Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ninomiya, Hiromasa; Akiba, Masato; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Fujiwara, Masami*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Inoue, Nobuyuki; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 49, p.S428 - S432, 2006/12
To contribute DEMO and ITER, the design to modify the present JT-60U into superconducting coil machine, named National Centralized Tokamak (NCT), is being progressed under nationwide collaborations in Japan. Mission, design and strategy of this NCT program is summarized.
 plasma operation
plasma operationTamai, Hiroshi; Akiba, Masato; Azechi, Hiroshi*; Fujita, Takaaki; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hashizume, Hidetoshi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Horiike, Hiroshi*; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ichimura, Makoto*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 45(12), p.1676 - 1683, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:44.52(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Design studies are shown on the National Centralized Tokamak facility. The machine design is carried out to investigate the capability for the flexibility in aspect ratio and shape controllability for the demonstration of the high-beta steady state operation with nation-wide collaboration, in parallel with ITER towards DEMO. Two designs are proposed and assessed with respect to the physics requirements such as confinement, stability, current drive, divertor, and energetic particle confinement. The operation range in the aspect ratio and the plasma shape is widely enhanced in consistent with the sufficient divertor pumping. Evaluations of the plasma performance towards the determination of machine design are presented.
Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Ide, Shunsuke
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 81(10), p.773 - 778, 2005/10
In steady-state tokamak fusion reactors, an efficient external current drive and a large fraction of the bootstrap current are required for non-inductive operation at low circulating power. NBI is a powerful and reliable actuator for current drive and heating. A negative ion-based NBI (N-NBI) with a high beam energy more than 350 keV has been installed in the JT-60U tokamak in order to study the NBI current drive and heating in an ITER relevant regime. This paper presents recent progress of N-NBI experiments and its system in JT-60U towards steady-state operation for ITER and tokamak fusion reactors.
Tamai, Hiroshi; Ishida, Shinichi; Kurita, Genichi; Shirai, Hiroshi; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Sakurai, Shinji; Matsukawa, Makoto; Sakasai, Akira
Fusion Science and Technology, 45(4), p.521 - 528, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The 1.5D time-dependent transport analysis has been carried out to investigate steady state operation scenarios with a central current hole by off-axis current drive schemes consistent with a high bootstrap current fraction for a large superconducting tokamak JT-60SC. A steady state operation scenario with HH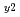 =1.4 and
=1.4 and 
 =3.7 has been obtained at I
=3.7 has been obtained at I =1.5 MA, B
=1.5 MA, B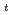 =2 T and q
=2 T and q =5 where non-inductive currents are developed during the discharge to form a current hole with beam driven currents by tangential off-axis beams in combination with bootstrap currents by additional on-axis perpendicular beams. The bootstrap fraction increases up to nearly 75% of the plasma current and the current hole region is enlarged up to about 30% of the minor radius at 35 s from the discharge initiation. The current hole is confirmed to be sustained afterward for a long duration of 60 s. The stability analysis shows that the beta limit with the conducting wall can be about
=5 where non-inductive currents are developed during the discharge to form a current hole with beam driven currents by tangential off-axis beams in combination with bootstrap currents by additional on-axis perpendicular beams. The bootstrap fraction increases up to nearly 75% of the plasma current and the current hole region is enlarged up to about 30% of the minor radius at 35 s from the discharge initiation. The current hole is confirmed to be sustained afterward for a long duration of 60 s. The stability analysis shows that the beta limit with the conducting wall can be about 
 =4.5, which is substantially above the no wall ideal MHD limit.
=4.5, which is substantially above the no wall ideal MHD limit.
Connor, J. W.*; Fukuda, Takeshi*; Garbet, X.*; Gormezano, C.*; Mukhovatov, V.*; Wakatani, Masahiro*; ITB Database Group; ITPA Topical Group on Transport and Internal Barrier Physics*
Nuclear Fusion, 44(4), p.R1 - R49, 2004/04
Times Cited Count:324 Percentile:74.42(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This paper first reviews the present state of theoretical and experimental knowledge regarding the formation and characteristics of ITBs in tokamaks. Specifically, the current status of theoretical modeling of ITBs is presented; then, an international ITB database based on experimental information extracted from some nine tokamaks is described and used to draw some general conclusions concerning the necessary conditions for ITBs to appear, comparing these with the theoretical models. The experimental situation regarding the steady-state, or at least quasi-steady-state, operation of tokamaks is reviewed and finally the issues and prospects for achieving such operational modes in ITER are discussed.
