Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Rodriguez, D.; 赤松 駿介*; Rossi, F.; 鈴木 敏*; 高橋 時音
Proceedings of 65th Annual Meeting of the Institute of Nuclear Materials Management (Internet), 9 Pages, 2024/07
Under the MEXT subsidy to promote nuclear security related activities, we will present the preliminary results from the new Fission Signature Assay Instrument that was fabricated and fully installed in November 2023. We will describe the instrument within the context of the JAEA-JRC collaboration development and the experimental activities planned with it in the larger context of finishing off Phase-III development.
Kyffin, J.*; Dia, A.*; Nkosi, G.*; Nizhnik, V.*; 林 昭彦; 長谷 竹晃
Proceedings of 65th Annual Meeting of the Institute of Nuclear Materials Management (Internet), 8 Pages, 2024/07
In collaboration with the Japan Safeguards Office, the Nuclear Material Control Centre, and the JAEA, the IAEA Department of Safeguards is implementing a new neutron detector system for the verification of plutonium hold-up in process gloveboxes at MOX fuel fabrication facilities in Japan. The previous verification technique utilised the so-called Super Glove Box Assay System (SBAS), which, while capable of detecting partial defects, is a heavy and bulky detector system that requires both significant operator support for safe assembly and positioning, and long measurement times. The recent development of a detector system based on two Plutonium Neutron Coincidence Collar (PNCL) miniature neutron slabs provides the capability of detecting gross defects with semi-quantitative plutonium mass measurement, and is sufficient in respect to inspections for timeliness purposes. For regular use, the Mini-slab detector offers several advantages, including improved safety, reduced operator support requirements and shorter measurement times. The Mini-slab detector satisfies the required verification role with a quarter of the inspector-days compared to SBAS. Furthermore, it has the capability to measure in tighter spaces, with the need for such use expected to grow as parts of these facilities begin decommissioning.
Rodriguez, D.; Rossi, F.; 高橋 時音
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 71(3), p.255 - 268, 2024/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Under the MEXT subsidy to improve nuclear security related capabilities, we are developing the delayed gamma-ray spectroscopic analysis technique. One goal is to develop an inverse Monte Carlo analysis method using spectra from simulations of the interrogation instrument for comparison to the actual measured spectra. This work presents the validity of the Monte Carlo foundation of the analysis compared to experimental results and other simulation codes.
Rodriguez, D.; 赤松 駿介*; Rossi, F.; 鈴木 敏*; 高橋 時音
第44回日本核物質管理学会年次大会会議論文集(インターネット), 4 Pages, 2023/11
Under the MEXT subsidy for improving nuclear material security related activities, we present the latest JAEA/ISCN delayed gamma-ray instrument, FSAI; preliminary characterization results; and the experimental and analysis development activities planned using it.
Rodriguez, D.; Abbas, K.*; Bertolotti, D.*; Bonaldi, C.*; Fontana, C.*; 藤本 正己*; Geerts, W.*; 小泉 光生; Macias, M.*; Nonneman, S.*; et al.
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Annual Meeting 2023 (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/05
Under the MEXT subsidy to improve nuclear security related activities, we present the overview of the JAEA-JRC delayed gamma-ray spectroscopic analysis project. We describe past results, recent joint experiments, and the final goals for this project.
Rossi, F.; 小泉 光生; Rodriguez, D.; 高橋 時音
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Annual Meeting 2023 (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/05
Since 2015, the Integrated Support Center for Nuclear Nonproliferation and Nuclear Security (ISCN) of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been working on the development of the Delayed Gamma-ray Spectroscopy non-destructive assay technique for the quantification of fissile-nuclide content in mixed nuclear materials. Thanks to the efforts and lessons learned from past experiments, the ISCN has successfully designed and fabricated a final integrated instrument. The instrument is composed of a moderator and dose shield where different neutron sources, like Cf-252 and neutron generators, can be inserted to irradiate the sample. Within the moderator, a series of neutron detectors are installed for perform prompt neutron analysis and continuous monitoring of the neutron source emission. Thanks to an innovative transfer system, the sample is then moved to the gamma-ray detector in less than 1.5s providing a fast and reliable movement while being safe from possible contamination. In this work, we will describe the design details of this new instrument. This work is supported by the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT) under the subsidy for the "promotion for strengthening nuclear security and the like".
