Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -dependence of spin exchange interactions in
-dependence of spin exchange interactions in  MnO
MnO (
( = Rare-Earth Ions)
= Rare-Earth Ions)Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Mochizuki, Hidenori*; Yoshizawa, Hideki*; Shintani, Hiroshi*; Kimura, Tsuyoshi*; Tokura, Yoshinori*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 74(9), p.2430 - 2433, 2005/09
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:79.83(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Magnon excitations have been investigated for PrMnO showing the
showing the 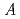 -type antiferromagnetic ordering and TbMnO
-type antiferromagnetic ordering and TbMnO forming a long-period spin ordering by inelastic neutron scattering. Combined with a result of LaMnO
forming a long-period spin ordering by inelastic neutron scattering. Combined with a result of LaMnO [K.~Hirota
[K.~Hirota  ], the systematic data revealed that the ferromagnetic exchange interaction between nearest-neighbor (NN) Mn sites within the
], the systematic data revealed that the ferromagnetic exchange interaction between nearest-neighbor (NN) Mn sites within the 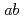 plane drastically decreases in
plane drastically decreases in  MnO
MnO as the ionic radius of
as the ionic radius of  is reduced. In addition, finite next-nearest-neighbor (NNN) coupling is evident in TbMnO
is reduced. In addition, finite next-nearest-neighbor (NNN) coupling is evident in TbMnO . In contrast, the exchange interaction along the
. In contrast, the exchange interaction along the  axis shows much weaker
axis shows much weaker  dependence consistent with the Mn-O-Mn bond angle. These observations confirm a scenario that explains the evolution of spin structures in
dependence consistent with the Mn-O-Mn bond angle. These observations confirm a scenario that explains the evolution of spin structures in  MnO
MnO in terms of the competition between the NN and NNN interactions [T.Kimura
in terms of the competition between the NN and NNN interactions [T.Kimura  ].
].
 Sr
Sr MnO
MnO
Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Yoshizawa, Hideki*; Kawasaki, Ryuichi*; Noda, Kohei*; Kuwahara, Hideki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 74(1), p.502 - 503, 2005/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.43(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The spin wave dispersion relation of the C-type antiferromagnetic structure in Nd Sr
Sr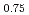 MnO
MnO was determined by neutron scattering. The spin exchange interactions show a large anisotropy, which evidences the d
was determined by neutron scattering. The spin exchange interactions show a large anisotropy, which evidences the d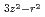 orbital ordering along the
orbital ordering along the  axis. The exchange interaction along the
axis. The exchange interaction along the  direction is fairly large and similar to the value in the ferromagnetic metallic phase, suggesting there is finite hopping of charges along the orbital chains.
direction is fairly large and similar to the value in the ferromagnetic metallic phase, suggesting there is finite hopping of charges along the orbital chains.
Takeda, Masayasu; Mibu, Ko*; Shinjo, Teruya*; Endo, Yasuo*; Suzuki, Junichi
Physical Review B, 70(10), p.104408_1 - 104408_9, 2004/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:40.22(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Detailed magnetic structure of spin-density waves (SDWs) in epitaxial Cr(001)/Sn multilayer was investigated by neutron scattering combined with M ssbauer spectroscopic studies. Monatomic Sn layers were embedded in 240 nm thick Cr(001) films with varying the periodic spacing from 4.2 to 16.2 nm. All samples were revealed to be a commensurate antiferromagnetic (CAF) phase at 300 K. The CAF structures changed to incommensurate SDW states with complex waveforms whose wavelength are controlled by the artificial periodicity at low temperatures although the CAF structure in the sample with the period of 4.2 nm persisted even at 10 K. The phase transition depends on the thickness of the Cr layers intervening between Sn monatomic layers. An appreciable phase slip in the SDW was observed during the phase transition in the sample with the period of 10.2 nm. The SDW structure is discussed by taking account of the competing forces between the nesting of Fermi surface and a pinning of antinodes at the Sn monatomic layers.
ssbauer spectroscopic studies. Monatomic Sn layers were embedded in 240 nm thick Cr(001) films with varying the periodic spacing from 4.2 to 16.2 nm. All samples were revealed to be a commensurate antiferromagnetic (CAF) phase at 300 K. The CAF structures changed to incommensurate SDW states with complex waveforms whose wavelength are controlled by the artificial periodicity at low temperatures although the CAF structure in the sample with the period of 4.2 nm persisted even at 10 K. The phase transition depends on the thickness of the Cr layers intervening between Sn monatomic layers. An appreciable phase slip in the SDW was observed during the phase transition in the sample with the period of 10.2 nm. The SDW structure is discussed by taking account of the competing forces between the nesting of Fermi surface and a pinning of antinodes at the Sn monatomic layers.
 Sn monatomioc layers
Sn monatomioc layersJiko, Norihiro*; Almokhtar, M.*; Takeda, Masayasu; Suzuki, Junichi; Shinjo, Teruya*; Mibu, Ko*
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 272-276(Part2), p.1233 - 1234, 2004/05
The growth-orientation dependence of magnetism of Cr/Sn and Fe/Cr/Sn/Cr multilayers was studied. For Fe/Cr/Sn/Cr multilayers, reduction of Cr magnetic moments was found in both (011)- and (001)-orientated samples, and the effect is larger in the former than the latter. In Cr/Sn multilayers, the (011)-oriented sample with the Cr layer thickness (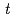
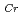
 ) of 80
) of 80
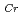
 80AA have a spin-density-wave structure with the wave vector perpendicular to the film plane.
80AA have a spin-density-wave structure with the wave vector perpendicular to the film plane.

Kubozono, Yoshihiro*; Mimura, Kazue*; Takabayashi, Yasuhiro*; Maeda, Hironobu*; Kashino, Setsuo*; Emura, Shuichi*; Nishihata, Yasuo; Uruga, Tomoya*; Tanaka, Tsunehiro*; Takahashi, Masao*
Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 6(Part3), p.564 - 566, 1999/05
The Rb K-edge XAFS spectra for the stable phase of RbC60 which is a quasi one-dimensional polymer were measured in the temperature range from 14.6 to 210 K in order to clarify the origin of the metal-insulator transition around 50 K. The distances and mean-square relative displacements between the Rb atom and the neighboring C atoms determined by XAFS exhibited no change around 50 K, implying that the metal-insulator transition originates from the SDW instablity.