Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 under hydrostatic pressure; A Combined neutron, X-ray, Raman, and first-principles calculation study
under hydrostatic pressure; A Combined neutron, X-ray, Raman, and first-principles calculation studyEfthimiopoulos, I.*; Klotz, S.*; Kunc, K.*; Baptiste, B.*; Chauvigne, P.*; Hattori, Takanori
Physical Review B, 111(13), p.134103_1 - 134103_13, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We present a comprehensive study of the high pressure behaviour of ReO using X-ray and neutron diffraction, Raman scattering and first-principles calculations to 15 GPa. We show that the ambient pressure
using X-ray and neutron diffraction, Raman scattering and first-principles calculations to 15 GPa. We show that the ambient pressure 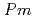
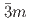 structure converts at 0.7 GPa in a continuous phase transition directly to a cubic phase with space group
structure converts at 0.7 GPa in a continuous phase transition directly to a cubic phase with space group 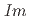
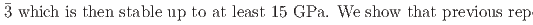 and rhombohedral
and rhombohedral 
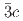 structures in this pressure range are an artifact due to an alteration of the sample by high-flux synchrotron X-ray radiation. The structural pressure dependence of the
structures in this pressure range are an artifact due to an alteration of the sample by high-flux synchrotron X-ray radiation. The structural pressure dependence of the 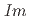
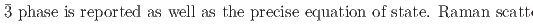 O samples are presented. The data shed light onto the unusual transition and densification mechanism due to progressive tilting of essentially rigid ReO
O samples are presented. The data shed light onto the unusual transition and densification mechanism due to progressive tilting of essentially rigid ReO octahedra.
octahedra.
Arai, Yosuke*; Kuroda, Kenta*; Nomoto, Takuya*; Tin, Z. H.*; Sakuragi, Shunsuke*; Bareille, C.*; Akebi, Shuntaro*; Kurokawa, Kifu*; Kinoshita, Yuto*; Zhang, W.-L.*; et al.
Nature Materials, 21(4), p.410 - 415, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:75.71(Chemistry, Physical)Ikeda, Takashi
Journal of Chemical Physics, 141(4), p.044501_1 - 044501_8, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:51.40(Chemistry, Physical)From both the polarized and depolarized Raman scattering spectra of supercritical water a peak located at around 1600 cm , attributed normally to bending mode of water molecules, was experimentally observed to vanish, whereas the corresponding peak remains clearly visible in the measured infrared (IR) absorption spectrum. In this computational study a theoretical formulation for analyzing the IR and Raman spectra is developed via first principles molecular dynamics combined with the modern polarization theory. We demonstrate that the experimentally observed peculiar behavior of the IR and Raman spectra for water are well reproduced in our computational scheme. We discuss the origins of a feature observed at 1600 cm
, attributed normally to bending mode of water molecules, was experimentally observed to vanish, whereas the corresponding peak remains clearly visible in the measured infrared (IR) absorption spectrum. In this computational study a theoretical formulation for analyzing the IR and Raman spectra is developed via first principles molecular dynamics combined with the modern polarization theory. We demonstrate that the experimentally observed peculiar behavior of the IR and Raman spectra for water are well reproduced in our computational scheme. We discuss the origins of a feature observed at 1600 cm in Raman spectra of ambient water.
in Raman spectra of ambient water.
Gordon, E. B.*; Kumada, Takayuki; Ishiguro, Masazumi; Aratono, Yasuyuki
Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Physics, 99(4), p.776 - 783, 2004/10
The solid Deuterium clusters for the first time isolated in a matrix of solid Helium have been investigated at T = 1.3K and P = 3 MPa by CARS (Coherent anti-Stokes Raman spectroscopy) technique. The Q1(J=0) and Q1(J=1) lines intensity, shape and positions have been studied as the functions of ortho- para content in the solid, as well as of clusters size. The strong effect of Raman scattering cross section sensitivity to the molecular environment nuclear spin state has been found in CARS; the ratio of probabilities for the scattering by para (J=1) and ortho (J=0) deuterium being equal to 1 in a gas is as high as 10,000 in nearly pure o-D2, whereas it is about 50 in spontaneous Raman scattering. This effect has been shown to give rise starting from cluster size corresponding to the phonon band onset.