青木 里英; 白藤 雅也; 野崎 天生; 阿久津 成美*; 宮地 紀子; 中村 仁宣
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Annual Meeting 2023 (Internet), 7 Pages, 2023/05
In order to ensure transparency in the peaceful use of nuclear materials in Japan, it is important to appropriately respond to safeguards activities conducted by the IAEA/Japan. In order to strengthen activities to appropriately respond to safeguards activities, JAEA has started the following one activity of (1) for all employees in JAEA to promote understanding and raise awareness of safeguards and three activities of (2) for the employees involved in safeguards activities to appropriately respond on-site to the activities since FY2020: (1) Education on the basis of safeguards, (2-1) Lectures, (2-2) Case studies and (2-3) Standardization of procedures related to safeguards response. In Activity (1), the employees were required to understand Safeguards framework, safeguards activities and provisions of information to Nuclear Regulation Authority in Japan with developed education material, and to pass a confirmation test in FY2022. Accordingly, it was confirmed that understanding for safeguards was successfully promoted since 100% employees passed the test. In Activity (2-1), lectures were provided by experts of safeguards to make the employees reacknowledged the importance of transparency in the peaceful use of nuclear materials and the effect of inappropriate response to safeguards activities. In Activity (2-2), a material for case studies was developed including examples of inappropriate response to safeguards activities and the case studies were conducted by the employees based on the material for recognizing familiar risks of safeguards. The result of questionnaire in FY2022 indicated participants tended to become deeply understanding of familiar risk in each site through the case studies. In Activity (2-3), standard safeguards procedure for whole JAEA was developed to improve the procedures in each site based on the standard procedure and to standardize the response to safeguards throughout JAEA.
Rodriguez, D.; 小泉 光生; Rossi, F.; 高橋 時音
Proceedings of 2022 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium, Medical Imaging Conference and Room Temperature Semiconductor Detector Conference (2022 IEEE NSS MIC RTSD) (Internet), 3 Pages, 2022/12
Under the MEXT subsidy to improve nuclear security related activity, we present our latest analytical development of delayed gamma spectroscopic (DGS) analysis for nuclear safeguards. We show the latest results from the ISCN DGS Monte Carlo and comparisons with measured spectra. We highlight differences with other simulation codes, which highlights discrepancies in fission yields from nuclear data and our future direction to improve this for optimal safeguards measurements and reduced uncertainty. We will also summarize how the analysis will be applied with a new instrument designed for small samples for validation of the DGS technique, as well as how this can be applied to full assemblies and alternative fuel cycles.
Rossi, F.; 小泉 光生; Rodriguez, D.; 高橋 時音
Proceedings of 2022 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium, Medical Imaging Conference and Room Temperature Semiconductor Detector Conference (2022 IEEE NSS MIC RTSD) (Internet), 2 Pages, 2022/11
To address challenges in the safeguard field for the verification of mixed nuclear materials, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency is developing the Delayed Gamma-ray Spectroscopy non-destructive assay technique. Minimally, this technique requires an external source to induce fission in the sample and a gamma-ray detector to collect the high-energy gamma rays emitted from the decay of fission products. In the development of this technique, deuterium-deuterium neutron generators will replace  Cf as the external neutron source. The emitted neutrons are then slowed down in the thermal energy range to enhance the delayed gamma-ray signature coming from the fissile nuclides in the sample. The fission product delayed gamma rays with energy above 3 MeV are then collected with a detector located away from the irradiation position to avoid neutron damage. The collected spectrum is then analyzed, and the peak ratios are used to verify the initial composition of the fissile nuclides. Further, source monitors are required to normalize for the source emission to estimate the fissile mass of the sample. In this work, we will first describe our latest development in designing a delayed gamma-ray spectrometer for small mixed nuclear material samples. We will present latest results obtained from activation experiment and neutron detector characterization. Finally, we will present the usage of a new transfer system designed, fabricated, and tested at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency laboratories. This work is supported by MEXT under the subsidy for the "promotion for strengthening nuclear security and the like". This work was done under the agreement between JAEA and EURATOM in the field of nuclear material safeguards research and development.
