Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 F used as tracer to study water uptake and transport imaging of a cowpea plant
F used as tracer to study water uptake and transport imaging of a cowpea plantNakanishi, Tomoko*; Tanoi, Keitaro*; Yokota, Harumi*; Kang, D.-J.*; Ishii, Ryuichi*; Ishioka, Noriko; Watanabe, Satoshi; Osa, Akihiko; Sekine, Toshiaki; Matsuhashi, Shimpei; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 249(2), p.503 - 507, 2001/08
We present the water uptake ability of cowpea (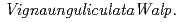 ) which has been regarded as one of the most drought resistant species among the pulse crops. It has been suggested that in the lower part of the stem, parenchymatous tissue for storing water had been developed for the function of deought resistance. We confirmed that in this tissue, water amount was high compared to the other stems by neutron radiography. Then the water uptake manner was measured by positron emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS) using
) which has been regarded as one of the most drought resistant species among the pulse crops. It has been suggested that in the lower part of the stem, parenchymatous tissue for storing water had been developed for the function of deought resistance. We confirmed that in this tissue, water amount was high compared to the other stems by neutron radiography. Then the water uptake manner was measured by positron emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS) using  F labeled water produced by a cyclotron. Comparing the water uptake manner of cowpea plant with that of common bean, cowpea plant was found to maintain high water uptake activity after drying treatment, suggesting the high drought resistant character.
F labeled water produced by a cyclotron. Comparing the water uptake manner of cowpea plant with that of common bean, cowpea plant was found to maintain high water uptake activity after drying treatment, suggesting the high drought resistant character.