Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kuroda, Shinji*; Marcet, S.*; Bellet-Amalric, E.*; Cibert, J.*; Mariette, H.*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Sakai, Takuro; Oshima, Takeshi; Ito, Hisayoshi
Physica Status Solidi (A), 203(7), p.1724 - 1728, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:30.02(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 (100) thin films by helium ion implantation
(100) thin films by helium ion implantationYamamoto, Shunya; Nagata, Shinji*; Takeyama, Akinori; Yoshikawa, Masahito
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 30(3), p.789 - 792, 2005/09
no abstracts in English
 ions
ionsLee, C. G.; Omura, Takahito*; Takeda, Yoshihiko*; Matsuoka, Saburo*; Kishimoto, Naoki*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 326(2-3), p.211 - 216, 2004/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:28.45(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Magnesium aluminate spinel of single crystal was irradiated with 60 keV Cu at a dose rate up to 100
at a dose rate up to 100  A/cm
A/cm , to a total dose of 3
, to a total dose of 3 10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm , in order to study changes in hardness and step-height swelling by high-flux implantation. Hardness determined by nano-indentation measurements steeply decreased with implantation. There is a strong negative correlation between dose-rate dependences of the hardness and the step-height swelling: the former decreases as the latter increases. The Rutherford Backscattering Spectrometry (RBS)/channeling measurements showed that the spinel is not completely amorphized over the dose-rate range in this study, and the radiation-induced softening observed is not due to amorphization. Results of optical absorbance suggested that radiation-induced point defects and their clusters on the anion sublattices of the spinel played an important role in the radiation-induced swelling under high-flux ion implantation.
, in order to study changes in hardness and step-height swelling by high-flux implantation. Hardness determined by nano-indentation measurements steeply decreased with implantation. There is a strong negative correlation between dose-rate dependences of the hardness and the step-height swelling: the former decreases as the latter increases. The Rutherford Backscattering Spectrometry (RBS)/channeling measurements showed that the spinel is not completely amorphized over the dose-rate range in this study, and the radiation-induced softening observed is not due to amorphization. Results of optical absorbance suggested that radiation-induced point defects and their clusters on the anion sublattices of the spinel played an important role in the radiation-induced swelling under high-flux ion implantation.
Sato, Takahiro; Ishii, Keizo*; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Sakai, Takuro; Oikawa, Masakazu*; Arakawa, Kazuo; Matsuyama, Shigeo*; Yamazaki, Hiromichi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 210, p.113 - 116, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.24(Instruments & Instrumentation)A new detection apparatus for both low energy X-rays and back-scattered protons of MeV energy and its measurement system were developed. The detection apparatus consists of a multi-element detector, pre-amplifiers with active reset system and so on. The detector elements are arranged in the shape of a pentagonal pyramid and fully cover the sample. On each one detection side, 9 detector elements are arranged. The entire detection system consists thus of 45 detector elements. The micro-beam irradiates the sample through the center of the pentagonal pyramid and X-rays emitted from the sample are detected in close to  geometry. This novel detection setup has about 10 times the sensitivity of a conventional Micro-PIXE camera. The counting rate of back-scattered protons per detection element is small despite lack of a passive absorber. It appears possible that X-rays from the very small quantity of elements could also be detected. The advantage over a conventional Micro-PIXE camera includes simultaneous detection of back-scattered protons from N, C and O.
geometry. This novel detection setup has about 10 times the sensitivity of a conventional Micro-PIXE camera. The counting rate of back-scattered protons per detection element is small despite lack of a passive absorber. It appears possible that X-rays from the very small quantity of elements could also be detected. The advantage over a conventional Micro-PIXE camera includes simultaneous detection of back-scattered protons from N, C and O.
Yamaki, Tetsuya; Umebayashi, Tsutomu; Sumita, Taishi*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Maekawa, Masaki; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Ito, Hisayoshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206(1-4), p.254 - 258, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:139 Percentile:98.78(Instruments & Instrumentation)Single crystalline titanium dioxide (TiO ) rutile were implanted with 200keV F
) rutile were implanted with 200keV F at a nominal fluence of 1
at a nominal fluence of 1 10
10 to 1
to 1 10
10 ions cm
ions cm and then thermally annealed in air up to 1200
and then thermally annealed in air up to 1200 for 5h. The radiation damage and its recovery during the subsequent annealing were analyzed by Rutherford backscattering spectrometry in channeling geometry and variable-energy positron annihilation spectroscopy. The lattice disorder was completely annealed at 1200
for 5h. The radiation damage and its recovery during the subsequent annealing were analyzed by Rutherford backscattering spectrometry in channeling geometry and variable-energy positron annihilation spectroscopy. The lattice disorder was completely annealed at 1200 by the diffusion of point defects to the surface acting as a sink. According to the secondary ion mass spectrometry, the F depth profile was shifted to a shallower region along with the damage recovery, finally producing an F-doped layer where the impurity concentration increased steadily towards the surface. The F doping proved to provide a small modification to the conduction-band edge of TiO
by the diffusion of point defects to the surface acting as a sink. According to the secondary ion mass spectrometry, the F depth profile was shifted to a shallower region along with the damage recovery, finally producing an F-doped layer where the impurity concentration increased steadily towards the surface. The F doping proved to provide a small modification to the conduction-band edge of TiO , as assessed by theoretical band calculations.