Cf as the external neutron source. The emitted neutrons are then slowed down in the thermal energy range to enhance the delayed gamma-ray signature coming from the fissile nuclides in the sample. The fission product delayed gamma rays with energy above 3 MeV are then collected with a detector located away from the irradiation position to avoid neutron damage. The collected spectrum is then analyzed, and the peak ratios are used to verify the initial composition of the fissile nuclides. Further, source monitors are required to normalize for the source emission to estimate the fissile mass of the sample. In this work, we will first describe our latest development in designing a delayed gamma-ray spectrometer for small mixed nuclear material samples. We will present latest results obtained from activation experiment and neutron detector characterization. Finally, we will present the usage of a new transfer system designed, fabricated, and tested at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency laboratories. This work is supported by MEXT under the subsidy for the "promotion for strengthening nuclear security and the like". This work was done under the agreement between JAEA and EURATOM in the field of nuclear material safeguards research and development.
Rodriguez, D.; 小泉 光生; Rossi, F.; 高橋 時音; Abbas, K.*; Nonneman, S.*; Pedersen, B.*; Oberstedt, S.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*
Proceedings of International Safeguards; Reflecting on the Past and Anticipating the Future, 7 Pages, 2022/10
Under the MEXT subsidy to develop nuclear security, the ISCN is investigating the Delayed Gamma-ray Spectroscopic analysis technique to evaluate mixed nuclear materials. Primarily we are focusing on developing the analysis for any form of mixed nuclear material, but dominantly used nuclear fuel that is challenging due to the long-lived fission products and minor actinides hiding the U and Pu signatures. We describe the analysis we are developing and the associated instrumentation to interrogate the sample. We show that this can be applied to small samples and assemblies, as well as alternative fuel cycle materials.
Rodriguez, D.; Abbas, K.*; 小泉 光生; Nonneman, S.*; Oberstedt, S.*; Pedersen, B.*; Rossi, F.; Schillebeeckx, P.*; 高橋 時音
Proceedings of INMM 63rd Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2022/09
Under the MEXT subsidy to develop nuclear security related technology, we present the overview and ISCN analysis development of the Delayed Gamma-ray Spectroscopic Analysis project. We summarize the past analysis and instrumentation results and highlight how this affects the evaluation of fissile nuclides in spent nuclear fuel. We further discuss the direction of the third development phase.
Rossi, F.; 小泉 光生; Rodriguez, D.; 高橋 時音
Proceedings of INMM 63rd Annual Meeting (Internet), 5 Pages, 2022/07
With the initial goal of fissile-nuclide content quantification in small samples containing uranium and plutonium, the Integrated Support Center for Nuclear Nonproliferation and Nuclear Security of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency is developing the Delayed Gamma-ray Spectroscopy non-destructive assay technique. For this, while in the past years several experiments were conducted to prove the feasibility of the technique, a new instrument was designed considering the previous lessons learned. It includes a modular insertion for different neutron sources, like radioisotopes or neutron generators; a gamma-ray detector with improved data acquisition system allowing for real-time dead-time correction; and a full new mechanism for the sample transfer between irradiation and measurement. Together with this, neutron detectors are integrated to supplement the DGS mass analysis and monitor the source intensity. In this work, we will describe the new instrument and the preliminary results obtained from instrument characterization compared to previous experiments. This work is supported by the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT) under the subsidy for the "promotion for strengthening nuclear security and the like". This work was done under the agreement between JAEA and EURATOM in the field of nuclear material safeguards research and development.
中谷 隆良; 清水 亮; 田崎 真樹子; 木村 隆志; 玉井 広史; 須田 一則
第42回日本核物質管理学会年次大会会議論文集(インターネット), 4 Pages, 2021/11
現在、原子力機構は保有する原子力施設の廃止措置を進めているところであり、対象には核物質を保有している施設もある。廃止措置作業では、核燃料物質を含む発生する放射性廃棄物の処理や保障措置終了手法も含め、核不拡散・透明性を維持しつつ、合理的な手法の検討は必要である。本研究では、国際原子力機関(IAEA)が整備するSafeguards by Design (SBD: 設計段階からの保障措置の検討)のガイダンス等を参考に、廃棄物処理に関して上記課題を考察する。
Rodriguez, D.; Abbas, K.*; 小泉 光生; Nonneman, S.*; Rossi, F.; 高橋 時音
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1014, p.165685_1 - 165685_10, 2021/10
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:43.33(Instruments & Instrumentation)Under the MEXT subsidy on research for improving nuclear security related development, we designed the Delayed Gamma-ray Californium Test (DGCT) instrument. From He-3 count-rate experiments performed in collaboration with the European Commission Joint Research Centre, we show the effective neutron flux entering the sample space. Further, we show delayed gamma-ray spectra of both U and Pu samples as well as a comparison to the background from Cf activation of the environment. Finally, we make comparisons to earlier spectra obtained using PUNITA, including relative fission capability, spectral signature, and mass correlations.
