Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Li, L.*; Miyamoto, Goro*; Zhang, Y.*; Li, M.*; Morooka, Satoshi; Oikawa, Katsunari*; Tomota, Yo*; Furuhara, Tadashi*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 184, p.221 - 234, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:52.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Maamoun, I.; Rushdi, M.*; Falyouna, O.*; Eljamal, R.*; Eljamal, O.*
Separation and Purification Technology, 308, p.122863_1 - 122863_16, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:44.82(Engineering, Chemical)Saito, Hiroyuki*; Machida, Akihiko*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Sato, Toyoto*; Orimo, Shinichi*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 587, p.412153_1 - 412153_6, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:24.90(Physics, Condensed Matter)The site occupancy of deuterium (D) atoms in face-centered-cubic nickel (fcc Ni) was measured along a cooling path from 1073 to 300 K at an initial pressure of 3.36 GPa via in situ neutron powder diffraction. Deuterium atoms predominantly occupy the octahedral (O) sites and slightly occupy the tetrahedral (T) sites of the fcc metal lattice. The O-site occupancy increases from 0.4 to 0.85 as the temperature is lowered from 1073 to 300 K. Meanwhile, the T-site occupancy remains c.a. 0.02. The temperature-independent behavior of the T-site occupancy is unusual, and its process is not yet understood. From the linear relation between the expanded lattice volume and D content, a D-induced volume expansion of 2.09(13) 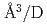 atom was obtained. This value is in agreement with the values of 2.14-2.2
atom was obtained. This value is in agreement with the values of 2.14-2.2 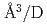 atom previously reported for Ni and Ni
atom previously reported for Ni and Ni Fe
Fe alloy.
alloy.
Watanabe, Masashi*; Yonezawa, Toshio*; Shobu, Takahisa; Shiro, Ayumi; Shoji, Tetsuo*
Corrosion, 72(9), p.1155 - 1169, 2016/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.62(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)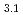 (OCOCH
(OCOCH )
)
 0.9H
0.9H O
OKozai, Naofumi; Mitamura, Hisayoshi; Fukuyama, Hiroyasu; Esaka, Fumitaka; Komarneni, S.*
Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 89(1-3), p.123 - 131, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:40.65(Chemistry, Applied)Layered transition metal hydroxide salt (LTMHS) is a group of anion-exchangeable layered compounds. Although LTMHSs have recentely attracted attention of researches on anion exchange and intercalation, very limited numbers of reports have been published on their synthesis, characteristics, and applications. This paper describes basic characteristics of a new LTMHS, nickel-copper hydroxide acetate. Hydrothermal Heating of an aqueous solution containing nickel acetate, copper acetate, and hydrogen peroxide to 150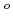 C for 4h yielded a layered compound with an analytical composition of NiCu(OH)
C for 4h yielded a layered compound with an analytical composition of NiCu(OH)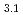 (OCOCH
(OCOCH )
) 0.9H
0.9H O. This compound does not take up Cl
O. This compound does not take up Cl and NO
and NO
 in aqueous solution but takes up multivalent anions and shows high selectivity in uptake of toxic SeO
in aqueous solution but takes up multivalent anions and shows high selectivity in uptake of toxic SeO
 and AsO
and AsO
 . This compound may find applicarion in the removal of those toxic anions form natural water and wastewater rich in Cl
. This compound may find applicarion in the removal of those toxic anions form natural water and wastewater rich in Cl and NO
and NO
 .
.