, as assessed by theoretical band calculations.
Wei, P.; Xu, Y.; Nagata, Shinji*; Narumi, Kazumasa; Naramoto, Hiroshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206(1-4), p.233 - 236, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:42.40(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
 films prepared by pulsed laser deposition
films prepared by pulsed laser depositionYamamoto, Shunya; Sumita, Taishi; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Miyashita, Atsumi; Naramoto, Hiroshi
Journal of Crystal Growth, 237-239(Part1), p.569 - 573, 2002/04
The epitaxial growth of TiO films has attracted much interest from the viewpoints of basic science and applications. In the present study, it is shown that TiO
films has attracted much interest from the viewpoints of basic science and applications. In the present study, it is shown that TiO films with anatase or rutile structure can be grown by pulsed laser deposition(PLD) with an ArF excimer laser under the controlled O
films with anatase or rutile structure can be grown by pulsed laser deposition(PLD) with an ArF excimer laser under the controlled O atmosphere. The TiO
atmosphere. The TiO films were prepared on the LaAlO
films were prepared on the LaAlO , LSAT SrTiO
, LSAT SrTiO and
and  -Al
-Al O
O single crystal substrates. The epitaxial films were analyzed by RBS and X-ray diffraction for investigating the crystallographic relationships with the substrates. The high quality anatase TiO
single crystal substrates. The epitaxial films were analyzed by RBS and X-ray diffraction for investigating the crystallographic relationships with the substrates. The high quality anatase TiO (001) films have been successfully grown on the LaAlO
(001) films have been successfully grown on the LaAlO (001), LSAT (001) and SrTiO
(001), LSAT (001) and SrTiO (001) substrates at temperatures above 500
(001) substrates at temperatures above 500 C. Also the high quality rutile TiO
C. Also the high quality rutile TiO (100) and (001) films were obtained on the
(100) and (001) films were obtained on the  -Al
-Al O
O (0001) and (10-10), respectively.The optical properties were characterized by optical absorption measurements. The optical band gaps for anatase and rutile TiO
(0001) and (10-10), respectively.The optical properties were characterized by optical absorption measurements. The optical band gaps for anatase and rutile TiO epitaxial films were evaluated to be 3.22 eV and 3.11 eV, respectively.
epitaxial films were evaluated to be 3.22 eV and 3.11 eV, respectively.
 films by pulsed laser deposition technique
films by pulsed laser deposition techniqueYamamoto, Shunya; Sumita, Taishi; Sugiharuto; Miyashita, Atsumi; Naramoto, Hiroshi
Thin Solid Films, 401(1-2), p.88 - 93, 2001/12
Times Cited Count:135 Percentile:96.91(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The epitaxial growth of high-quality TiO films has attracted much interest from the viewpoints of basic science and applications. In this study, it is shown that TiO
films has attracted much interest from the viewpoints of basic science and applications. In this study, it is shown that TiO films with anatase and rutile structure can be prepared by pulsed laser deposition (PLD) with a Nd-YAG laser under the controlled O
films with anatase and rutile structure can be prepared by pulsed laser deposition (PLD) with a Nd-YAG laser under the controlled O atmosphere. The TiO
atmosphere. The TiO films with 200 nm thickness were prepared on the SrTiO
films with 200 nm thickness were prepared on the SrTiO , LaAlO
, LaAlO , LSAT and
, LSAT and  -Al
-Al O
O single crystal substrates. The epitaxial films were analyzed by Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) combined with channeling and X-ray diffraction for the crystallographic relationships with the substrates. The high quality anatase TiO
single crystal substrates. The epitaxial films were analyzed by Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) combined with channeling and X-ray diffraction for the crystallographic relationships with the substrates. The high quality anatase TiO (001) films have been successfully prepared on the LaAlO
(001) films have been successfully prepared on the LaAlO (001), LSAT (001) and SrTiO
(001), LSAT (001) and SrTiO (001) substrates about 500
(001) substrates about 500 C substrate temperature. Also the high quality rutile TiO
C substrate temperature. Also the high quality rutile TiO (100) and TiO
(100) and TiO (001) films were obtained on the
(001) films were obtained on the  -Al
-Al O
O (0001) and (10
(0001) and (10 0), respectively.
