Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Okubo, Takahiro*; Ibaraki, Moe*; Tachi, Yukio; Iwadate, Yasuhiko*
Applied Clay Science, 123, p.148 - 155, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:75.95(Chemistry, Physical)The pore distribution of water-saturated compacted clay (Na-montmorillonite at 0.8 and 1.4 g/cm saturated by three salt concentrations) was evaluated using
saturated by three salt concentrations) was evaluated using  H NMR relaxometry and freezing point depression. The populations of interlayer water with four hydrated state and non-interlayer water were calculated from the assumed thresholds. The sample with lower density exhibits higher population of non-interlayer water up to 55%. Low-temperature
H NMR relaxometry and freezing point depression. The populations of interlayer water with four hydrated state and non-interlayer water were calculated from the assumed thresholds. The sample with lower density exhibits higher population of non-interlayer water up to 55%. Low-temperature  H NMR experiments in view of freezing point depression indicated that mesopore water in approximately 4 nm space observed in the calorimetric study was considered as non-interlayer water and the threshold temperature. The result showed that population of non-interlayer water by expected from freezing point depression agreed with
H NMR experiments in view of freezing point depression indicated that mesopore water in approximately 4 nm space observed in the calorimetric study was considered as non-interlayer water and the threshold temperature. The result showed that population of non-interlayer water by expected from freezing point depression agreed with  H NMR relaxometry within 10%. Correlation experiments between longitudinal (
H NMR relaxometry within 10%. Correlation experiments between longitudinal (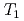 ) and transverse relation times (
) and transverse relation times (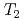 ) at -10
) at -10 C suggested that high-mobility bulk-like water molecules existed at a clay density of 1.4 g/cm
C suggested that high-mobility bulk-like water molecules existed at a clay density of 1.4 g/cm .
.
Ochs, M.*; Lothenbach, B.*; Shibata, Masahiro; Yui, Mikazu
Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 29(1), p.129 - 136, 2004/01
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:49.66(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)Compacted bentonite is foreseen as the buffer material in the engineered barrier system of the geological disposal system. To derive  d values and diffusion coefficients of radionuclides for performance assessment, it is critical to be able to describe the chemistry of the pore solution and to understand how it is influenced by different factors. This paper presents a sensitivity analysis on the influence of important parameters on porewater chemistry in compacted bentonite. The principal parameters varied were the fractions of calcite, gypsum, and NaCl dissolving from bentonite, and pCO
d values and diffusion coefficients of radionuclides for performance assessment, it is critical to be able to describe the chemistry of the pore solution and to understand how it is influenced by different factors. This paper presents a sensitivity analysis on the influence of important parameters on porewater chemistry in compacted bentonite. The principal parameters varied were the fractions of calcite, gypsum, and NaCl dissolving from bentonite, and pCO . Model calculations treated ion exchange reactions of smectite and protonation/deprotonation at the edge of smectite using the diffuse layer model. Some calculations consider electric double layer effects in the porespace. The model results show that two powerful pH buffer systems are operative in compacted bentonite: Amphoteric edge SOH sites and the carbonate buffer system. If pCO
. Model calculations treated ion exchange reactions of smectite and protonation/deprotonation at the edge of smectite using the diffuse layer model. Some calculations consider electric double layer effects in the porespace. The model results show that two powerful pH buffer systems are operative in compacted bentonite: Amphoteric edge SOH sites and the carbonate buffer system. If pCO is imposed externally, the resulting porewater pH is mainly controlled by the carbonate buffer. If bentonite is treated as a closed system, the buffering action of the SOH sites becomes more important. In both cases, the dissolution of calcite and gypsum from the bentonite is important. If the development of an electric double layer in the bentonite pores is considered, entire porespace may be occupied with diffuse layers, leaving no space for free porewater, at higher dry densities (1200 kg/m
is imposed externally, the resulting porewater pH is mainly controlled by the carbonate buffer. If bentonite is treated as a closed system, the buffering action of the SOH sites becomes more important. In both cases, the dissolution of calcite and gypsum from the bentonite is important. If the development of an electric double layer in the bentonite pores is considered, entire porespace may be occupied with diffuse layers, leaving no space for free porewater, at higher dry densities (1200 kg/m ).
).
Nagao, Seiya; Yanase, Nobuyuki; Yamamoto, Masayoshi*; Kofuji, H.*; Sorin, Yoshiki*; Amano, Hikaru
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 252(2), p.225 - 232, 2002/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:50.42(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Nagao, Seiya*;
Science of the Total Environment, 117-118, p.439 - 447, 1992/00
no abstracts in English
; ; ;
Kozan Chishitsu, 40(5), p.323 - 336, 1990/00
no abstracts in English
 Pellet
PelletJAERI-M 7158, 23 Pages, 1977/07
no abstracts in English
Tachi, Yukio; Yotsuji, Kenji; Ito, Tsuyoshi; Suyama, Tadahiro
no journal, ,
The integrated sorption and diffusion (ISD) model was applied for systems coexisting multispecies Sr (divalent cation Sr and neutral SrSO
and neutral SrSO (aq)) in compacted montmorillonite. Effective diffusion coefficients (De) and distribution coefficients (Kd) of Sr in compacted Na-montmorillonite (dry density of 800 kg/m
(aq)) in compacted montmorillonite. Effective diffusion coefficients (De) and distribution coefficients (Kd) of Sr in compacted Na-montmorillonite (dry density of 800 kg/m ) saturated with three types of Na
) saturated with three types of Na SO
SO solutions (0.05, 0.1, 0.5 M) were measured by the trough-diffusion method. The De and Kd values decreased drastically with increasing porewater salinity. The De for multispecies Sr was determined as the harmonic weight-average considering the two species distribution and their log De values, based on comparison with reactive-transport calculations using the PHREEQC. As a result, the De trend could be quantitatively express by the ISD model considering multispecies contributions. The thermodynamic sorption model considering ion exchange reactions could provide reasonable account of Kd trend as functions of salinity.
solutions (0.05, 0.1, 0.5 M) were measured by the trough-diffusion method. The De and Kd values decreased drastically with increasing porewater salinity. The De for multispecies Sr was determined as the harmonic weight-average considering the two species distribution and their log De values, based on comparison with reactive-transport calculations using the PHREEQC. As a result, the De trend could be quantitatively express by the ISD model considering multispecies contributions. The thermodynamic sorption model considering ion exchange reactions could provide reasonable account of Kd trend as functions of salinity.