Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hayashizaki, Kohei; Hirooka, Shun; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Saito, Kosuke
Ceramics (Internet), 8(1), p.24_1 - 24_12, 2025/03
Kim, M.*; Lee, C.*; Sugita, Yutaka; Kim, J.-S.*; Jeon, M.-K.*
Geomechanics for Energy and the Environment, 41, p.100628_1 - 100628_9, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Energy & Fuels)This study investigates the impact of primary variables selection on the modeling of non-isothermal two-phase flow, by using the numerical work on the full-scale Engineered Barrier System (EBS) experiment conducted at Horonobe URL as part of the DECOVALEX-2023 project. A validated numerical model is employed to simulate the coupled thermo-hydrological behavior of heterogeneous porous media within the EBS. Two different primary variable schemes are compared in discretizing the governing equations, revealing significant difference in results.
Hojo, Tomohiko*; Koyama, Motomichi*; Kumai, Bakuya*; Zhou, Y.*; Shibayama, Yuki; Shiro, Ayumi*; Shobu, Takahisa; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Ajita, Saya*; Akiyama, Eiji*
ISIJ International, 65(2), p.284 - 296, 2025/02
Uesawa, Shinichiro; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(11), p.1438 - 1452, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)We developed a deep learning-based bubble detector with a Shifted window Transformer (Swin Transformer) to detect and segment individual bubbles among overlapping bubbles. To verify the performance of the detector, we calculated its average precision (AP) with different number of training images. The mask AP increased with the increase in the number of training images when there were less than 50 images but remained constant when there were more than 50 images. It was observed that the AP for the Swin Transformer and ResNet were almost the same when there were more than 50 images; however, when few training images were used, the AP of the Swin Transformer were higher than that of the ResNet. Furthermore, with regard to the increase in void fraction, the AP of the Swin Transformer showed a decrease similar to that in the case of the ResNet; however, for few training images, the AP of the Swin Transformer was higher than that of the ResNet in all void fractions. Moreover, we confirmed the detector trained with synthetic bubble images was able to segment overlapping bubbles and deformed bubbles in a bubbly flow experiment. Thus, we verified that the new bubble detector with Swin Transformer provided higher AP than the detector with ResNet for fewer training images.
Brear, D. J.*; Kondo, Satoru; Sogabe, Joji; Tobita, Yoshiharu*; Kamiyama, Kenji
JAEA-Research 2024-009, 134 Pages, 2024/10
The SIMMER-III/SIMMER-IV computer codes are being used for liquid-metal fast reactor (LMFR) core disruptive accident (CDA) analysis. The sequence of events predicted in a CDA is often influenced by the heat exchanges between LMFR materials, which are controlled by heat transfer coefficients (HTCs) in the respective materials. The mass transfer processes of melting and freezing, and vaporization and condensation are also controlled by HTCs. The complexities in determining HTCs in a multi-component and multi-phase system are the number of HTCs to be defined at binary contact areas of a fluid with other fluids and structure surfaces, and the modes of heat transfer taking into account different flow topologies representing flow regimes with and without structure. As a result, dozens of HTCs are evaluated in each mesh cell for the heat and mass transfer calculations. This report describes the role of HTCs in SIMMER-III/SIMMER-IV, the heat transfer correlations implemented and the calculation of HTCs in all topologies in multi-component, multi-phase flows. A complete description of the physical basis of HTCs and available experimental correlations is contained in Appendices to this report. The major achievement of the code assessment program conducted in parallel with code development is summarized with respect to HTC modeling to demonstrate that the coding is reliable and that the model is applicable to various multi-phase problems with and without reactor materials.
