Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Li, L.*; Miyamoto, Goro*; Zhang, Y.*; Li, M.*; Morooka, Satoshi; Oikawa, Katsunari*; Tomota, Yo*; Furuhara, Tadashi*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 184, p.221 - 234, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:52.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Maekawa, Fujio
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 98(5), p.201 - 205, 2022/05
The nuclear transmutation technology is a powerful solution to the "nuclear waste" problem that accompanies nuclear power generation. The Accelerator Driven System (ADS), which combines a high-intensity accelerator and a subcritical core, is a promising tool for nuclear transmutation. In this paper, we will explain the significance and principle of nuclear transmutation by ADS, design examples of ADS, partitioning and transmutation technology and its effects, required performance of high-intensity accelerators, overseas trends, etc.
Sasaki, Yuji
Bunri Gijutsu, 52(2), p.103 - 107, 2022/03
We develop all-inclusive partitioning method for actinides and fission products in high-level radioactive waste. This process is based on the sequential solvent extraction. In order to recover Cs and Sr for the management by interim storage, crown ether compounds are employed. For the removal of Pd and Mo due to production of a stable vitrified object, methylimino-dioctylacetamide (MIDOA) is taken as an extractant. DGA can extract both actinides and trivalent lanthanides. In order to separate each other, dietylenetriamine-triacetic-diamide (DTBA) for the stripping reagent of MA. For the mutual separation of Am/Cm, DGA and DOODA extraction system is taken into consideration.
Morita, Yasuji; Fukushima, Masahiro; Kashima, Takao*; Tsubata, Yasuhiro
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-013, 38 Pages, 2020/09
Critical Masses of Cm, Am and the mixture were calculated in metal-water mixtures with water reflector as a basic data for criticality safety assessment of minor actinide separation process. In the mixture of Cm-244 and Cm-245, higher ratio of Cm-245 gives smaller critical mass, but the amount of Cm-245 in the critical mass can be obtained by concentration of Cm-245 in the Cm mixture without depending on the Cm-245 ratio. Critical mass of Cm isotope mixture with 30% Cm-245 was smaller than that of Pu isotope mixture in the practical reprocessing (71% Pu-239 + 17% Pu-240 + 12% Pu-241). When Cm is separated from other element including Am and the solution is concentrated, measure for the critical accident has to be taken. Critical mass of Am-242m is smaller than that of Cm-245, but the ratio of Am-242m in the Am contained in practical spent fuel is small enough, about several percent, and therefore the critical accident by Am does not have to be considered. That by the mixture of Am and Cm does not either.
 CEN and JAEA for Partitioning and Transmutation through Accelerator-Driven System
CEN and JAEA for Partitioning and Transmutation through Accelerator-Driven SystemWorking Group for Collaboration between SCK CEN and JAEA for P&T through ADS
CEN and JAEA for P&T through ADS
JAEA-Review 2017-003, 44 Pages, 2017/03
This technical report reviews Research and Development (R&D) programs for the Partitioning and Transmutation (P&T) technology through Accelerator-Driven System (ADS) at Studiecentrum voor Kernenergie/Centre d'Etude de l' nergie Nucl
nergie Nucl aire (SCK
aire (SCK CEN) and Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The results obtained in the present Collaboration Arrangement between the two organizations for the ADS are also summarized, and possible further collaborations and mutual realizations in the future are sketched.
CEN) and Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The results obtained in the present Collaboration Arrangement between the two organizations for the ADS are also summarized, and possible further collaborations and mutual realizations in the future are sketched.
Suzuki, Hideya; Tsubata, Yasuhiro; Kurosawa, Tatsuya; Shibata, Mitsunobu; Kawasaki, Tomohiro; Urabe, Shunichi*; Matsumura, Tatsuro
Analytical Sciences, 32(4), p.477 - 479, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:71.28(Chemistry, Analytical)An impeccable, high-performance new reagent called alkyl diamide amine (ADAAM) was examined from the viewpoint of mutual separation of Am(III) and Eu(III). ADAAM has three donor atoms, one soft N-donor atom and two hard O-donor atoms, in the central frame. The combination of soft and hard atoms affords a tridentate donor set of atoms that ensures remarkable extractability and selectivity of Am(III) and Eu(III) in highly acidic media.
