Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ito, Tatsuya; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kuwano, Ryo*; Godo, Masao*; Yoshida, Yoichi*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 226, p.112198_1 - 112198_5, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)In recent years, the use of radiation-resistant resins of polyimide and polyether ether ketone becomes increasing as vessels for irradiation and unsealed radioisotope experiments. However, in our radiolysis experiments, the possibility of interaction between radiolysis products of water and the resin was found, suggesting concerns that the resin may affect reactions in water in radiation fields. To clarify the interaction, dichromate (Cr O
O
 ) reduction and hydrogen peroxide (H
) reduction and hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) formation in
) formation in  -radiolysis of water were compared with and without the resin. The Cr
-radiolysis of water were compared with and without the resin. The Cr O
O
 reduction amount in aqueous solution with the resin became larger than that without the resin at the same dose, indicating the promotion of Cr
reduction amount in aqueous solution with the resin became larger than that without the resin at the same dose, indicating the promotion of Cr O
O
 reduction by the resin. On the other hand, the H
reduction by the resin. On the other hand, the H O
O formation in pure water with and without an electron scavenger were almost independent of the presence of resin. These suggested the interaction between hydroxyl radical and the resin in contact with water in radiation fields.
formation in pure water with and without an electron scavenger were almost independent of the presence of resin. These suggested the interaction between hydroxyl radical and the resin in contact with water in radiation fields.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tokyo Institute of Technology*
JAEA-Review 2024-022, 59 Pages, 2024/09
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2022, this report summarizes the research results of the "Investigation of effects of nano interfacial phenomena on dissolution aggregation of alpha nanoparticles by using micro nano technologies" conducted in FY2022. To ensure the safety of retrieval and storage management of nuclear fuel debris generated by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident, understanding of dissolution-denaturation behavior of the fuel debris alpha particles is one of the most crucial issues. This research aims to create novel microfluidic real-time measurement device for elucidating dissolution, aggregation, and denaturation processes of metal oxide nanoparticles under various solution environments, and clarify their nano-size and interfacial effects.
Watanabe, Tomoaki; Yamane, Yuichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(7), p.958 - 966, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The total fission energy released in a criticality accident involving fissile solution boiling tends to be high because the relatively high fission power continues during boiling. Simulating fission power change correctly during boiling seems essential to estimate the total fission energy. Fission power during boiling changes depending on fissile concentration and volume as the solution evaporates. In this study, we investigated the effect of concentration and volume change on estimated total fission energy for a long time of boiling. We introduced a model calculating the evaporation of fissile solution into the modified quasi-steady-state method to simulate power change during boiling. Three CRAC experiments and the Idaho Chemical Processing Plant (ICPP) criticality accident in 1959 were analyzed. As a result, the calculated energy considering concentration and volume change during boiling reproduced the measured energy well.
 Li-glass detector to gamma rays by a coincidence method
Li-glass detector to gamma rays by a coincidence methodIto, Fumiaki*; Lee, J.; Hironaka, Kota; Takahashi, Tone; Suzuki, Satoshi*; Mochimaru, Takanori*; Hori, Junichi*; Terada, Kazushi*; Koizumi, Mitsuo
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1064, p.169465_1 - 169465_9, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Koyama, Shinichi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 66(2), p.74 - 78, 2024/02
, 66(2), p.74 - 78, 2024/02
For the steady removal of fuel debris from the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), it is an urgent issue to establish analysis technology and systems for fuel debris samples with unknown properties (unknown samples). For this purpose, through analysis tests using samples with known properties (simulated fuel debris) and discussions among experts, the validity of analysis results and the factors that cause errors has been identified. In addition to knowing the current level of analysis accuracy, studies are being conducted to understand and improve the influencing factors. This paper introduces a part of the development of infrastructure for analysis and evaluation technology of "nuclides and element content."