0), respectively.
Onuki, Toshihiko; Kozai, Naofumi; Samadfam, M.; Yamamoto, Shunya; Narumi, Kazumasa; Naramoto, Hiroshi; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Sakai, Takuro; Murakami, Takashi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 181(1-4), p.644 - 648, 2001/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.43(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
 -anatase film on Si(001) substrate with TiN and SrTiO
-anatase film on Si(001) substrate with TiN and SrTiO as buffer layers
as buffer layersSugiharuto; Yamamoto, Shunya; Sumita, Taishi; Miyashita, Atsumi
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 13(13), p.2875 - 2881, 2001/04
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:60.81(Physics, Condensed Matter)An epitaxial TiO -anatase thin film was grown on the Si(001) substrate with SrTiO
-anatase thin film was grown on the Si(001) substrate with SrTiO /TiN as the buffer layers by pulsed laser deposition technique under an oxygen gas supply. The characterization of the epitaxial TiO
/TiN as the buffer layers by pulsed laser deposition technique under an oxygen gas supply. The characterization of the epitaxial TiO -anatase film was performed using the X-ray diffraction method. The crystallographic relationships between the TiO
-anatase film was performed using the X-ray diffraction method. The crystallographic relationships between the TiO -anatase film and SrTiO
-anatase film and SrTiO /TiN buffer layers were analyzed by the
/TiN buffer layers were analyzed by the  -2
-2 scan and pole figure measurement. The growth direction of the films was determined as
scan and pole figure measurement. The growth direction of the films was determined as 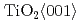 /
/ 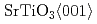 /
/ 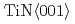 /
/ 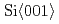 and their in-plane relationship
and their in-plane relationship 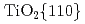 //
// 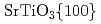 //
// 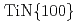 //
// 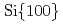 . The crystalline quality of TiO
. The crystalline quality of TiO -anatase was examined by the rocking curve analysis. The composition of the thin film packaging was characterized by Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) using 2.0 MeV
-anatase was examined by the rocking curve analysis. The composition of the thin film packaging was characterized by Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) using 2.0 MeV  He beam.
He beam.
Naramoto, Hiroshi; Yamamoto, Shunya; Narumi, Kazumasa
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 161-163, p.534 - 538, 2000/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:26.58(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Wu, Z. P.*; Miyashita, Atsumi; Yamamoto, Shunya; Abe, Hiroaki; Nashiyama, Isamu; Narumi, Kazumasa; Naramoto, Hiroshi
Journal of Applied Physics, 86(9), p.5311 - 5313, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:60 Percentile:88.31(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Iwase, Akihiro; L.E.Rehn*; P.M.Baldo*; L.Funk*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 271-272, p.321 - 325, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.69(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Sakai, Takuro; ; Hirao, Toshio; Kamiya, Tomihiro; ; ; Matsuyama, Shigeo*; ; Ishii, Keizo*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 136-138, p.390 - 394, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:78.28(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English

Aoki, Yasushi; Yamamoto, Shunya; Takeshita, Hidefumi; Naramoto, Hiroshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 136-138, p.400 - 403, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:52.97(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Yamamoto, Shunya; Naramoto, Hiroshi; Narumi, Kazumasa; Tsuchiya, Bun*; Aoki, Yasushi; Kudo, Hiroshi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 134(3-4), p.400 - 404, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:40.19(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Tsuchiya, Bun*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Narumi, Kazumasa; Aoki, Yasushi*; Naramoto, Hiroshi; Morita, Kenji*
Thin Solid Films, 335(1-2), p.134 - 137, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:15.36(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Onuki, Toshihiko; Kozai, Naofumi; Isobe, Hiroshi; Murakami, Takashi*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Aoki, Yasushi; Naramoto, Hiroshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 34(1), p.58 - 62, 1997/01
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:78.80(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 crystals with RBS/PIXE/XRD
crystals with RBS/PIXE/XRDR.Q.Zhang*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Dai, Z.*; Narumi, Kazumasa; Aoki, Yasushi*; Naramoto, Hiroshi; Miyashita, Atsumi
International Journal of PIXE, 7(3&4), p.265 - 275, 1997/00
no abstracts in English
Yamamoto, Shunya; Naramoto, Hiroshi; Aoki, Yasushi
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 253-254, p.66 - 69, 1997/00
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:43.69(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English