Vauchy, R.; Hirooka, Shun; Horii, Yuta; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Murakami, Tatsutoshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 599, p.155233_1 - 155233_11, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The fluorite exsolution/recombination in U Pu
Pu O
O (y = 0.30 and 0.45) and PuO
(y = 0.30 and 0.45) and PuO was investigated using differential scanning calorimetry. The results are in relatively good agreement with the literature data, except for plutonia. Our values indicate that the critical temperature of the miscibility gap in Pu-O is 30
was investigated using differential scanning calorimetry. The results are in relatively good agreement with the literature data, except for plutonia. Our values indicate that the critical temperature of the miscibility gap in Pu-O is 30 50 K lower than previously reported. Finally, the systematic experimental procedure allowed us refining the locus of the solvus existing in hypostoichiometric U
50 K lower than previously reported. Finally, the systematic experimental procedure allowed us refining the locus of the solvus existing in hypostoichiometric U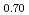 0Pu
0Pu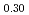 O
O , U
, U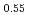 Pu
Pu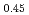 O
O , and PuO
, and PuO dioxides.
dioxides.
Sogabe, Joji; Ishida, Shinya; Tagami, Hirotaka; Okano, Yasushi; Kamiyama, Kenji; Onoda, Yuichi; Matsuba, Kenichi; Yamano, Hidemasa; Kubo, Shigenobu; Kubota, Ryuzaburo*; et al.
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Fuel Cycle (GLOBAL2024) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/10
In the frame of France-Japan collaboration, the calculational methodologies were defined and assessed, and the phenomenology and the severe accident consequences were investigated in a pool-type sodium-cooled fast reactor.
Fukuda, Takanari; Yamashita, Susumu; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 14th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation, and Safety (NTHOS-14) (Internet), 12 Pages, 2024/08
The VOF method is a type of CFDs that is most widely applied to multiphase flow analysis involving advective interfaces, and several interface-capturing schemes have been developed for an accurate advection of VOF values. However, the performance of these schemes has typically been evaluated only for limited numerical problems where velocity fields are spatially orderly and fixed in time. Few studies have been conducted to evaluate the performance of these schemes for more realistic and complex conditions, such as gas-liquid two-phase flows in nuclear reactors. Therefore, in this study, three-dimensional analysis of bubble flows has been conducted using the interface-capturing schemes of THINC and THINC/WLIC, which have been developed relatively recently. Evaluation is performed using more engineering indicators such as the number, volume, and trajectory of bubbles, which can influence the void fraction distribution in reactor cores. The results of these comparisons showed that the VOF value could be significantly diffused, leading to numerical brake-up and dissipation of the bubbles, with the influence of interface-capturing scheme.
Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Aizawa, Kazuya; Yamasaki, Michiaki*; Kawasaki, Takuro
Nihon Zairyo Gakkai Dai-58-Kai X Sen Zairyo Kyodo Ni Kansuru Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu, p.58 - 60, 2024/07
Harjo, S.
Isotope News, (793), p.13 - 16, 2024/06
no abstracts in English
Ono, Ayako; Okamoto, Kaoru*; Makino, Yasushi*; Hosokawa, Shigeo*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of Specialist Workshop on Advanced Instrumentation and Measurement Techniques for Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics and Severe Accidents (SWINTH-2024) (USB Flash Drive), 13 Pages, 2024/06
JAEA has been developing an advanced neutronic/thermal-hydraulics coupling simulation system. In the coupling simulation system, the detailed thermal-hydraulics codes based on an interface-capturing method (JUPITER or TPFIT) will be adopted to simulate thermal-hydraulics behavior in a fuel bundle. The experimental data and findings relating to the gas-liquid two-phase flow in a fuel bundle are especially required to validate JUPITER/TPFIT. In this study, we therefore develop a measurement method by combining Laser-Doppler Velocimetry (LDV) and photodiodes, which can access to a small flow channel such as a subchannel of a fuel bundle. The developed measurement method is validated by comparison with the measument by a electrical conductance probe. Finally, we obtain experimental data on local flow structures and interactions between gas and liquid phases. The developed measurement method is actually applied to an air-water dispersed bubbly flow to confirm its capability.
Ishida, Shinya; Fukano, Yoshitaka; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Okano, Yasushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(5), p.582 - 594, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:27.70(Nuclear Science & Technology)Li, X.*; Zhu, R.*; Xin, J.*; Luo, M.*; Shang, S.-L.*; Liu, Z.-K.*; Yin, C.*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Dippenaar, R. J.*; Higo, Yuji*; et al.
