Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sakamoto, Masahiro; Okumura, Keisuke; Kanno, Ikuo; Matsumura, Taichi; Terashima, Kenichi; Riyana, E. S.; Kaneko, Junichi*; Mizokami, Masato*; Mizokami, Shinya*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 10 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Metcalfe, R.*; Tachi, Yukio; Sasao, Eiji; Kawama, Daisuke*
Science of the Total Environment, 957, p.177375_1 - 177375_17, 2024/12
A safety case for an underground radioactive waste repository must show that groundwater will not in future transport radionuclides from the repository to the near-surface environment (the biosphere) in harmful quantities. Safety cases are developed step-wise throughout a programme to site and develop a repository. At early stages, before a site is selected, safety cases are generic and based on simplified safety assessment models of the disposal system that have conservative parameter values. Later, when site-specific conditions are known, more realistic models are needed for the long-term geo-environmental evolution and their impacts on radionuclide migration/retention. Uplift is one such environmental change, which may be particularly important in countries near active tectonic plate boundaries, such as Japan. Here we review the state of knowledge about how the properties of fractured granitic rocks evolve during uplift, based on studies in Japan. Hence, we present conceptual models and a generic scenario for mass transport and retardation processes in uplifting granitic rocks as a basis for realistic numerical models to underpin safety assessment.
Minari, Eriko*; Kabasawa, Satsuki; Mihara, Morihiro; Makino, Hitoshi; Asano, Hidekazu*; Nakase, Masahiko*; Takeshita, Kenji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(7), p.793 - 803, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:41.50(Nuclear Science & Technology)Park, Y.-J.*; Sawada, Atsushi; Ozutsumi, Takenori*; Tanaka, Tatsuya*; Hashimoto, Shuji*; Morita, Yutaka*
Proceedings of 3rd International Conference on Discrete Fracture Network Engineering (DFNE 2022) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2022/00
Safety analysis for underground disposal facilities for high-level radioactive waste requires thorough understanding of long-term groundwater flow and nuclide migration processes in geologic media. In the coastal subsurface systems, groundwater flow is defined by the complex interactions between freshwater of meteoric origin and denser saline water from the sea. In addition, sea levels are expected to fluctuate significantly due to a transgression and regression of the sea over the millions of years for safety analysis. This study presents long-term evolution of groundwater environment such as salinity concentration and flow velocity with focus of the interaction between fractures and matrix blocks in regional and near-field scale analysis framework for groundwater flow and nuclide migration for underground disposal facilities in hypothetical fractured crystalline coastal systems.
Sugiyama, Daisuke*; Nakabayashi, Ryo*; Tanaka, Shingo*; Koma, Yoshikazu; Takahatake, Yoko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(4), p.493 - 506, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.20(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kitamura, Akira
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-020, 164 Pages, 2021/03
Part of JAEA's Thermodynamic Database (JAEA-TDB) for solubility and speciation of radionuclides (JAEA-TDB-RN) for performance assessment of geological disposal of high-level radioactive and TRU wastes has been updated with subsuming the database for geochemical calculations (JAEA-TDB-GC). This report has focused to update JAEA-TDB-RN after selecting change in standard Gibbs free energy of formation (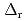
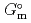 ), change in standard enthalpy change of formation (
), change in standard enthalpy change of formation (


 ), standard molar entropy (
), standard molar entropy (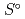
 ) and, heat capacity (
) and, heat capacity (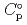 ), change in standard Gibbs free energy of reaction (
), change in standard Gibbs free energy of reaction (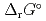
 ), change in standard enthalpy change of reaction (
), change in standard enthalpy change of reaction (
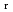


 ) and standard entropy change of reaction (
) and standard entropy change of reaction (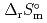 ) as well as logarithm of equilibrium constant (log
) as well as logarithm of equilibrium constant (log
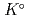 ) at standard state. The extent of selection of these thermodynamic data enables to evaluate solubility and speciation of radionuclides at temperatures other than 298.15 K. Furthermore, the latest thermodynamic data for iron which have been critically reviewed, selected and compiled by the Nuclear Energy Agency within Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD/NEA) have been accepted. Most of previously selected log
) at standard state. The extent of selection of these thermodynamic data enables to evaluate solubility and speciation of radionuclides at temperatures other than 298.15 K. Furthermore, the latest thermodynamic data for iron which have been critically reviewed, selected and compiled by the Nuclear Energy Agency within Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD/NEA) have been accepted. Most of previously selected log
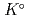 have been refined to confirm internal consistency with JAEA-TDB-GC. Text files of the updated JAEA-TDB have been provided for geochemical calculation programs of PHREEQC and Geochemist's Workbench.
have been refined to confirm internal consistency with JAEA-TDB-GC. Text files of the updated JAEA-TDB have been provided for geochemical calculation programs of PHREEQC and Geochemist's Workbench.
Saito, Tatsuo; Kobayashi, Shinichi*; Zaitsu, Tomohisa*; Shimo, Michikuni*; Fumoto, Hiromichi*
Hoken Butsuri (Internet), 55(2), p.86 - 91, 2020/06
Safety cases for disposal of uranium bearing waste and NORM with uranium has not yet been fully developed in Japan, because of safety assessment of extraordinary long timespan and uncertainty in unexpected incidents with uncompleted radon impact evaluation measures arising from uranium waste disposal facility in far future. Our task group of radiation protection for wastes with natural radioactive nuclides studied some safety cases with disposal of uranium bearing waste and NORM in terms of nuclides, U-235, U-238 and their progenies, and comprehensively discussed the current state of their disposal in comparison to the ideas of international organizations such as ICRP and IAEA. We developed our ideas for long term uncertainty and radon with the knowledge of experts in each related area of direction, repeating discussions, focusing out the orientation of each directions, and outlined the recommendations with our suggestions of solving important issues in the future to be addressed.
