Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 168(2), p.190 - 196, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.75(Environmental Sciences)Deposit energy distribution in microscopic site in a living cell is important information for understanding of biological effects of energetic heavy ion beams. In this work, a wall-less tissue equivalent proportional counter has been used for the measurement of lineal energy (y) distributions and dose-mean of y (yD) at radial direction of 30 MeV H at TIARA, for the verification of the microdosimetric function of PHITS. The measured yf(y) summed in radial direction agree with the corresponding data from the microdosimetric calculations using the PHITS code fairly well. The yD of 30 MeV proton beam presents the smallest value at r = 0.0 and gradually increase with radial distance, while the values of heavy ions such as iron showed rapid decrease with radial distance. This experimental result demonstrates that the stochastic deposit energy distribution of high-energy protons in microscopic region is rather constant both in the core and in the penumbra region of the track structure.
Tanaka, Hiroki; Yamagishi, Hideshi; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Aizawa, Kazuya
JAERI-Research 2005-010, 16 Pages, 2005/04
We have been developing the 2-d position-sensitive neutron detector with individual readout as next-generation-type detector system for neutron scattering experiments using intense pulsed neutron source. The detection system is designed to fulfill the specifications required for each neutron spectrometer, such as a count rate, efficiency, neutron/ -ray ratio, a spatial resolution and a size, by using suitable detector heads. The fundamental and imaging performances of the developed system assembled with a Multi-wire proportional counter head were evaluated using a collimated neutron beam. The system worked stably for long hours at the gas pressure of 5 atm with a mixture of 30% C
-ray ratio, a spatial resolution and a size, by using suitable detector heads. The fundamental and imaging performances of the developed system assembled with a Multi-wire proportional counter head were evaluated using a collimated neutron beam. The system worked stably for long hours at the gas pressure of 5 atm with a mixture of 30% C H
H (0.26 atm
(0.26 atm  He)at gas gain of 450. The spatial resolutions were 1.4, 1.6 mm (FWHM) for a cathode- and a back strip- direction, respectively, considering a beam size. It was also confirmed that the spatial uniformity of the detection efficiency over the whole sensitive detection area was rather good,
He)at gas gain of 450. The spatial resolutions were 1.4, 1.6 mm (FWHM) for a cathode- and a back strip- direction, respectively, considering a beam size. It was also confirmed that the spatial uniformity of the detection efficiency over the whole sensitive detection area was rather good,  8 % deviation from the average with the optimum discrimination level.
8 % deviation from the average with the optimum discrimination level.
Yoshizawa, Michio; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Saegusa, Jun; Nemoto, Hisashi*; Yoshida, Makoto
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 110(1-4), p.81 - 84, 2004/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:22.91(Environmental Sciences)The facility of Radiation Standards (FRS) of JAERI has equipped with the concrete-moderated neutron calibration fields as simulated workplace neutron fields. The fields use an Am-Be (37GBq) neutron source placed in the narrow space surrounded by concrete wall and bricks to produce scattered neutrons. The neutron spectra of the fields were measured with Bonner multi-sphere spectrometer system (BMS), spherical recoil-proton proportional counters (RPCs), and a liquid scintillation counter (NE-213). The results were compared with each other, and the neutron spectra and the ambient dose equivalent rate, 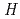
 (10), were agreed well within the uncertainty. The angular distributions of neutron fluence were calculated by the MCNP-4B2 Monte Carlo code to obtain the reference personal dose equivalent rate,
(10), were agreed well within the uncertainty. The angular distributions of neutron fluence were calculated by the MCNP-4B2 Monte Carlo code to obtain the reference personal dose equivalent rate, 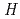
 (10). The calculated results show that the scattered neutrons have a wide variety of incident angles. The reference
(10). The calculated results show that the scattered neutrons have a wide variety of incident angles. The reference 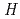
 (10) values considered the angular distribution were found to be 10-18% smaller than those without consideration.
(10) values considered the angular distribution were found to be 10-18% smaller than those without consideration.
