Jun; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Yoshizawa, Michio; Yoshida, Makoto
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 110(1-4), p.91 - 95, 2004/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:28.48(Environmental Sciences)For the accurate estimation of neutron dose equivalents, it is important to calibrate dosemeters in the field whose energy spectrum is similar to that in the workplace. For the purpose, studies are made toward the built of the spectrum changeable neutron calibration fields with the Van-de-Graff accelerator in the FRS in JAERI. The fields are produced by bombarding proton or deuteron beam from the accelerator to suitable targets surrounded by quasi-cylindrical moderators and absorbers of various materials. In the fields, neutron spectra with wide range energy index should be provided with sufficient fluence rate for the calibration of dosemeters. The objectives and conceptual design of the fields are discussed here, followed by the test simulation results of neutron spectra produced by various arrangements of a target and moderators.
Fusion Neutron Laboratory
JAERI-Review 2004-017, 163 Pages, 2004/07
no abstracts in English
Haruyama, Mitsuo; Takase, Misao*; Tobita, Hiroshi; Mori, Takamasa
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 3(2), p.185 - 192, 2004/06
no abstracts in English
Shiroya, Seiji*; Misawa, Tsuyoshi*; Unesaki, Hironobu*; Ichihara, Chihiro*; Kobayashi, Keiji*; Nakamura, Hiroshi*; Shin, Kazuo*; Imanishi, Nobutsugu*; Kanazawa, Satoshi*; Mori, Takamasa
JAERI-Tech 2004-025, 93 Pages, 2004/03
In view of the future plan of Research Reactor Institute, Kyoto University, the present study consisted of (1) the transmission experiments of high energy neutrons through materials, (2) experimental simulation of ADSR using the Kyoto University Critical Assembly(KUCA), and (3) conceptual neutronics design study on KUR type ADSR using the MCNP-X code. Through the present study, valuable knowledge on the basic nuclear characteristics of ADSR, which is indispensable to promote the study on ADSR, was obtained both theoretically and experimentally. For the realization of ADSR, it is considered to be necessary to accumulate results of research steadily. For this purpose, it is inevitable (1) to compile the more precise nuclear data for the wide energy range, (2) to establish experimental techniques for reactor physics study on ADSR including subcriticality measurement and absolute neutron flux measurement, and (3) to develop neutronics calculation tools which take into account the neutron generation process by the spallation reaction and the delayed neutron behavior.
Verzilov, Y. M.; Ochiai, Kentaro; Sato, Satoshi; Wada, Masayuki*; Yamauchi, Michinori*; Nishitani, Takeo
JAERI-Research 2004-005, 30 Pages, 2004/03
no abstracts in English
Verzilov, Y. M.; Ochiai, Kentaro; Nishitani, Takeo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.395 - 398, 2004/03
no abstracts in English
Verzilov, Y. M.; Ochiai, Kentaro; Nishitani, Takeo
JAERI-Research 2003-019, 25 Pages, 2003/09
no abstracts in English