Sasa, Toshinobu
AAPPS Bulletin, 24(5), p.13 - 17, 2014/10
To reduce the burden of radiological nuclides contained in spent nuclear fuel, Partitioning-Transmutation (P-T) technology is noted as an option for nuclear waste management in the new national strategic energy policy. As for the system for waste transmutation, an accelerator-driven system is desirable as a dedicated transmutor. To perform basic studies for an accelerator-driven system, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency has promoted the design of the Transmutation Experimental Facility within the framework of the J-PARC project. A lead-bismuth spallation target, which is bombarded with 400 MeV - 250 kW protons, and a low-power subcritical reactor will be installed in the facility. Construction will start within a few years after the national review of P-T technology.
Oigawa, Hiroyuki; Yokoo, Takeshi*; Nishihara, Kenji; Morita, Yasuji; Ikeda, Takao*; Takaki, Naoyuki*
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/10
The benefit of implementing Partitioning and Transmutation (P&T) of high-level wastes was parametrically surveyed. The possible reduction of the geological repository area was estimated. By recycling minor actinides (MA), the repository area required for unit spent fuel was reduced significantly in the case of MOX-LWR. This effect was caused by removal of  Am which is a long-term heat source. By partitioning the fission products, in addition to MA recycling, further 70-80% reduction from the MA-recovery case can be expected for both UO
Am which is a long-term heat source. By partitioning the fission products, in addition to MA recycling, further 70-80% reduction from the MA-recovery case can be expected for both UO and MOX. This significant reduction was independent of the cooling time before the partitioning process.
and MOX. This significant reduction was independent of the cooling time before the partitioning process.
Oigawa, Hiroyuki; Minato, Kazuo; Kimura, Takaumi; Morita, Yasuji; Arai, Yasuo; Nakayama, Shinichi; Nishihara, Kenji
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/10
JAERI is engaging in the R&D on the Double-strata Fuel Cycle concept in accordance with the results of the check and review on the Partitioning and Transmutation (PT) technology made by the Atomic Energy Commission of Japan in 2000. As for the partitioning process, after the establishment of the "4-group Partitioning Process Concept", an innovative concept called ARTIST is also being studied. As for the fuel technology, minor actinide nitrides such as NpN and AmN were synthesized and their material properties have been measured. To reprocess the irradiated fuel, the pyrochemical process has been studied. The R&D of the accelerator-driven transmutation system are in progress for an accelerator, lead-bismuth, and a subcritical reactor. In addition, JAERI has started the high-intensity proton accelerator project (J-PARC), which includes the Transmutation Experimental Facility (TEF) as the Phase-II. The impact of PT technology on the backend of the nuclear energy utilization is also being discussed.
Nakayama, Shinichi; Morita, Yasuji; Nishihara, Kenji; Oigawa, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/10
The effects of partitioning-transmutation (PT) technology to waste management was assessed based on the chemical and physical properties and estimated amounts of radioactively contaminated wastes that may be generated in the JAERI's PT cycle. The volume of high-level waste after partitioning was about a third that of non-partitioned vitrified waste form. The required repository area was about sixth, which implies increase in capacity of geologic repositories.
Yamaguchi, Isoo*; Morita, Yasuji; Fujiwara, Takeshi; Yamagishi, Isao
JAERI-Tech 2005-054, 61 Pages, 2005/09
The HLW-79Y-4T type transportation cask for liquid radioactive fuel material (commonly called "Cendrillon") was imported from France and modified for Japanese regulation in order to obtain high-level radioactive liquid waste (HLW) for partitioning tests in JAERI by transportation from Tokai Establishment of Japan Nuclear Fuel Cycle Development Institute. The cask was used for the HLW transportation five times from 1982 to 1990. After that, it was kept and maintained for next transportation of HLW from facilities outside JAERI. Finally, we decided to decompose the cask because HLW can be obtained in JAERI Tokai. For the decomposition, radiation dose and contamination by radioactivity was first measured and then the methods to reduce those levels were determined. The cask was decomposed after the decontamination to separate the part that has high radiation level. The separated part was put in a vessel specially prepared. The present report describes those procedures for the decomposition of the transportation cask.
