Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sakasegawa, Hideo; Nakajima, Motoki*; Kato, Taichiro*; Nozawa, Takashi*; Ando, Masami*
Materials Today Communications (Internet), 40, p.109659_1 - 109659_8, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:30.18(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nanometric oxide particles play an important role in improving the creep property of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened (ODS) steels. In our previous research, we examined a microstructural feature known as prior particle boundary (PPB). PPB refers to the surface of mechanically alloyed (MA) powders before consolidation. We revealed that the ODS steel with fine PPBs produced from smaller MA powders, exhibited shorter creep rupture times, compared to that with coarse PPBs produced from larger MA powders. The size of MA powders had an impact on the creep property. In this study, we examined the shape of MA powders, which were non-spherical shapes. Such shapes have the potential to induce anisotropic creep behavior. We conducted small punch creep tests on specimens with two different orientations to study the possible anisotropy. The results revealed that the creep rupture times varied depending on the orientation of specimen, thus indicating anisotropic creep property.
 Pu
Pu O
O powder using master sintering curve theory
powder using master sintering curve theoryNakamichi, Shinya; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Hirooka, Shun; Vauchy, R.; Murakami, Tatsutoshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 595, p.155072_1 - 155072_11, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) ceramics
ceramicsVauchy, R.; Hirooka, Shun; Watanabe, Masashi; Yokoyama, Keisuke; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Nakamichi, Shinya; Murakami, Tatsutoshi
Ceramics International, 49(2), p.3058 - 3065, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:63.47(Materials Science, Ceramics)Kawaguchi, Koichi; Segawa, Tomoomi; Ishii, Katsunori
Funtai Kogakkai-Shi, 59(6), p.283 - 290, 2022/06
In the Japan Atomic Energy Agency, in order to effectively use the out-of-standard pellets in the fuel manufacturing process for high-speed furnaces, we are developing techniques for crushing and reusing them with raw material powder. By analyzing in detail the particle size distribution before and after grinding, it was shown that the grinding powder is composed of three different component particles having different characteristics of the particle size distribution. In addition, we examined the method of predicting pulverized powder particle size distribution from the supply powder particle size distribution.
 C absorber material on melt progression and chemical forms of iodine or cesium under severe accident conditions
C absorber material on melt progression and chemical forms of iodine or cesium under severe accident conditionsHidaka, Akihide
Insights Concerning the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Accident, Vol.4; Endeavors by Scientists, p.341 - 356, 2021/10
Kawaguchi, Koichi; Segawa, Tomoomi; Yamamoto, Kazuya; Makino, Takayoshi; Iso, Hidetoshi; Ishii, Katsunori
Funtai Kogakkai-Shi, 57(9), p.478 - 484, 2020/09
A collision plate type jet mill is assumed to be a pulverizer that can control the particle size for nuclear fuel fabrication. The collision plate type jet mill consists of two modules, a classifier and a mill chamber. Coarse component of powder is cycled in the equipment and finally pulverized into objective particle size. In this report, simulated crushed powders were classified and pulverized step by step, and particle size distribution were compared. The collision plate type jet mil can produce objective size particles with low overgrinding.
 C absorber material on melt progression and chemical forms of iodine or cesium under severe accident conditions
C absorber material on melt progression and chemical forms of iodine or cesium under severe accident conditionsHidaka, Akihide
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 14(1), p.51 - 61, 2015/03
B C used mainly for BWR and EPR absorbers could cause phenomena which never happen in PWR with Ag-In-Cd absorbers during severe accident. B
C used mainly for BWR and EPR absorbers could cause phenomena which never happen in PWR with Ag-In-Cd absorbers during severe accident. B C would make a eutectic interaction with stainless steel and enhance melt relocation. Boron oxidation could increase H
C would make a eutectic interaction with stainless steel and enhance melt relocation. Boron oxidation could increase H generation and change of liberated carbon to CH
generation and change of liberated carbon to CH could enhance CH
could enhance CH I generation. HBO
I generation. HBO generated during B
generated during B C oxidation could be changed to CsBO
C oxidation could be changed to CsBO by combining with Cs. This may increase Cs deposition in reactor coolant system. There could be differences in configuration, surface area, stainless steel-B
by combining with Cs. This may increase Cs deposition in reactor coolant system. There could be differences in configuration, surface area, stainless steel-B C weight ratio between B
C weight ratio between B C powder and pellet absorbers. Present issue is to clarify effect of these differences on full scale melt progression, B
C powder and pellet absorbers. Present issue is to clarify effect of these differences on full scale melt progression, B C oxidation and source term. Advancement of this research domain could contribute to further sophistication of prediction tool for melt progression and source terms, and treatment of organic iodide formation in safety evaluation.
C oxidation and source term. Advancement of this research domain could contribute to further sophistication of prediction tool for melt progression and source terms, and treatment of organic iodide formation in safety evaluation.