Rossi, F.; Abbas, K.*; 小泉 光生; Lee, H.-J.; Rodriguez, D.; 高橋 時音
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Virtual Annual Meeting (Internet), 7 Pages, 2021/08
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency is developing the Delayed Gamma-ray Spectroscopy (DGS) non-destructive assay technique to quantify the fissile-nuclide content in small samples of mixed nuclear materials. One of our primary goals is to develop a compact and efficient DGS instrument to be easily installable into analytical laboratories. The instrument should include an external neutron source and a gamma-ray detection system along with other supporting systems like sample transfer and neutron monitoring. One of the challenges is to design a compact and efficient moderator for commercial neutron sources (e.g. neutron generators or sealed radioactive sources) that emit neutrons with high energy. However, to be able to enhance the gamma-ray signal from fissile materials, thermal neutrons are best due to their higher fission cross-sections. The choice of viable neutron source (neutron spectrum and strength) depends on several considerations (e.g. sample type and interrogation pattern), but also affect the gamma-ray measurement and the consequence analysis. In this work, we will first describe the evaluation results of our Delayed Gamma-ray Test Spectrometer using a  Cf source (DGTS-C) from the first experiment carried out in PERLA in collaboration with the European Commission, Joint Research Centre. In association, we will describe how it provided guidance for our demonstration irradiator. Further, we will present our final moderator design concept for a deuterium-deuterium (D-D) neutron generator and present the latest results of data-model comparisons, including those with our PUNITA results. This work is supported by the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT) under the subsidy for the "promotion for strengthening nuclear security and the like". This work was done under the agreement between JAEA and EURATOM in the field of nuclear material safeguards research and development.
Cf source (DGTS-C) from the first experiment carried out in PERLA in collaboration with the European Commission, Joint Research Centre. In association, we will describe how it provided guidance for our demonstration irradiator. Further, we will present our final moderator design concept for a deuterium-deuterium (D-D) neutron generator and present the latest results of data-model comparisons, including those with our PUNITA results. This work is supported by the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT) under the subsidy for the "promotion for strengthening nuclear security and the like". This work was done under the agreement between JAEA and EURATOM in the field of nuclear material safeguards research and development.
Rodriguez, D.; Bogucarska, T.*; 小泉 光生; Lee, H.-J.; Pedersen, B.*; Rossi, F.; 高橋 時音; Varasano, G.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 997, p.165146_1 - 165146_13, 2021/05
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:24.88(Instruments & Instrumentation)Under the MEXT subsidy to strengthen nuclear security related research, the ISCN is developing delayed gamma-ray spectroscopy (DGS) for nuclear safeguards. Here we present results from experiments using the PUNITA instrument in collaboration with JRC-Ispra to evaluate the gamma-ray spectral dependence on interrogation time patterns and number of cycles. Specifically, we investigated the observable gamma rays useful to quantify the  Pu and
Pu and  U contributions. Of the time patterns tested in this study, we determined that irradiating the sample for 60-
U contributions. Of the time patterns tested in this study, we determined that irradiating the sample for 60- followed by a gamma-ray measurement of 60-
followed by a gamma-ray measurement of 60- was the best for a comparable one-hour total interrogation time.
was the best for a comparable one-hour total interrogation time.
Rossi, F.; 小泉 光生; Lee, H.-J.; Rodriguez, D.; 高橋 時音; Abbas, K.*; Bogucarska, T.*; Crochemore, J.-M.*; Pedersen, B.*; Varasano, G.*
61st Annual Meeting of the Institute of Nuclear Materials Management (INMM 2020), Vol.2, p.907 - 911, 2021/00
Delayed Gamma-ray Spectroscopy (DGS) is a nondestructive assay technique with the capability to quantify the fissile composition of small nuclear material samples from reprocessing plants. In recent years, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency in collaboration with the Joint Research Centre performed several experiments using uranium and plutonium standard samples. In this paper, we present some of our recent experiment results showing the feasibility of DGS for fissile mass estimation. In particular, we interrogate uranium samples of different enrichment and we are showing that we were able to qualify significant peaks even for a depleted uranium sample above 2.7 MeV. Applying correction factors for neutron self-shielding and gamma self-absorption, we obtained a mass linear correlation when considering total integrated counts above 3.3 MeV as well as specific individual peak counts. This work is supported by the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT) under the subsidy for the "promotion for strengthening nuclear security and the like". This work was done under the agreement between JAEA and EURATOM in the field of nuclear material safeguards research and development.