Morita, Yasuji; Kubota, Masumitsu*
JAERI-Review 2005-041, 35 Pages, 2005/09
Research and development on Partitioning in JAERI are reviewed in the present report from the beginning to the development of the 4-Group Partitioning Process and its test with real high-level liquid waste (HLLW). In the 3-Group Partitioning Process established in around 1980, elements in HLLW are separated into 3 groups of transuranium element group, Sr-Cs group and the other element group. The 4-Group Partitioning Process subsequently developed contains the separation of Tc-platinum group metals additionally. The process was tested to demonstrate its performance with real concentrated HLLW. Until then, various separation methods for various elements were studied and selection and optimization of the separation methods were carried out to establish the process. Review of the experience, findings and results is very important and valuable for future study on partitioning. The present report is prepared from this point of view.
Morita, Yasuji; Asakura, Toshihide; Mineo, Hideaki; Hotoku, Shinobu; Uchiyama, Gunzo
JAERI-Conf 2005-007, p.25 - 30, 2005/08
Researches on process safety of reprocessing, development of an advanced reprocessing and partitioning of high-level liquid waste(HLLW) have been conducted in NUCEF - BECKY (Back-end Fuel Cycle Key Elements Research Facility), which has alpha-gamma concrete cells and many glove-boxes. This paper presents 10 year accomplishment of the above researches and future activities to be conducted in the field of separation process development.
Yamaguchi, Isoo*; Suzuki, Shinichi; Sasaki, Yuji; Yamagishi, Isao; Matsumura, Tatsuro; Kimura, Takaumi
JAERI-Tech 2005-037, 56 Pages, 2005/07
For the development of the reprocessing of spent nuclear fuels, the solvent extraction using the mixer-settler equipment is greatly available. This method has the advantages of the treatment of the large mass of materials and continuous operations. In case of the application of the mixer-settler devise, the precise calculation using the distribution ratio of metals in order to determine the metal concentration at each stage is indispensable. This calculation is performed in the development of ARTIST process. The metal concentration in each stage of ARTIST process is calculated by the simulation using excel software equipped with counter-current equations. This method is not taken into consideration of the change of acid concentration, therefore, we developed the new method to calculate the metal concentration even after acidity change. This method can calculate not only the metal concentration at each extraction step but also at each stage of mixer-settler. Using this calculation, we evaluated the optimum condition of solvent extraction in ARTIST process.
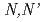 -dimethyl-
-dimethyl-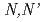 -diphenylpyridine-2,6-dicarboxyamide(DMDPhPDA) from nitric acid solutions
-diphenylpyridine-2,6-dicarboxyamide(DMDPhPDA) from nitric acid solutionsShimada, Asako; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Narita, Hirokazu; Tachimori, Shoichi; Okuno, Kenji*
Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange, 22(2), p.147 - 161, 2004/03
Times Cited Count:68 Percentile:81.34(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The distribution ratios of lanthanides with 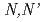 -dimethyl-
-dimethyl-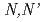 -diphenylpyridine-2,6-dicarboxyamide(DMDPhPDA) from 1-5M nitric acid solutions were determined and the extraction mechanism was discussed on the basis of the slope analyses of acid and ligand concentration dependencies and lanthanide patterns (variation of the distribution ratio as a function of ionic radius). The lanthanide extractions were explained through two mechanisms from the standpoint of the formation of the extracted complex as follows: (1) the formation of inner-sphere complex with two DMDPhPDA molecules for light lanthanides in the extraction from HNO
-diphenylpyridine-2,6-dicarboxyamide(DMDPhPDA) from 1-5M nitric acid solutions were determined and the extraction mechanism was discussed on the basis of the slope analyses of acid and ligand concentration dependencies and lanthanide patterns (variation of the distribution ratio as a function of ionic radius). The lanthanide extractions were explained through two mechanisms from the standpoint of the formation of the extracted complex as follows: (1) the formation of inner-sphere complex with two DMDPhPDA molecules for light lanthanides in the extraction from HNO less than 3M, and (2) the formation of outer-sphere complex with the third DMDPhPDA molecules in addition to the inner-sphere complex in the extraction of light lanthanides from HNO
less than 3M, and (2) the formation of outer-sphere complex with the third DMDPhPDA molecules in addition to the inner-sphere complex in the extraction of light lanthanides from HNO more than 3M, and those of heavy lanthanides from 1-5M HNO
more than 3M, and those of heavy lanthanides from 1-5M HNO solutions. Nitric acid concentration is more influential than the ligand concentration in the formation of outer-sphere complex.