Kinoshita, Ryoma; Sasaki, Yuji; Kaneko, Masashi; Matsumiya, Masahiko*; Shinoku, Kota*; Shiroishi, Hidenobu*
Hydrometallurgy, 222, p.106159_1 - 106159_12, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:23.52(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Solvent extraction is conducted using a total of 20 metals revealing high stability constants with Cl and hexahexyl-nitrilotriacetamide (NTAamide(C6)) extractant. The metals used here may behave as anions at high Cl concentrations, and NTAamide(C6), which contains a tertiary N atom, is protonated under acidic conditions. Most of the metal ions in this study display higher distribution ratios (D(M)) from HCl than those from HNO , and exhibit 1:1 stoichiometries with NTAamide. Following the experimental results, the association constants and distribution coefficients of the group 12 elements are calculated via ion-pair extraction modeling using density functional theory calculations, and the simulations of D yield calculated values with the same trend as that of the measured values.
, and exhibit 1:1 stoichiometries with NTAamide. Following the experimental results, the association constants and distribution coefficients of the group 12 elements are calculated via ion-pair extraction modeling using density functional theory calculations, and the simulations of D yield calculated values with the same trend as that of the measured values.
 dissolution in bicarbonate solution with H
dissolution in bicarbonate solution with H O
O ; The Effect of temperature
; The Effect of temperatureMcGrady, J.; Kumagai, Yuta; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Kirishima, Akira*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Watanabe, Masayuki
RSC Advances (Internet), 13(40), p.28021 - 28029, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.35(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Upon nuclear waste canister failure and contact of spent nuclear fuel with groundwater, the UO matrix of spent fuel will interact with oxidants in the groundwater generated by water radiolysis. Bicarbonate (HCO
matrix of spent fuel will interact with oxidants in the groundwater generated by water radiolysis. Bicarbonate (HCO
 ) is often found in groundwater, and the H
) is often found in groundwater, and the H O
O induced oxidative dissolution of UO
induced oxidative dissolution of UO in bicarbonate solution has previously been studied under various conditions. Temperatures in the repository at the time of canister failure will differ depending on the location, yet the effect of temperature on oxidative dissolution is unknown. To investigate, the decomposition rate of H
in bicarbonate solution has previously been studied under various conditions. Temperatures in the repository at the time of canister failure will differ depending on the location, yet the effect of temperature on oxidative dissolution is unknown. To investigate, the decomposition rate of H O
O at the UO
at the UO surface and dissolution of U
surface and dissolution of U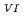 in bicarbonate solution (0.1, 1, 10 and 50 mM) was analysed at various temperatures (10, 25, 45 and 60
in bicarbonate solution (0.1, 1, 10 and 50 mM) was analysed at various temperatures (10, 25, 45 and 60  C). At [HCO
C). At [HCO
 ]
] 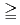 1 mM, the apparent equilibrium concentration of U
1 mM, the apparent equilibrium concentration of U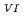 decreased with increasing temperature. This was attributed to the formation of U
decreased with increasing temperature. This was attributed to the formation of U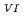 -bicarbonate species at the surface and a change in the mechanism of H
-bicarbonate species at the surface and a change in the mechanism of H O
O decomposition from oxidative to catalytic. At 0.1 mM, no obvious correlation between temperature and U dissolution was observed, and thermodynamic calculations indicated this was due to a change in the surface species. A pathway to explain the observed dissolution behaviour of UO
decomposition from oxidative to catalytic. At 0.1 mM, no obvious correlation between temperature and U dissolution was observed, and thermodynamic calculations indicated this was due to a change in the surface species. A pathway to explain the observed dissolution behaviour of UO in bicarbonate solution as a function of temperature was proposed.
in bicarbonate solution as a function of temperature was proposed.