Sakai, Mikio; Yamamoto, Toshihiro; Murazaki, Minoru; Miyoshi, Yoshinori
Nuclear Technology, 149(2), p.141 - 149, 2005/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.49(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the conventional criticality evaluation of the nuclear powder system, the effects of particulate behavior have not been considered. In other words, it is difficult to reflect the particle behavior into the conventional criticality evaluation. We have developed a novel criticality evaluation code to resolve this issue. The criticality evaluation code, coupling a Discrete Element Method simulation code with a continuous-energy Monte Carlo transport code, makes it possible to study the effect of the particulate behavior on a criticality evaluation. The criticality evaluation code has been applied to the powder system of the MOX fuel powder agitation process. The criticality evaluations have been performed under mixing the MOX fuel powder in a stirred vessel to investigate the effects of the powder boundary deformation and particulate mixture conditions on the criticality evaluation. The evaluation results revealed that the powder uniformity mixture condition and the boundary deformation could make the neutron effective multiplication factor decrease.
Yamamoto, Toshihiro; Miyoshi, Yoshinori
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 91, p.583 - 584, 2004/11
MOX powder and additives are mixed in the process of MOX fuel fabrication. A non-uniform mixing state of MOX powder and additives occurs during the homogenization mixing process. However, ordinary criticalit safety evaluations for mixtures assume that the mixtures have a uniform distribution of the mixing state. A non-uniform distribution of the mixing state in a sphere, which maximizes the effective neutron multiplication factor, was obtained using a concept of the fuel importance. As a result, the central portion of the sphere is composed of an optimal moderation region, and the surrounding region is composed of pure MOX powder. While keff is 0.545 for the uniform distribution, keff for the optimal non-uniform distribution is 0.590. That is, keff increases by 0.045.
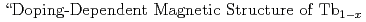 Ca
Ca MnO
MnO rqrq
rqrqMachida, Akihiko; Moritomo, Yutaka*; Oyama, Kenji*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 72(5), P. 1312, 2003/05
In order to investigate interrelation between the lattice structure and the magnetic structure, we have performed Rietveld structural analysis on the neutron powder patterns for Tb Ca
Ca MnO
MnO at low temperature. In the concentration range of
at low temperature. In the concentration range of 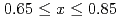 , we observed the Bragg reflections due to the CE-like- and C-type structures. In this range, the powder patterns were reproduce by the two-phase model with
, we observed the Bragg reflections due to the CE-like- and C-type structures. In this range, the powder patterns were reproduce by the two-phase model with 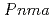 and
and 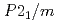 symmetries. The fractions of these phases change against concentration
symmetries. The fractions of these phases change against concentration  . This variation of the fraction for the
. This variation of the fraction for the 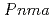 phase is similar to the variation of the integrated intensities of the CE-like-type magnetic Bragg reflections. This indicates that the
phase is similar to the variation of the integrated intensities of the CE-like-type magnetic Bragg reflections. This indicates that the 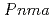 phase is responsible for the CE-like spin-ordering. Furthermore, we discussed interrelation between the detailed lattice structure and magnetic structure.
phase is responsible for the CE-like spin-ordering. Furthermore, we discussed interrelation between the detailed lattice structure and magnetic structure.
 Fe
Fe Al
Al at 65K
at 65KS.Ridwan*; H.Mujamilah*; M.Gunawan*; P.Marsongkohadi*; Q.W.Yan*; P.L.Zhang*; X.D.Sun*; Z.H.Cheng*; Minakawa, Nobuaki;
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 65(2), p.348 - 350, 1996/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:36.26(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Okuno, Hiroshi; Naito, Yoshitaka;
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 31(9), p.986 - 995, 1994/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:27.68(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Nagao, Seiya;
Geochemical Journal, 25, p.187 - 197, 1991/00
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:36.54(Geochemistry & Geophysics)no abstracts in English
; Fujine, Sachio; Maeda, Mitsuru; Adachi, Takeo; Sakurai, Tsutomu;
Proc. of the 3rd Int. Conf. on Nuclear Fuel Reprocessing and Waste Management,Vol. 2, p.682 - 686, 1991/00
no abstracts in English
 and NOx by powdery materials in radiation treatment of exhaust gases
and NOx by powdery materials in radiation treatment of exhaust gases; ;
Int.J.Appl.Radiat.Isot., 36(10), p.807 - 812, 1985/00
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:82.79(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
; ;
Kogai To Taisaku, 21(7), p.629 - 634, 1985/00
no abstracts in English
 O
O powders in nitric acid
powders in nitric acid;
Ind.Eng.Chem.,Process Des.Dev., 23, p.122 - 125, 1984/00
no abstracts in English
; ;
Nucl.Chem.Waste Manage., 3, p.131 - 137, 1982/00
no abstracts in English
;
Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 8(3), p.334 - 335, 1969/09
no abstracts in English
 pellet in air; Effect of heat-treatment of pellet on particle size distribution of powders produced
pellet in air; Effect of heat-treatment of pellet on particle size distribution of powders produced; ; Ishikawa, Niro;
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 5(12), p.652 - 653, 1968/00
Times Cited Count:14no abstracts in English