CALPHAD; Computer Coupling of Phase Diagrams and Thermochemistry, 84, p.102641_1 - 102641_6, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Thermodynamics)Hagihara, Koji*; Mayama, Tsuyoshi*; Yamasaki, Michiaki*; Harjo, S.; Tokunaga, Toko*; Yamamoto, Kazuki*; Sugita, Mika*; Aoyama, Kairi*; Gong, W.; Nishimoto, Soya*
International Journal of Plasticity, 173, p.103865_1 - 103865_21, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:98.17(Engineering, Mechanical)Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Horiguchi, Naoki; Furuichi, Hajime*; Katono, Kenichi*
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2023/05
Song, K.*; Ito, Kei*; Ito, Daisuke*; Odaira, Naoya*; Saito, Yasushi*; Matsushita, Kentaro; Ezure, Toshiki; Tanaka, Masaaki
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/05
Gas entrainment (GE) phenomena caused by a free surface vortex may cause the disturbance in core power of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR). For this reason, the entrained gas flow rate by the GE should be evaluated accurately for the practical safety design of SFRs. In this study, for the purpose of examining the applicability of CFD for the accurate evaluation of GE phenomena, a CFD is applied to the simulation of the free surface vortex and accompanied GE phenomena in a cylindrical vessel with a suction pipe, and the CFD results and the experimental data of the GE are compared. As a result, the CFD and experiments show similar two-phase flow pattern inside the suction pipe, and the shape of the gas core at the free surface is also very similar. Therefore, it is confirmed that the CFD can predict the GE phenomena triggered by a free surface vortex properly and accurately within the acceptable error range.
Kwon, H.*; Sathiyamoorthi, P.*; Gangaraju, M. K.*; Zargaran, A.*; Wang, J.*; Heo, Y.-U.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Lee, B.-J.*; Kim, H. S.*
Acta Materialia, 248, p.118810_1 - 118810_12, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:99.20(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Mg/LPSO dual-phase magnesium alloy monitored by
Mg/LPSO dual-phase magnesium alloy monitored by  neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionHarjo, S.; Gong, W.; Aizawa, Kazuya; Kawasaki, Takuro; Yamasaki, Michiaki*; Mayama, Tsuyoshi*; Kawamura, Yoshihito*
Materials Transactions, 64(4), p.766 - 773, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:74.17(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) ceramics
ceramicsVauchy, R.; Hirooka, Shun; Watanabe, Masashi; Yokoyama, Keisuke; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Nakamichi, Shinya; Murakami, Tatsutoshi
Ceramics International, 49(2), p.3058 - 3065, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:65.95(Materials Science, Ceramics)Horiguchi, Naoki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Kaneko, Akiko*; Abe, Yutaka*
Proceedings of 12th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS12) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2022/10
For safety evaluation of nuclear reactors in severe accidents, it is important to estimate physical quantities of fragments generated from the molten fuel jet, which falls in a pool and breaks up. The evaluation method has been developed for the behavior as liquid jet with hydrodynamic interaction including fuel coolant interaction (FCI). In case of a shallow pool assumed in ex-vessel, the molten fuel jet is assumed to behave as wall-impinging liquid jet and to form liquid film flow spreading on the floor with/without fragmentation. In our research, focusing on hydrodynamic interaction and the transient 3-dimensional spreading on the floor, we have developed the evaluation method by numerical simulation using the two-phase flow simulation code with interface tracking method (TPFIT) developed by JAEA and, the experimental method using the 3D-LIF method in liquid-liquid system for the validation data. In our previous studies, we investigated the wall-impinging liquid jet behavior with fragmentation and observed that the liquid film flow had some characteristic parts transiently. Since it indicates that the quantities change depending on the parts and affect the safety evaluation, it is important to measure the quantities of the fragments generated from each part. This paper explains the measurement of the physical quantities of the fragments generated from each part of the wall-impinging liquid jet in a shallow pool for the validation of the numerical simulation. We conducted an experiment with the 3D-LIF method and segmented the experimental data based on the fragmentation point over the liquid film flow using the dispersed phase tracking method, developed by JAEA. Then, we measured the diameter and amount of the fragments from the segmented experimental data and investigated their changing trend.