Imai, Makoto*; Shirai, Toshizo*; Saito, Manabu*; Haruyama, Yoichi*; Ito, Akio*; Imanishi, Nobutsugu*; Fukuzawa, Fumio*; Kubo, Hirotaka
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.7, p.323 - 326, 2006/00
no abstracts in English
Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Takano, Masahide; Ito, Akinori; Akabori, Mitsuo; Minato, Kazuo; Kizaki, Minoru
JAERI-Tech 2005-051, 13 Pages, 2005/09
An apparatus has been developed to measure the thermal diffusivities of minor actinide (MA) compounds. By installing the laser flash apparatus in a glove box with highly purified inert gas atmosphere, the thermal diffusivities measurement of MA compounds of  -decay nuclides was enabled. A new sample holder has been also developed to measure the thermal diffusivities of very small samples. The performance of this new apparatus was confirmed by measuring the thermal diffusivities of small samples of tantalum, nickel and cerium oxides. The thermal diffusivity values obtained in this work agreed well with the literature values and the values measured by a conventional thermal diffusivities measurement apparatus. Accordingly, this apparatus was found to be useful for thermal diffusivities measurement of MA compounds.
-decay nuclides was enabled. A new sample holder has been also developed to measure the thermal diffusivities of very small samples. The performance of this new apparatus was confirmed by measuring the thermal diffusivities of small samples of tantalum, nickel and cerium oxides. The thermal diffusivity values obtained in this work agreed well with the literature values and the values measured by a conventional thermal diffusivities measurement apparatus. Accordingly, this apparatus was found to be useful for thermal diffusivities measurement of MA compounds.
Konishi, Hiroyuki; Yamashita, Masato*; Uchida, Hitoshi*; Mizuki, Junichiro
Proceedings of 16th International Corrosion Congress (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/09
XANES measurements of rust layers formed on Fe, Fe-Cr alloys and Fe-Ni alloys exposed to a Cl-rich atmosphere have been performed using synchrotron radiation in order to clarify the relation between the structural properties of the rust layer on weathering steel and anticorrosive alloying elements and/or chloride ions. The XANES spectra around Cl K-edge revealed that the rust layer on the Fe-based binary alloys contains unidentified chloride in addition to akagan iteite. The Fe K-edge XANES results indicated that the rust layers are composed mainly of well-known iron oxides, goethite, akagan
iteite. The Fe K-edge XANES results indicated that the rust layers are composed mainly of well-known iron oxides, goethite, akagan ite, lepidocrocite and magnetite. In particular, the mole ratio of akagan
ite, lepidocrocite and magnetite. In particular, the mole ratio of akagan ite in the rust layers on the Fe-Ni alloys is relatively higher than that of the Fe-Cr alloys. The Cr K-edge XANES spectra of the rust layers on the Fe-Cr alloys depends on the Cr alloy content. Therefore, the local structure of Cr in the rust layer is variable with the Cr density. In contrast, the Ni K-edge XANES results show that the local structure of Ni in the rust layer are unique in a certain Ni content range.
ite in the rust layers on the Fe-Ni alloys is relatively higher than that of the Fe-Cr alloys. The Cr K-edge XANES spectra of the rust layers on the Fe-Cr alloys depends on the Cr alloy content. Therefore, the local structure of Cr in the rust layer is variable with the Cr density. In contrast, the Ni K-edge XANES results show that the local structure of Ni in the rust layer are unique in a certain Ni content range.
