Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 dissolution in bicarbonate solution with H
dissolution in bicarbonate solution with H O
O ; The Effect of temperature
; The Effect of temperatureMcGrady, J.; Kumagai, Yuta; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Kirishima, Akira*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Watanabe, Masayuki
RSC Advances (Internet), 13(40), p.28021 - 28029, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.35(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Upon nuclear waste canister failure and contact of spent nuclear fuel with groundwater, the UO matrix of spent fuel will interact with oxidants in the groundwater generated by water radiolysis. Bicarbonate (HCO
matrix of spent fuel will interact with oxidants in the groundwater generated by water radiolysis. Bicarbonate (HCO
 ) is often found in groundwater, and the H
) is often found in groundwater, and the H O
O induced oxidative dissolution of UO
induced oxidative dissolution of UO in bicarbonate solution has previously been studied under various conditions. Temperatures in the repository at the time of canister failure will differ depending on the location, yet the effect of temperature on oxidative dissolution is unknown. To investigate, the decomposition rate of H
in bicarbonate solution has previously been studied under various conditions. Temperatures in the repository at the time of canister failure will differ depending on the location, yet the effect of temperature on oxidative dissolution is unknown. To investigate, the decomposition rate of H O
O at the UO
at the UO surface and dissolution of U
surface and dissolution of U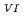 in bicarbonate solution (0.1, 1, 10 and 50 mM) was analysed at various temperatures (10, 25, 45 and 60
in bicarbonate solution (0.1, 1, 10 and 50 mM) was analysed at various temperatures (10, 25, 45 and 60  C). At [HCO
C). At [HCO
 ]
] 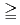 1 mM, the apparent equilibrium concentration of U
1 mM, the apparent equilibrium concentration of U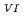 decreased with increasing temperature. This was attributed to the formation of U
decreased with increasing temperature. This was attributed to the formation of U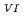 -bicarbonate species at the surface and a change in the mechanism of H
-bicarbonate species at the surface and a change in the mechanism of H O
O decomposition from oxidative to catalytic. At 0.1 mM, no obvious correlation between temperature and U dissolution was observed, and thermodynamic calculations indicated this was due to a change in the surface species. A pathway to explain the observed dissolution behaviour of UO
decomposition from oxidative to catalytic. At 0.1 mM, no obvious correlation between temperature and U dissolution was observed, and thermodynamic calculations indicated this was due to a change in the surface species. A pathway to explain the observed dissolution behaviour of UO in bicarbonate solution as a function of temperature was proposed.
in bicarbonate solution as a function of temperature was proposed.
 O
O decomposition at the U
decomposition at the U O
O surface in bicarbonate solution
surface in bicarbonate solutionMcGrady, J.; Kumagai, Yuta; Watanabe, Masayuki; Kirishima, Akira*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kitamura, Akira; Kimuro, Shingo
RSC Advances (Internet), 11(46), p.28940 - 28948, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:24.90(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Irisawa, Eriko; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Kato, Chiaki; Motooka, Takafumi; Ban, Yasutoshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(4), p.337 - 344, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:58.28(Nuclear Science & Technology)Iwai, Yasunori
Fusion Engineering and Design, 98-99, p.1796 - 1799, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.21(Nuclear Science & Technology)Hydrophobic platinum catalysts have been widely applied in the field of nuclear fusion for the exchange reactions of hydrogen isotopes between hydrogen and vapor in the water detritiation system, and for the oxidation of tritium on the atmospheric detritiation system. Hydrophobic platinum catalysts are hardly susceptible to water mist and water vapor. Hydrophobic platinum catalysts are produced by supporting platinum directly on hydrophobic polymer beads. For the hydrophobic polymer, styrene - divinyl benzene (SDB) has been applied in Japan. It can be pointed out that the upgrade in catalytic activity of hydrophobic catalyst is expected to downsize the catalytic reactor based on a hard look at a large increase in flow rate in future. The upgrade in catalytic activity of two types of commercial Pt/SDB catalysts was found when they were irradiated with electron beams. After irradiation with electron beams, the catalytic activity was evaluated by means of overall reaction rate constant for the oxidation of tritium. The overall reaction rate constant increased as increase in dose. The constant showed the peak value in the dose between 500 to 1000 kGy. After the peak, the constant decreased as increase in dose. The overall reaction rate constant at the peak was 6 times larger than that evaluated with unirradiated. The mechanical strength of irradiated Pt/SDB kept sound until 1500 kGy. The irradiation is a promising method to the upgrading in catalytic activity of Pt/SDB catalyst.