Kohara, Shinji*; Suzuya, Kentaro; Takeuchi, Ken*; Loong, C.-K.*; Grimsditch, M.*; Weber, J. K. R.*; Tangeman, J. A.*; Key, T. S.*
Science, 303(5664), p.1649 - 1652, 2004/03
Times Cited Count:162 Percentile:95.93(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Inorganic glasses normally exhibit a network of interconncted covalent-bonded structural elements that has no long-range order. In silicate glasses the network formers are based on SiO -tetrahedra interconnected via oxygen atoms at the corners. Conventional wisdom then implies that alkaline and alkaline-earth orthosilicate materials cannot be vitrified because they do not contain sufficient network forming SiO
-tetrahedra interconnected via oxygen atoms at the corners. Conventional wisdom then implies that alkaline and alkaline-earth orthosilicate materials cannot be vitrified because they do not contain sufficient network forming SiO to establish the needed interconnectivity. We have studied a bulk magnesium orthosilicate glass obtained by containerless melting-and-cooling. We find that the role of network former is largely taken on by corner- and edge-sharing of highly distorted ionic Mg-O species that adopt 4-, 5- and 6-coordination with oxygen. The results suggest that similar novel glassy phases may be found in the containerless environment of interstellar space.
to establish the needed interconnectivity. We have studied a bulk magnesium orthosilicate glass obtained by containerless melting-and-cooling. We find that the role of network former is largely taken on by corner- and edge-sharing of highly distorted ionic Mg-O species that adopt 4-, 5- and 6-coordination with oxygen. The results suggest that similar novel glassy phases may be found in the containerless environment of interstellar space.
Baba, Yuji
Radioisotopes, 47(3), p.240 - 247, 1998/03
no abstracts in English
Sasaki, Teikichi
Hoshako, 9(3), p.233 - 243, 1996/06
no abstracts in English
Yokoyama, Keiichi; Kobayashi, Takanori*
no journal, ,
We report a consideration on the non-linear optical response of molecules rotationally excited by impulsive Raman scattering. An ensemble of molecules which are cascadedly excited and de-excited among the rotational levels by a several numbers of Raman transitions is not uniform in spatial coherence and depend on the number of transition the molecule undergoes. Therefore, there is a possibility to obtain signal waveforms which cannot be explained by the conventional analysis method which ignores the non-locality of the density operator. In this study, we adopted non-local density operator to calculate non-linear optical response in such case. As a result, we predicted that significant angular dependence of observed signal appear due to the spherical wave of input pump laser pulse. We qualitatively confirmed the analysis reproduce the observed waveform.
Yokoyama, Atsushi
no journal, ,
Bustard et al. proposed a technique for molecular alignment and orientation named a hybrid Raman scattering technique, in which a weak, linearly polarized short pump pulse creates a rotational coherence, and then a circularly polarized amplification pulse enhances the rotational coherence by transient stimulated Raman scattering. We simulate the degree of alignment for N by solving time-dependent Schr
by solving time-dependent Schr dinger equations and examined the possibility of the enhancement by this technique. The degree of alignment is enhanced, when right-circularly polarized photons scatters to left-circularly polarized photon. On the other hand, it is suppressed when left-circularly polarized photons scatters to right-circularly polarized photon.
dinger equations and examined the possibility of the enhancement by this technique. The degree of alignment is enhanced, when right-circularly polarized photons scatters to left-circularly polarized photon. On the other hand, it is suppressed when left-circularly polarized photons scatters to right-circularly polarized photon.