Konishi, Hiroyuki; Yamashita, Masato*; Uchida, Hitoshi*; Mizuki, Junichiro
Materials Transactions, 46(2), p.329 - 336, 2005/02
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:81.21(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Chloride in atmosphere considerably reduces the corrosion resistance of conventional weathering steel containing a small amount of Cr. Ni is an effective anticorrosive element for improving the corrosion resistance of steel in a Cl-rich environment. In order to clarify the structure of the protective rust layer of weathering steel, Cl and Fe K-edge X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) spectra of atmospheric corrosion products (rust) formed on Fe, Fe-Ni and Fe-Cr alloys exposed to Cl-rich atmosphere were measured. The Fe K-XANES measurements enable the characterization of a mixture of iron oxides such as rust. The chemical composition of the rust was determined by performing pattern fitting of the measured spectra. All the rust is composed mainly of goethite, akagan ite, lepidocrocite and magnetite. Among these iron oxides, akagan
ite, lepidocrocite and magnetite. Among these iron oxides, akagan ite in particular is the major component in the rust. Additionally, the amount of akagan
ite in particular is the major component in the rust. Additionally, the amount of akagan ite in the rust of Fe-Ni alloy is much greater than that in rust of Fe-Cr alloy. Akagan
ite in the rust of Fe-Ni alloy is much greater than that in rust of Fe-Cr alloy. Akagan ite is generally considered to facilitate the corrosion of steel, but our results indicate that akagan
ite is generally considered to facilitate the corrosion of steel, but our results indicate that akagan ite in the rust of Fe-Ni alloy is quantitatively different from that in rust of Fe-Cr alloy and does not facilitate the corrosion of steel. The shoulder peak observed in Cl K-XANES spectra reveals that the rust contains a chloride other than akagan
ite in the rust of Fe-Ni alloy is quantitatively different from that in rust of Fe-Cr alloy and does not facilitate the corrosion of steel. The shoulder peak observed in Cl K-XANES spectra reveals that the rust contains a chloride other than akagan ite. The energy of the shoulder peak does not correspond to that of any well-known chlorides. In the measured spectra, there is no proof that Cl, by combining with the alloying element, inhibits the alloying element from acting in corrosion resistance. The shoulder peak appears only when the content of the alloying element is lower than a certain value. This suggests that the generation of the unidentified chloride is related to the corrosion rate of steel.
ite. The energy of the shoulder peak does not correspond to that of any well-known chlorides. In the measured spectra, there is no proof that Cl, by combining with the alloying element, inhibits the alloying element from acting in corrosion resistance. The shoulder peak appears only when the content of the alloying element is lower than a certain value. This suggests that the generation of the unidentified chloride is related to the corrosion rate of steel.
Konishi, Hiroyuki; Yamashita, Masato*; Uchida, Hitoshi*; Mizuki, Junichiro
Materials Transactions, 45(12), p.3356 - 3359, 2004/12
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:52.31(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Cl K-edge XANES measurements of atmospheric corrosion products (rust) formed on Fe, Fe-Ni and Fe-Cr alloys in chloride pollution have been performed using synchrotron radiation in order to clarify roles of anticorrosive alloying elements and of Cl in the corrosion resistance of weathering steel. The spectra of binary alloys show a shoulder structure near the absorption edge. The intensity of the shoulder peak depends on the kind and amount of the alloying element, whereas the energy position is invariant. This indicates that Cl is not combined directly with alloying elements in the rust.
Matsubayashi, Masahito; Katagiri, Masaki
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 529(1-3), p.389 - 393, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.84(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Hirofumi; Nishi, Masataka; Sugisaki, Masayasu*
JAERI-Research 2003-018, 32 Pages, 2003/09
Tritium transport behavior in materials, which is essential for the safety evaluation of the fusion reactor, has to be evaluated by either tritium properties or extrapolated value from protium or deuterium (D) to tritium (T) using the isotope effect theory. However, there are still some uncertainties on estimation of T behavior in materials, because there are only a few T transport properties data in materials, and it is not completely proven the application of the isotope effect theory to T due to the lack of T data. Therefore, in order to understand the tritium transport properties in materials, isotope effects on diffusion and surface recombination between T and D in/on nickel, whose hydrogen transport properties were well known, were investigated by comparing the obtained properties of T with those of D measured under the same conditions with the ion driven permeation method. Though obtained diffusion coefficient of T was larger than that of D, and activation energy of diffusion of T was smaller than that of D as the contrary to the classical diffusion theory, those were shown to be explained with a modified diffusion theory by introducing higher vibration temperatures in nickel than previous reported values. In addition, the isotope effect on surface recombination coefficient between D and T was shown to be explained using a modified solution model as well as diffusion.