Yuasa, Kanako; Enomoto, Kazuyuki*; Maekawa, Yasunari; Kato, Jun*; Yamashita, Takashi*; Yoshida, Masaru
Journal of Photopolymer Science and Technology, 17(1), p.21 - 28, 2004/07
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:30.50(Polymer Science)The electron beam (EB)-induced reactions of arylsulfonic acid esters, phenyl p-toluenesulfonate (1a), phenyl benzenesulfonate (1b), and phenyl 1-naphthalenesulfonate (1c), were examined in the balk state. The EB irradiation of 1a afforded the Fries rearrangement products, o- and p-hydroxyphenyl p-tolylsulfones (2a and 3a), phenol (5), and the oxidation product of 2a, o,p-dihydroxyphenyl p-tolylsulfone (4a), which has not been observed in photolysis. The irradiation of 1b, which is liquid at room temperature, gave Fries products, 5, and the oxidation product, o,p-dihydroxyphenyl phenylsulfone. On the other hand, the EB-induced reaction of 1c proceeded with the lowest reactivity through crystal to crystal transformation to afford Fries products and 5, but not oxidation product. The mechanistic study reveals that oxidation product 4a generated by the oxidation reaction of ortho-Fries product 2a but not para-isomer 3a with an active oxidant, which should result from the decomposition of 1a.
 molecular beam
molecular beamOkada, Michio*; Moritani, Kosuke; Goto, Seishiro*; Kasai, Toshio*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden
Journal of Chemical Physics, 119(14), p.6994 - 6997, 2003/10
Times Cited Count:42 Percentile:77.62(Chemistry, Physical)The oxidation of Cu(001) with hyperthermal O molecular beams was investigated using X-ray photoemission spectroscopy in conjunction with a synchrotron light source. The efficiency of oxidation is higher than that with ambient thermal O
molecular beams was investigated using X-ray photoemission spectroscopy in conjunction with a synchrotron light source. The efficiency of oxidation is higher than that with ambient thermal O . Further oxidation under oxygen coverage larger than 0.5 ML occurs rather inefficiently even for the 2.3 eV beam irradiation. We found such slow oxidation of Cu corresponding to the initial stage of the Cu
. Further oxidation under oxygen coverage larger than 0.5 ML occurs rather inefficiently even for the 2.3 eV beam irradiation. We found such slow oxidation of Cu corresponding to the initial stage of the Cu O formation can be interpreted in terms of a collision-induced-adsorption mechanism. The kinetics of the dissociative adsorption is well described using the first order kinetics in a simple Langmuir-type adsorption model.
O formation can be interpreted in terms of a collision-induced-adsorption mechanism. The kinetics of the dissociative adsorption is well described using the first order kinetics in a simple Langmuir-type adsorption model.
 molecular beams under 1000 K
molecular beams under 1000 KTeraoka, Yuden; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Moritani, Kosuke
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 42(7B), p.4671 - 4675, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:19.83(Physics, Applied)The oxidation reaction mechanisms for Si(001) by O molecules have been investigated in a surface temperature region from 860 K to 1300 K and in an incident energy region from 0.6 eV to 3.0 eV. Synchrotron Radiation photoemission spectroscopy was used for surface analysis. Si-2p photoemission spectra were measured during molecular beam irradiation so that their dependences on surface temperature and incident energy were clarified. SiO molecules, desorbed from the surface at high temperature region, were also detected by a quadrupole mass analyzer using
molecules have been investigated in a surface temperature region from 860 K to 1300 K and in an incident energy region from 0.6 eV to 3.0 eV. Synchrotron Radiation photoemission spectroscopy was used for surface analysis. Si-2p photoemission spectra were measured during molecular beam irradiation so that their dependences on surface temperature and incident energy were clarified. SiO molecules, desorbed from the surface at high temperature region, were also detected by a quadrupole mass analyzer using  O
O molecular beams to measure SiO desorption yield depending on surface temperature and incident energy. Consequently, a reaction scheme, oxide layers formation, etching, and coexistence of both reactions, is determined by the incident energy under 1000 K.
molecular beams to measure SiO desorption yield depending on surface temperature and incident energy. Consequently, a reaction scheme, oxide layers formation, etching, and coexistence of both reactions, is determined by the incident energy under 1000 K.
Kida, Takashi; Umeda, Miki; Sugikawa, Susumu
JAERI-Data/Code 2003-001, 29 Pages, 2003/03
MOX dissolution using silver-mediated electrochemical method will be employed for the preparation of plutonium nitrate solution in the criticality safety experiments in NUCEF. A simulation code for the MOX dissolution has been developed for the operating support. In this report an outline of the simulation code is proposed and a comparison with the experimental data and a parameter study on the MOX dissolution rate are described.The principle of this code is based on Zundelevich's model for PuO dissolution using Ag
dissolution using Ag . The influence of nitrous acid on the material balance of Ag
. The influence of nitrous acid on the material balance of Ag and the surface area of MOX powder on the basis of particle size distribution are taken into consideration in this model. A comparison with experimental data was carried out to confirm a validity of this model. It was confirmed that the behavior of MOX dissolution could adequately be simulated using the appropriate MOX dissolution rate constant. The parameters affecting the dissolution rate were studied, it was found that MOX particle size was major governing factor on the dissolution rate.