 pellet in molten Zr cladding
pellet in molten Zr claddingIto, Ayumi*; Yamashita, Susumu; Tasaki, Yudai; Kakiuchi, Kazuo; Kobayashi, Yoshinao*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(4), p.450 - 459, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Suzuki, Tomoya*; Otsubo, Ukyo*; Ogata, Takeshi*; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Kobayashi, Toru; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Matsuoka, Mitsuaki*; Murayama, Norihiro*; Narita, Hirokazu*
Separation and Purification Technology, 308, p.122943_1 - 122943_7, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:15.39(Engineering, Chemical)HNO leaching is used in recycling Pd metal from spent products that primarily contain Ag, and most Pd residues are separated from solutions containing Ag(I). However, a small amount of Pd(II) often remains in these Ag(I) solutions. Therefore, the separation of Pd(II) and Ag(I) in HNO
leaching is used in recycling Pd metal from spent products that primarily contain Ag, and most Pd residues are separated from solutions containing Ag(I). However, a small amount of Pd(II) often remains in these Ag(I) solutions. Therefore, the separation of Pd(II) and Ag(I) in HNO solutions is essential to promote efficient Pd recycling. In this study, the separation of Pd(II) and Ag(I) in HNO
solutions is essential to promote efficient Pd recycling. In this study, the separation of Pd(II) and Ag(I) in HNO solutions was investigated using four N-donor-type adsorbents functionalized with amine (R-Amine), iminodiacetic acid (R-IDA), pyridine (R-Py), or bis-picolylamine (R-BPA). R-Amine, R-IDA, and R-Py selectively adsorbed Pd(II) over Ag(I), Cu(II), Ni(II), and Fe(III) from HNO
solutions was investigated using four N-donor-type adsorbents functionalized with amine (R-Amine), iminodiacetic acid (R-IDA), pyridine (R-Py), or bis-picolylamine (R-BPA). R-Amine, R-IDA, and R-Py selectively adsorbed Pd(II) over Ag(I), Cu(II), Ni(II), and Fe(III) from HNO solutions (0.3-7 M), but R-Amine exhibited a lower Pd adsorption efficiency. In contrast,
solutions (0.3-7 M), but R-Amine exhibited a lower Pd adsorption efficiency. In contrast,  90% of Pd(II), Ag(I), and Cu(II) were adsorbed by R-BPA over the entire range of HNO
90% of Pd(II), Ag(I), and Cu(II) were adsorbed by R-BPA over the entire range of HNO concentrations. Structural analyses of the adsorbed metal ions using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy revealed the separation mechanisms of the N-donor-type adsorbents. Pd(II) adsorption on R-IDA, R-Py, and R-BPA occurred via Pd(II) coordination of the functional groups (iminodiacetic acid, pyridine, and bis-picolylamine, respectively), whereas that on R-Amine occurred via anion exchange of NO
concentrations. Structural analyses of the adsorbed metal ions using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy revealed the separation mechanisms of the N-donor-type adsorbents. Pd(II) adsorption on R-IDA, R-Py, and R-BPA occurred via Pd(II) coordination of the functional groups (iminodiacetic acid, pyridine, and bis-picolylamine, respectively), whereas that on R-Amine occurred via anion exchange of NO
 with [Pd(NO
with [Pd(NO )
) ]
] . The coordinative adsorption mechanisms resulted in the higher Pd(II) adsorption behaviors of R-IDA, R-Py, and R-BPA. HCl (5.0 M) and thiourea (0.1 M) eluents desorbed 83% of Pd(II) from R-IDA and 95% from R-Py, respectively. R-Py was the most effective Pd(II) adsorbent based on adsorption selectivity and desorption efficiency.
. The coordinative adsorption mechanisms resulted in the higher Pd(II) adsorption behaviors of R-IDA, R-Py, and R-BPA. HCl (5.0 M) and thiourea (0.1 M) eluents desorbed 83% of Pd(II) from R-IDA and 95% from R-Py, respectively. R-Py was the most effective Pd(II) adsorbent based on adsorption selectivity and desorption efficiency.
 /Fe(0) by bacteria
/Fe(0) by bacteriaLiu, J.; Dotsuta, Yuma; Kitagaki, Toru; Takano, Masahide; Onuki, Toshihiko; Kozai, Naofumi
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR2022) (Internet), 2 Pages, 2022/10
Nuclear fuel debris, consisting primarily of nuclear fuel and structural material, was formed during the Fukushima Daiichi NPP accident and exists in the cooling water accumulated in the primary containment vessels. Microorganisms living in groundwater may come into contact with the fuel debris and react with it. To assess the degradation of fuel debris, it is necessary to evaluate the interactions between microorganisms and fuel debris. Here we performed an experimental study on bacterial degradation. A mixed powder of UO and Fe(0) was used as a fuel debris simulant. Bacillus subtilis, which is widespread bacteria in nature and thought to be present at the accident site, was used. The mixed powder was exposed to the Bacillus subtilis in a liquid medium for some days. It was found that the oxidative dissolution of the U(IV) and Fe(0) was accelerated by B. subtilis. A fraction of the dissolved U(VI) was precipitated together with iron precipitates which are probably amorphous Fe(III) hydroxides. The study indicates that microorganisms would cause the degradation of fuel debris.