Yamagishi, Hideshi; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Masaoka, Sei; Aizawa, Kazuya
Review of Scientific Instruments, 75(7), p.2340 - 2345, 2004/07
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:45.04(Instruments & Instrumentation)A new instrument system with the capability of secondary-particle discrimination (InSPaD) was studied for the development of two-dimensional neutron detectors (2D-ND) filled with helium-3 gas and with high spatial resolution. The InSPaD can discriminate between the tracks of a proton and a triton created in the nuclear reaction  He(
He( ,
, )
) by simply setting the level of discriminators appropriately in each signal channel, and the system exhibits a high spatial resolution, high counting rate, low background, and stability. The simulations of the 2D-ND equipped with the InSPaD revealed spatial resolutions of 0.46 mm in full width at half maximum for a 10% mixture of C
by simply setting the level of discriminators appropriately in each signal channel, and the system exhibits a high spatial resolution, high counting rate, low background, and stability. The simulations of the 2D-ND equipped with the InSPaD revealed spatial resolutions of 0.46 mm in full width at half maximum for a 10% mixture of C H
H with helium-3 at 0.3 MPa. The results of neutron-detection experiments using a microstrip gas chamber, including the range of the secondary particles and the pulse-height distribution, agreed well with the simulated results, indicating the feasibility of the InSPaD.
with helium-3 at 0.3 MPa. The results of neutron-detection experiments using a microstrip gas chamber, including the range of the secondary particles and the pulse-height distribution, agreed well with the simulated results, indicating the feasibility of the InSPaD.
Endo, Akira; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro; Sumita, Kenji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 40(8), p.628 - 630, 2003/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.06(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Murazaki, Minoru; Uno, Yuichi; Miyoshi, Yoshinori
JAERI-Tech 2003-029, 107 Pages, 2003/03
We have measured neutron flux distribution around the core tank of STACY heterogeneous core by position sensitive proportional counter (PSPC) to develop the method to measure reactivity for subcritical systems. The neutron flux distribution data in the position accuracy of  13mm have been obtained in the range of uranium concentration of 50g/L to 210g/L both in critical and in subcritical state. The prompt neutron decay constant,
13mm have been obtained in the range of uranium concentration of 50g/L to 210g/L both in critical and in subcritical state. The prompt neutron decay constant,  , was evaluated from the measurement data of pulsed neutron source experiments. We also calculated distribution of neutron flux and
, was evaluated from the measurement data of pulsed neutron source experiments. We also calculated distribution of neutron flux and  He reaction rates at the location of PSPC by using continuous energy Monte Carlo code MCNP. The measurement data was compared with the calculation results. As results of comparison, calculated values agreed generally with measurement data of PSPC with Cd cover in the region above half of solution height, but the difference between calculated value and measurement data was large in the region below half of solution height. On the other hand, calculated value agreed well with measurement data of PSPC without Cd cover.
He reaction rates at the location of PSPC by using continuous energy Monte Carlo code MCNP. The measurement data was compared with the calculation results. As results of comparison, calculated values agreed generally with measurement data of PSPC with Cd cover in the region above half of solution height, but the difference between calculated value and measurement data was large in the region below half of solution height. On the other hand, calculated value agreed well with measurement data of PSPC without Cd cover.
Kinouchi, Nobuyuki; Oishi, Tetsuya; Yoshida, Makoto
Radioisotopes, 50(5), p.183 - 189, 2001/05
no abstracts in English
Ogawa, Toshihide; ; Hoshino, Katsumichi; Odajima, Kazuo; Maeda, Hikosuke
JAERI-M 94-021, 45 Pages, 1994/02
no abstracts in English
Yoshida, Makoto; ; Wu, Y.*; ; Uritani, Akira*; Mori, Chizuo*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 330, p.158 - 164, 1993/00
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:66.56(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Yoshida, Makoto; Yoshizawa, Michio; Minami, Kentaro
Radioisotopes, 39(9), p.396 - 399, 1990/09
no abstracts in English
 Gas in Gas Detectors for Heavy Ions
Gas in Gas Detectors for Heavy Ions; ;
JAERI-M 84-145, 29 Pages, 1984/08
no abstracts in English
;
Nuclear Instruments and Methods, 91(1), p.57 - 60, 1971/00
no abstracts in English
;
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 7(6), p.285 - 290, 1970/06
Times Cited Count:5no abstracts in English
H.J.Delafield*; W.G.Sparke*; ; W.R.Loosemore*; J.A.Dennis*
Nucleonic Instrumentation IEE Conference Publication No.47, p.223 - 228, 1968/00
no abstracts in English