 melt containing K
melt containing K TaF
TaF ; Electrochemical study
; Electrochemical studyMehmood, M.*; Kawaguchi, Nobuaki*; Maekawa, Hideki*; Sato, Yuzuru*; Yamamura, Tsutomu*; Kawai, Masayoshi*; Kikuchi, Kenji
Materials Transactions, 44(2), p.259 - 267, 2003/02
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:51.20(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Electrochemical study has been carried out on the electro-deposition of tantalum in LiF-NaF-CaF melt containing K
melt containing K TaF
TaF at 700
at 700 C. This has been done for determining the mechanistic features for preparing electrolytic coating of tantalum on nickel and tungsten substrates. Electro-deposition of metallic tantalum occurs primarily by electro-reduction of Ta(V). Pure metallic tantalum without any entrapped salt is successfully deposited on tungsten by galvanostatic polarization at reasonably low current densities. An additional feature on nickel is the formation of an intermetallic compound at potential 0.25V nobler than that of pure tantalum as a result of underpotential deposition of tantalum. This intermetallic compound covers the surface within a short time followed by deposition of pure tantalum, although intermetallic compound keeps growing at the interface of pure tantalum deposit and the substrate as a result of diffusion.
C. This has been done for determining the mechanistic features for preparing electrolytic coating of tantalum on nickel and tungsten substrates. Electro-deposition of metallic tantalum occurs primarily by electro-reduction of Ta(V). Pure metallic tantalum without any entrapped salt is successfully deposited on tungsten by galvanostatic polarization at reasonably low current densities. An additional feature on nickel is the formation of an intermetallic compound at potential 0.25V nobler than that of pure tantalum as a result of underpotential deposition of tantalum. This intermetallic compound covers the surface within a short time followed by deposition of pure tantalum, although intermetallic compound keeps growing at the interface of pure tantalum deposit and the substrate as a result of diffusion.
Konno, Chikara; Fischer, U.*; Perel, R.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(Suppl.2), p.1045 - 1048, 2002/08
no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Hirofumi; Hayashi, Takumi; Kakuta, Toshiya*; Suzuki, Takumi; Nishi, Masataka
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 297(3), p.285 - 291, 2001/09
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:78.30(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The isotope effect on the implantation-driven permeation of pure tritium (T) and deuterium (D) through nickel was investigated, respectively. The rate-determining processes of backward flow at the upstream surface and permeation at the down-stream surface were found to be as follows: recombination on up-stream surface and diffusion at down-stream side in a lower temperature region, whereas recombination on both surfaces in a higher temperature region for T and D, respectively. The diffusion coefficients of T and D derived by analyzing the obtained transient data of permeation in the lower temperature region were in good agreement with literature data of deuterium. The obtained activation energy of diffusion for T and D suggested the tendency of mass dependence. The surface recombination coefficients for both isotopes were also derived and showed in good agreement with literature data. As a result, the experimental results indicated the surface recombination could be attributed to the isotope effect of the permeation between T and D rather than the diffusion.
 ion implanted SUS304 stainless steel by in situ SR-XPS and ex situ scanning tunnelling microscope
ion implanted SUS304 stainless steel by in situ SR-XPS and ex situ scanning tunnelling microscopeLi, Y.; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro
Corrosion Science, 43(5), p.903 - 917, 2001/05
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:63.17(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 XPS using synchrotron radiation
XPS using synchrotron radiationLi, Y.; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro
Journal of Materials Science, 35(24), p.6123 - 6130, 2000/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:21.17(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Nagao, Yoshiharu; Shimakawa, Satoshi; ;
JAERI-Tech 95-006, 46 Pages, 1995/02
no abstracts in English
; Watanabe, Kazuo
Bunseki Kagaku, 42, p.T43 - T47, 1993/00
no abstracts in English
Nagasaki, Takanori; ; Ono, Hideo
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 191-194, p.258 - 262, 1992/00
no abstracts in English