and Fe(0) was used as a fuel debris simulant. Bacillus subtilis, which is widespread bacteria in nature and thought to be present at the accident site, was used. The mixed powder was exposed to the Bacillus subtilis in a liquid medium for some days. It was found that the oxidative dissolution of the U(IV) and Fe(0) was accelerated by B. subtilis. A fraction of the dissolved U(VI) was precipitated together with iron precipitates which are probably amorphous Fe(III) hydroxides. The study indicates that microorganisms would cause the degradation of fuel debris.
 and CrUO
and CrUO
Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kusaka, Ryoji; Kumagai, Yuta; Nakada, Masami; Watanabe, Masayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nagai, Takayuki; Sato, Nobuaki*; Kirishima, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 568, p.153847_1 - 153847_10, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:51.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)FeUO , CrUO
, CrUO , and Fe
, and Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO are monouranates containing pentavalent U. Even though these compounds have similar crystal structures, their formation conditions and thermal stability are significantly different. To determine the factors causing the difference in thermal stability between FeUO
are monouranates containing pentavalent U. Even though these compounds have similar crystal structures, their formation conditions and thermal stability are significantly different. To determine the factors causing the difference in thermal stability between FeUO and CrUO
and CrUO , their crystal structures were evaluated in detail. A Raman band was observed at 700 cm
, their crystal structures were evaluated in detail. A Raman band was observed at 700 cm in all the samples. This Raman band was derived from the stretching vibration of the O-U-O axis band, indicating that Fe
in all the samples. This Raman band was derived from the stretching vibration of the O-U-O axis band, indicating that Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO was composed of a uranyl-like structure in its lattice regardless of its "x"' value. M
was composed of a uranyl-like structure in its lattice regardless of its "x"' value. M ssbauer measurements indicated that the Fe in FeUO
ssbauer measurements indicated that the Fe in FeUO and Fe
and Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO were trivalent. Furthermore, Fe
were trivalent. Furthermore, Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO lost its symmetry around Fe
lost its symmetry around Fe with increasing electron densities around Fe
with increasing electron densities around Fe , as the abundance of Cr increased. These results suggested no significant structural differences between FeUO
, as the abundance of Cr increased. These results suggested no significant structural differences between FeUO and CrUO
and CrUO . Thermogravimetric measurements for UO
. Thermogravimetric measurements for UO , FeUO
, FeUO , and CrUO
, and CrUO showed that the temperature at which FeUO
showed that the temperature at which FeUO decomposed under an oxidizing condition (approximately 800
decomposed under an oxidizing condition (approximately 800  C) was significantly lower than the temperature at which the decomposition of CrUO
C) was significantly lower than the temperature at which the decomposition of CrUO started (approximately 1250
started (approximately 1250  C). Based on these results, we concluded that the decomposition of FeUO
C). Based on these results, we concluded that the decomposition of FeUO was triggered by an "in-crystal" redox reaction, i.e., Fe
was triggered by an "in-crystal" redox reaction, i.e., Fe
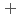 U
U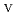
 Fe
Fe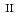
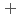 U
U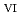 , which would not occur in the CrUO
, which would not occur in the CrUO lattice because Cr
lattice because Cr could never be reduced under the investigated condition. Finally, the existence of Cr
could never be reduced under the investigated condition. Finally, the existence of Cr in FexCr
in FexCr UO
UO effectively suppressed the decomposition of the Fe
effectively suppressed the decomposition of the Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO crystal, even at a very low Cr content.
crystal, even at a very low Cr content.