Rodriguez, D.; 小泉 光生; Rossi, F.; 瀬谷 道夫; 高橋 時音; Bogucarska, T.*; Crochemore, J.-M.*; Pedersen, B.*; 高峰 潤
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(8), p.975 - 988, 2020/08
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:34.76(Nuclear Science & Technology)Present safeguards verification methods of high-radioactivity nuclear material use destructive analysis techniques since passive nondestructive techniques are incapable of determining the nuclear material content. To improve this verification process, the JAEA and EC-JRC Ispra, Italy have been collaborating to develop delayed gamma-ray spectroscopy for composition analysis of the fissile nuclides as an aspect of the MEXT subsidy for improving nuclear security and the like. Multiple experiments were performed over three years using PUNITA to interrogate U and Pu samples to determine the signature from the short-lived fission products. We observed many gamma rays useful to determine the composition of a mixed nuclear material sample. Presented here are the results of these measurements with correlations to the interrogation, mass, volume, and sample homogeneity.
青木 健; Chirayath, S. S.*; 相楽 洋*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 141, p.107325_1 - 107325_7, 2020/06
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:17.49(Nuclear Science & Technology)PREATORコード及び68の属性入力データを用いて、高温ガス炉のTRU燃料サイクルにおける不活性母材燃料の核拡散抵抗性を評価し、軽水炉を用いたウラン-プルトニウム混合酸化物(MOX)燃料サイクルと比較した。本研究の目的は不活性母材燃料の化学的安定性や燃料照射による核拡散抵抗性に対する影響を同定することである。不活性母材燃料特有の低いプルトニウム含有量や黒鉛セラミックス被覆、 U不使用といった物質的特性がMOX燃料に対する相対的な核拡散抵抗性の向上に寄与することを明らかにした。また未照射不活性母材燃料(1か月の転用適時性検知目標を有する未照射直接使用物質)の包括的核拡散抵抗値は照射済MOX燃料(3か月の転用適時性検知目標を有する照射済照射直接使用物質)と同程度であることを明らかにした。最終結果は不活性母材燃料の管理における保障措置の査察頻度の低減を示唆している。
U不使用といった物質的特性がMOX燃料に対する相対的な核拡散抵抗性の向上に寄与することを明らかにした。また未照射不活性母材燃料(1か月の転用適時性検知目標を有する未照射直接使用物質)の包括的核拡散抵抗値は照射済MOX燃料(3か月の転用適時性検知目標を有する照射済照射直接使用物質)と同程度であることを明らかにした。最終結果は不活性母材燃料の管理における保障措置の査察頻度の低減を示唆している。
 Cf for safeguards verification measurements
Cf for safeguards verification measurementsRodriguez, D.; Rossi, F.; 高橋 時音; 瀬谷 道夫; 小泉 光生
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 148, p.114 - 125, 2019/06
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:47.17(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Delayed gamma-ray spectroscopy is an active-NDA technique used to determine the composition of HRNM samples by peak-ratio comparison of GRs above 3-MeV from the short-lived fission products. Filtering out the passive GRs from long-lived FPs reduces the DGS signal, so thermal neutrons are used to induce more fission events from fissile nuclides. We are developing a compact system to moderate  2-MeV neutrons that are easier to moderate than 14-MeV neutrons from DT generators. This work describes the ideal moderator optimization for a
2-MeV neutrons that are easier to moderate than 14-MeV neutrons from DT generators. This work describes the ideal moderator optimization for a  Cf source that results in
Cf source that results in 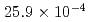 cm
cm
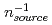 passing through the sample space with
passing through the sample space with  70% of those below 1-eV. Practical modifications resulted in
70% of those below 1-eV. Practical modifications resulted in  20% reductions compared to the optimized design. Evaluations of DGS signals and backgrounds conclude that only a 21-MBq
20% reductions compared to the optimized design. Evaluations of DGS signals and backgrounds conclude that only a 21-MBq  Cf source is required.
Cf source is required.