Sugiyama, Daisuke*; Nakabayashi, Ryo*; Koma, Yoshikazu; Takahatake, Yoko; Tsukamoto, Masaki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(9-10), p.881 - 890, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.76(Nuclear Science & Technology) U/
U/ U ratio for a trace amount of uranium: Search for an extinct radionuclide
U ratio for a trace amount of uranium: Search for an extinct radionuclide 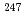 Cm in the early solar system
Cm in the early solar systemChai, J.; Miyamoto, Yutaka; Kokubu, Yoko; Magara, Masaaki; Sakurai, Satoshi; Usuda, Shigekazu; Oura, Yasuji*; Ebihara, Mitsuru*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 272(2), p.397 - 401, 2007/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.25(Chemistry, Analytical)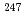 Cm is an important nuclide because it has the next-shortest half-life (1.6
Cm is an important nuclide because it has the next-shortest half-life (1.6 10
10 yr) from
yr) from  Pu among the transuranic nuclides. The disintegration of
Pu among the transuranic nuclides. The disintegration of 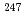 Cm to
Cm to  U by three
U by three  decays and two
decays and two  decays and the chemical fractionation between Cm and U during the formation of solid materials in early solar system lead to changes in the ratios of
decays and the chemical fractionation between Cm and U during the formation of solid materials in early solar system lead to changes in the ratios of  U to
U to  U. This variation may provide strict constraints on the time interval between the last r-process nucleosynthetic event and the formation of the solar system. It is important to develop a practical analysis protocol to determine the isotope ratio of trace uranium in geochemical and environment samples. As uranium is the least abundant element in our solar system, analytical techniques with high sensitivity and precision are required. In this study, a double focusing inductively coupled plasma mass spectory was applied to measure isotopic ratio of uranium. By one set data obtained from the EDTA phase of the Jilin meteorite sample, the upper limit of
U. This variation may provide strict constraints on the time interval between the last r-process nucleosynthetic event and the formation of the solar system. It is important to develop a practical analysis protocol to determine the isotope ratio of trace uranium in geochemical and environment samples. As uranium is the least abundant element in our solar system, analytical techniques with high sensitivity and precision are required. In this study, a double focusing inductively coupled plasma mass spectory was applied to measure isotopic ratio of uranium. By one set data obtained from the EDTA phase of the Jilin meteorite sample, the upper limit of 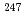 Cm in the early solar system was calculated and
Cm in the early solar system was calculated and 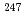 Cm/
Cm/ U
U  0.003 was obtained.
0.003 was obtained.
Yokoyama, Sumi; Sato, Kaoru; Noguchi, Hiroshi; Tanaka, Susumu; Iida, Takao*; Furuichi, Shinya*; Kanda, Yukio*; Oki, Yuichi*; Kaneto, Taihei*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 116(1-4), p.401 - 405, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.17(Environmental Sciences)The physicochemical property of radionuclides suspended in the air is an important parameter to evaluate internal doses due to the inhalation of the airborne radionuclides and to develop the air monitoring system in high-energy proton accelerator facilities. This study focuses on the property of radioactive airborne chlorine ( Cl and
Cl and 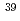 Cl) and sulfur (
Cl) and sulfur ( S) formed from Ar gas by irradiation with high-energy neutrons. As a result of the irradiation to a mixture of Ar gas and dry air,
S) formed from Ar gas by irradiation with high-energy neutrons. As a result of the irradiation to a mixture of Ar gas and dry air,  Cl and
Cl and 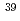 Cl existed as non-acidic gas and
Cl existed as non-acidic gas and  S was present as acidic gas. Further, it was found that in the high-energy neutron irradiation to aerosol containing-Ar gas, the higher the amount of radioactive aerosols becomes, the lower that of radioactive acidic gas becomes.
S was present as acidic gas. Further, it was found that in the high-energy neutron irradiation to aerosol containing-Ar gas, the higher the amount of radioactive aerosols becomes, the lower that of radioactive acidic gas becomes.
; ; Kitao, Kensuke*
JAERI-Data/Code 98-008, 73 Pages, 1998/03
no abstracts in English
Mukaiyama, Takehiko
Genshiryoku eye, 44(2), p.15 - 19, 1998/02
no abstracts in English
Togawa, Orihiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 33(10), p.792 - 803, 1996/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:32.75(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Kimura, Hideo; Takahashi, Tomoyuki; ; Matsuzuru, Hideo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 32(3), p.206 - 217, 1995/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:42.72(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Hisashi; Kanazawa, Katsuo; Fujiki, Kazuo
The 3rd JSME/ASME Joint Int. Conf. on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE),Vol. 4, 0, p.1785 - 1789, 1995/00
no abstracts in English
Kimura, Hideo; Takahashi, Tomoyuki; ; Matsuzuru, Hideo
JAERI-Research 94-028, 50 Pages, 1994/11
no abstracts in English
; ; Kitao, Kensuke*
JAERI-M 94-059, 112 Pages, 1994/03
no abstracts in English
Kimura, Hideo
JAERI-M 92-115, 48 Pages, 1992/08
no abstracts in English
; ; ; ; ; ; Kimura, Hideo; Munakata, Masahiro
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 34(4), p.342 - 364, 1992/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:27.12(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
; Kitao, Kensuke*
JAERI-M 92-051, 115 Pages, 1992/03
no abstracts in English