Liu, J.; Dotsuta, Yuma; Sumita, Takehiro; Kitagaki, Toru; Onuki, Toshihiko; Kozai, Naofumi
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 331(6), p.2785 - 2794, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:51.78(Chemistry, Analytical)Remnant nuclear fuel debris in the damaged nuclear reactors at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) has contacted the groundwater containing microorganisms for over ten years. Herein, we report the possibility of bacterial alteration of fuel debris. We investigated the physical and chemical changes of fuel debris simulants (FDS) in the powder and pellet forms via exposure to two ubiquitous bacteria, Pseudomonas fluorescens and Bacillus subtilis. In the experiments using FDS composed of the powders of Fe(0), solid solution of CeO and ZrO
and ZrO , and SiO
, and SiO , Ce, Zr, and Si were hardly dissolved, while Fe was dissolved, a fraction of the dissolved Fe was present in the liquid phase as Fe(II) and Fe(III), and the rest was precipitated as the nano-sized particles of iron (hydr)oxides. In the experiment using P. fluorescens and FDS pellet pieces prepared by melting the Fe(0) particles and solid solution of CeO
, Ce, Zr, and Si were hardly dissolved, while Fe was dissolved, a fraction of the dissolved Fe was present in the liquid phase as Fe(II) and Fe(III), and the rest was precipitated as the nano-sized particles of iron (hydr)oxides. In the experiment using P. fluorescens and FDS pellet pieces prepared by melting the Fe(0) particles and solid solution of CeO and ZrO
and ZrO , the bacteria selectively gathered on the Fe(0) particle surface and made corrosion pits. These results suggest that bacteria in groundwater corrode the iron in fuel debris at FDNPP, change fuel debris into porous one, releasing the nano-sized iron (hydr)oxide particles into the water.
, the bacteria selectively gathered on the Fe(0) particle surface and made corrosion pits. These results suggest that bacteria in groundwater corrode the iron in fuel debris at FDNPP, change fuel debris into porous one, releasing the nano-sized iron (hydr)oxide particles into the water.
Momma, Yuichiro*; Sakairi, Masatoshi*; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Otani, Kyohei
Zairyo To Kankyo, 71(5), p.133 - 137, 2022/05
The effect of the corrosion inhibitor on the corrosion of steel under a thin solution layer was investigated. As a result of forming a thin solution layer with a thickness of 1.0-0.2 mm on the specimen, adding a mixed solution of sodium molybdate and aluminum lactate as a corrosion inhibitor, and performing electrochemical measurement, the corrosion inhibitor suppresses the anodic reaction. And in the thin solution layer, it was suggested that the morphology of the protective layer structure by the corrosion inhibitor changed according to the amount of liquid as compared with the bulk immersion.
Momma, Yuichiro*; Sakairi, Masatoshi*; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Otani, Kyohei
Zairyo To Kankyo, 71(4), p.121 - 125, 2022/04
The effect of solution layer thickness on the atmospheric corrosion of carbon steel was investigated using novel devices fabricated by a 3D printer. These novel devices allowed us to control the solution layer thickness precisely. Potentiodynamic polarization measurements were performed under thickness-controlled solution layer, and oxygen diffusion limiting current density ( ) and anodic current density (
) and anodic current density ( ) were measured. As the solution layer become thinner,
) were measured. As the solution layer become thinner,  increased and
increased and  decreased. This result indicates that corrosion accelerates when the solution layer becomes thinner. The diffusion coefficient of oxygen was calculated as 3.20
decreased. This result indicates that corrosion accelerates when the solution layer becomes thinner. The diffusion coefficient of oxygen was calculated as 3.20 10
10 cm
cm s
s from the relationship between
from the relationship between  and solution layer thickness, and the critical diffusion thickness was estimated to be 0.87 mm.
and solution layer thickness, and the critical diffusion thickness was estimated to be 0.87 mm.