and the surface area of MOX powder on the basis of particle size distribution are taken into consideration in this model. A comparison with experimental data was carried out to confirm a validity of this model. It was confirmed that the behavior of MOX dissolution could adequately be simulated using the appropriate MOX dissolution rate constant. The parameters affecting the dissolution rate were studied, it was found that MOX particle size was major governing factor on the dissolution rate.
 molecular beams
molecular beamsTeraoka, Yuden; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Hyomen Kagaku, 23(9), p.553 - 561, 2002/09
no abstracts in English
 analysis using high resolution synchrotron radiation photoemission spectroscopy for initial oxidation of H
analysis using high resolution synchrotron radiation photoemission spectroscopy for initial oxidation of H O pre-adsorbed Si(001) surfaces induced by supersonic O
O pre-adsorbed Si(001) surfaces induced by supersonic O molecular beams at room temperature
molecular beams at room temperatureYoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden
Atomic Collision Research in Japan, No.28, p.105 - 107, 2002/00
The oxidation states up to Si states were formed when the translational kinetic energy of O
states were formed when the translational kinetic energy of O was 3.0 eV. The time evolustions of each Si oxidation states were in situ measured by using the high resolution photoemission spectroscopy.The translational kinetic energy of 3.0eV randomly enhanced the oxidation on Si(001) surface up to the second layer Si backbonds. It was found that the Si
was 3.0 eV. The time evolustions of each Si oxidation states were in situ measured by using the high resolution photoemission spectroscopy.The translational kinetic energy of 3.0eV randomly enhanced the oxidation on Si(001) surface up to the second layer Si backbonds. It was found that the Si was not observed, thus the dimer Si atoms at the top layer was not surrounded by four oxygen atoms at the initial oxidation stage.
was not observed, thus the dimer Si atoms at the top layer was not surrounded by four oxygen atoms at the initial oxidation stage.
 molecular beams
molecular beamsTeraoka, Yuden; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
SPring-8 Research Frontiers 2000/2001, p.48 - 50, 2001/00
no abstracts in English
Fujii, Kimio
JAERI-Research 99-050, 99 Pages, 1999/08
no abstracts in English
; ; ; ; ; ; Kimura, Hideo; Munakata, Masahiro
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 34(4), p.342 - 364, 1992/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:27.12(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
; ; ;
JAERI 1281, 36 Pages, 1982/10
no abstracts in English
 and -water reactions and cladding temperature estimation for rapidly-heated fuel rods under an RIA condition
and -water reactions and cladding temperature estimation for rapidly-heated fuel rods under an RIA condition; ;
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 19(5), p.368 - 383, 1982/05
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:68.45(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
; ; ; ;
JAERI-M 9475, 22 Pages, 1981/05
no abstracts in English
Ikezoe, Yasumasa;
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 51(4), p.1016 - 1019, 1978/04
Times Cited Count:5no abstracts in English
; ; ;
JAERI-M 6601, 26 Pages, 1976/06
no abstracts in English
; Naito, Keiji;
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 4(2), p.111 - 117, 1962/00
no abstracts in English
Serizawa, Hiroyuki; Osawa, Takahito; Oishi, Yuji*; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Kondo, Keietsu; Shohoji, Nobumitsu*; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
no journal, ,
A new reaction model for evaluating the activity of oxygen and hydrogen atoms of H O molecules is proposed. The surprisingly high value of the activity implies that the production process of volatile metal hydroxides might be reconsidered.
O molecules is proposed. The surprisingly high value of the activity implies that the production process of volatile metal hydroxides might be reconsidered.
Kumagai, Yuta; Fidalgo, A. B.*; Jonsson, M.*
no journal, ,
Radiation-induced oxidative dissolution of nuclear fuel is anticipated in the geological repository of spent fuel and after severe accidents, where the fuel would be in direct contact with water. Therefore, understanding of the oxidative dissolution of UO is indispensable to estimate radioactive release. This study has addressed effects of hyperstoichiometry of UO
is indispensable to estimate radioactive release. This study has addressed effects of hyperstoichiometry of UO and adsorption of organic compounds on the process. Comparison between hyperstoichiometric UO
and adsorption of organic compounds on the process. Comparison between hyperstoichiometric UO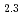 and stoichiometric UO
and stoichiometric UO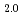 demonstrated that the reactivity of UO
demonstrated that the reactivity of UO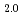 approaches that of UO
approaches that of UO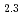 by the H
by the H O
O reaction. The result indicates formation of hyperstoichiometric surface layer during the oxidative dissolution. Phthalic acid, which was used as a model compound, suppressed the U dissolution by
reaction. The result indicates formation of hyperstoichiometric surface layer during the oxidative dissolution. Phthalic acid, which was used as a model compound, suppressed the U dissolution by  -ray irradiation but had little involvement in the H
-ray irradiation but had little involvement in the H O
O reaction, in spite of adsorption exceeding 1 molecule/nm
reaction, in spite of adsorption exceeding 1 molecule/nm . The results suggest an involvement of radical intermediate derived from phthalic acid in the surface reaction.
. The results suggest an involvement of radical intermediate derived from phthalic acid in the surface reaction.