solutions. Nitric acid concentration is more influential than the ligand concentration in the formation of outer-sphere complex.
Kurata, Yuji; Takizuka, Takakazu; Osugi, Toshitaka; Takano, Hideki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 301(1), p.1 - 7, 2002/02
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:59.88(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Watanabe, Masayuki; Tatsugae, Ryozo*; Shirahashi, Koichi; Morita, Yasuji; Kubota, Masumitsu*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 250(2), p.377 - 379, 2001/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:47.93(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Tachimori, Shoichi
JAERI-Research 2001-048, 23 Pages, 2001/10
A new chemical process, ARTIST process, is proposed for the treatment of spent nuclear fuel. The main concept of the ARTIST process is to recover and stock all actinides (Ans) in two groups, uranium (U) and a mixture of transuranics (TRU), to preserve their resource value and to dispose solely fission products (FPs). The process composed of two main steps, an U exclusive isolation and a total recovery of TRU; which copes with the nuclear non-proliferation measures, and additionally Pu separation process and soft N-donor process if requested, and optionally processes for separation of long-lived FPs. These An products: U-product and TRU-product, are to be solidified by calcination and allowed to the interim stockpile for future utilization. These separations are achieved by use of amidic extractants in accord with the CHON principle. The technical feasibility of the ARTIST process was explained by the performance of both the branched-alkyl monoamides the diglycolic amide (TODGA) in thorough extraction of all TRU by tridentate fashon.
Yamagishi, Isao
JAERI-Review 2001-027, 52 Pages, 2001/07
The present study deals with the survey of inorganic ion-exchangers suitable for separation and immobilization of Sr and Cs contained in acidic high-level liquid waste. For separation and immobilization of Cs, crystalline silicotitanate seems to be the most promising exchanger. For selective separation of Sr, there is no promising exchanger up to now. Sintered ceramics are favorable waste forms of inorganic ion-exchangers. Their stabilities are largely influenced by composition of exchangers, qualities of ceramics and disposal scenario.
Matsunaga, Takeshi
JAERI-Review 2001-018, 121 Pages, 2001/06
The present report reviews a series of studies conducted in JAERI which have dealt with the behavior of atmospherically-derived radionuclides in a fluvial environment. The studies cited here firstly include investigations of the evaluation of the transport rate of the atmospherically-derived 137Cs, 210Pb and 7Be from the ground via a river to the downstream areas where the affected water is consumed. The studies validated i) the importance of suspended particulate materials in the fluvial discharge of those radionuclides, and ii) a methodology to estimate the discharge of those radionuclides. Secondly, studies in rivers and lakes in the vicinity of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant revealed the role of natural dissolved organics in affecting the dissolution and transport of 239,240Pu, 241Am through complexation to form soluble species with the aid of a chemical equilibrium model The same sort of a model was also applied successfully for the behavior of iron and manganese (hydr)oxides in river recharged aquifers which could bear riverborne radionuclides.