Kitagaki, Toru; Yoshida, Kenta*; Liu, P.*; Shobu, Takahisa
npj Materials Degradation (Internet), 6(1), p.13_1 - 13_8, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.33(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Wada, Yuki; Furuichi, Noriyuki*; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*
European Journal of Mechanics B, Fluids, 91, p.233 - 243, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:39.16(Mechanics) O
O decomposition at the U
decomposition at the U O
O surface in bicarbonate solution
surface in bicarbonate solutionMcGrady, J.; Kumagai, Yuta; Watanabe, Masayuki; Kirishima, Akira*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kitamura, Akira; Kimuro, Shingo
RSC Advances (Internet), 11(46), p.28940 - 28948, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:24.90(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Hemmi, Ko; Walker, A.*; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji
Radiochimica Acta, 109(7), p.539 - 546, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.64(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Plutonium(IV) sorption onto quartz in carbonate solutions was systematically investigated under anaerobic conditions to analyze the sorption behaviors of Pu(IV) with a non-electrostatic model (NEM). Pu(IV) sorption data was obtained from batch sorption experiments as a function of pH and carbonate concentration. The Pu(IV) sorption onto quartz showed similar tendencies to Th(IV), which is considered to be chemically analogous as a tetravalent actinoid. The distribution coefficient,  d, of Pu(IV) onto quartz showed inverse proportionality to the square of the total carbonate concentration under the investigated pH conditions of 8 to 11. The modeling study, however, revealed a Th(IV) sorption model, which is
d, of Pu(IV) onto quartz showed inverse proportionality to the square of the total carbonate concentration under the investigated pH conditions of 8 to 11. The modeling study, however, revealed a Th(IV) sorption model, which is  SOTh(OH)
SOTh(OH)
 and
and  SOThOH(CO
SOThOH(CO )
)
 , could not be applied to simulate the Pu(IV) sorption onto quartz. It was inferred that the electrostatic repulsion between negatively charged ligands limited the formation of
, could not be applied to simulate the Pu(IV) sorption onto quartz. It was inferred that the electrostatic repulsion between negatively charged ligands limited the formation of  SOM(OH)
SOM(OH)
 and
and  SOMOH(CO
SOMOH(CO )
)
 for Pu(IV) with smaller ionic radii than Th(IV). The Pu(IV) sorption model was developed as
for Pu(IV) with smaller ionic radii than Th(IV). The Pu(IV) sorption model was developed as  SOPu(OH)
SOPu(OH) and
and  SOPu(OH)
SOPu(OH)
 . In addition, data of Pu(IV) sorption onto muscovite was obtained in order to be compared with data for quartz.
. In addition, data of Pu(IV) sorption onto muscovite was obtained in order to be compared with data for quartz.
Nakanishi, Ryuzo; Oba, Hironori; Saeki, Morihisa; Wakaida, Ikuo; Tanabe, Rie*; Ito, Yoshiro*
Optics Express (Internet), 29(4), p.5205 - 5212, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:87.64(Optics)Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) combined with liquid jets was applied to the detection of trace sodium (Na) in aqueous solutions. The sensitivities of two types of liquid jets were compared: a liquid cylindrical jet with a diameter of 500  m and a liquid sheet jet with a thickness of 20
m and a liquid sheet jet with a thickness of 20  m. Compared with the cylindrical jet, the liquid sheet jet effectively reduced the splash from the laser-irradiated surface and produced long-lived luminous plasma. The limit of detection (LOD) of Na was determined to be 0.57
m. Compared with the cylindrical jet, the liquid sheet jet effectively reduced the splash from the laser-irradiated surface and produced long-lived luminous plasma. The limit of detection (LOD) of Na was determined to be 0.57  g/L for the sheet jet and 10.5
g/L for the sheet jet and 10.5  g/L for the cylindrical jet. The LOD obtained for the sheet jet was comparable to those obtained for commercially available inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometers.
g/L for the cylindrical jet. The LOD obtained for the sheet jet was comparable to those obtained for commercially available inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometers.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2020-039, 59 Pages, 2021/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2019. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of high-resolution imaging camera for alpha dust" conducted in FY2019. We have developed an imaging camera with a position resolution of less than approximately 10  m to monitor alpha dust in the nuclear plant during the decommissioning process, because the operators avoid to drawing in such dusts. Moreover, we have developed real-time monitor system with optical fiber and scintillator under high dose-rate condition.
m to monitor alpha dust in the nuclear plant during the decommissioning process, because the operators avoid to drawing in such dusts. Moreover, we have developed real-time monitor system with optical fiber and scintillator under high dose-rate condition.