Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Lee, C. G.; Iguchi, Kazunari; Esaka, Fumitaka; Magara, Masaaki; Sakurai, Satoshi; Watanabe, Kazuo; Usuda, Shigekazu
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 245(2), p.440 - 444, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.64(Instruments & Instrumentation)The etching rates of fission track detectors made of polycarbonate containing uranium particles were measured after thermal neutron irradiation with fluence of 8 10
10 n/cm
n/cm , in order to study the influence of uranium enrichment on the etching rate that was calculated from the weight loss by etching. There is a strong correlation between the etching rate of detector and the enrichment E of uranium particle: the former increases as the latter increases. Particularly, the etching rate per particle was proportional to E
, in order to study the influence of uranium enrichment on the etching rate that was calculated from the weight loss by etching. There is a strong correlation between the etching rate of detector and the enrichment E of uranium particle: the former increases as the latter increases. Particularly, the etching rate per particle was proportional to E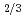 rather than E
rather than E , which is probably due to the overlapping of fission tracks. The etching behaviors of detector revealed that the existence of two different etching rate regions, a nonlinear region in the beginning of etching process and a subsequent constant region, which was explained as the opening of fission tracks and the broadening of opened tracks, respectively.
, which is probably due to the overlapping of fission tracks. The etching behaviors of detector revealed that the existence of two different etching rate regions, a nonlinear region in the beginning of etching process and a subsequent constant region, which was explained as the opening of fission tracks and the broadening of opened tracks, respectively.
Iguchi, Kazunari; Esaka, Konomi; Lee, C. G.; Inagawa, Jun; Esaka, Fumitaka; Onodera, Takashi; Fukuyama, Hiroyasu; Suzuki, Daisuke; Sakurai, Satoshi; Watanabe, Kazuo; et al.
Radiation Measurements, 40(2-6), p.363 - 366, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:58.78(Nuclear Science & Technology)In particle analysis for safeguards environmental samples, the fission track technique is very important to detect sub-micrometer particles containing uranium. In the technique the authors developed, the particles were recovered onto the polycarbonate membrane filter. The filter was dissolved in solvent and dried to form a thin film of detector, in which the particles were confined. After thermal neutron irradiation and etching, the particles of interest in the detector were easily identified with fission tracks, and were picked up for isotope ratio analysis. It was found, however, that the particles in the vicinity of the detector surface may fall off during the etching process. Therefore, optimization of the etching condition is required. In this work, the effects of etching time and enrichment of uranium in particles were investigated. Preliminary results suggest that etching time should be shorter with the increase in the enrichment.