Kamiya, Kensaku; Kimura, Haruyuki; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Kawashima, Hisato; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Sato, Masayasu; Miura, Yukitoshi; JFT-2M Group
Nuclear Fusion, 43(10), p.1214 - 1219, 2003/10
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:71.35(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Kamiya, Kensaku; Kimura, Haruyuki; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Kawashima, Hisato; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Sato, Masayasu; Miura, Yukitoshi; JFT-2M Group
Nuclear Fusion, 43(10), p.1214 - 1219, 2003/10
no abstracts in English
Ishida, Shinichi; Abe, Katsunori*; Ando, Akira*; Cho, T.*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Goto, Seiichi*; Hanada, Kazuaki*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Hino, Tomoaki*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 43(7), p.606 - 613, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:67.95(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Kamiya, Kensaku; Kimura, Haruyuki; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Kawashima, Hisato; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Isei, Nobuaki; Sato, Masayasu; Shinohara, Koji
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 78(12), p.1361 - 1367, 2002/12
no abstracts in English
Ninomiya, Hiromasa; Kitsunezaki, Akio; Shimizu, Masatsugu; Kuriyama, Masaaki; JT-60 Team; Kimura, Haruyuki; Kawashima, Hisato; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Sato, Masayasu; Isei, Nobuaki; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 42(1), p.7 - 31, 2002/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:24.24(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to establish scientific basis for the sustainment of highly integrated performance required in the advanced steady-state operation, JT-60U has been optimizing the discharge control scenarios of improved confinement plasmas and expanding the operation regions. Promising results toward the steady-state tokamak were obtained. The detail of such results is reported. JFT-2M has performed advanced and basic research for the development of high performance tokamak plasma as well as the structural material for a fusion reactor. The toroidal ripple reduction with ferritic steel plates outside the vacuum vessel was successfully demonstrated. No adverse effects were observed in the pre-testing on compatibility between ferritic steel plates, covering ~20% of the inside wall of the vacuum vessel, and plasma. The results of TRIAM-1M is also reported.
Tamai, Hiroshi; Ishida, Shinichi; Kurita, Genichi; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Fujita, Takaaki; Shirai, Hiroshi; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Matsukawa, Makoto; Sakasai, Akira; Sakurai, Shinji; et al.
Proceedings of 29th European Physical Society Conference on Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 4 Pages, 2002/00
This paper presents the feasibility and issues of steady state operation with a central current hole for JT-60SC, the superconducting tokamak to be modified from JT-60, from the view of reactor applicability of the current hole. An impact of the current hole on fusion engineering would stand in no necessity of central current drive leading to a remarkable reduction of neutral beam injection energy. The 1.5D time-dependent transport code analysis is made with using thermal and particle transport coefficients deduced from observations in JT-60U as a function of the magnetic shear. A steady state operation with HHy2~1.6 and beta_N~4 is obtained at Ip=1.5 MA, Bt=2 T and q95=4.5 by off-axis beams of 11.2 MW. The bootstrap fraction of ~75% of the plasma current and the current hole region of ~30% of the minor radius are sustained up to 70 s. The results suggest that a bootstrap current evolution near the current hole region and a relation between the location of ITB and the central current hole region are important to achieve a steady state plasma compatible with the current hole.
Polevoi, A. R.; Nishio, Satoshi; Ushigusa, Kenkichi
JAERI-Tech 2000-001, p.16 - 0, 2000/01
no abstracts in English
Ozeki, Takahisa; Ishii, Yasutomo; S.R.Hudson*; Tokuda, Shinji; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Yamagiwa, Mitsuru; ; ; D.Monticello*; ; et al.
Fusion Energy 1998 (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
W.Liu*; Miura, Yukitoshi; JFT-2M Group
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 74(7), p.753 - 757, 1998/07
no abstracts in English
; Nagashima, Keisuke; Ushigusa, Kenkichi; Kikuchi, Mitsuru
Fusion Engineering and Design, 38(4), p.417 - 428, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:43.70(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Kato, Takako*; Kubo, Hirotaka; Shimizu, Katsuhiro
Proc. of 1996 Int. Conf. on Plasma Physics, Vol.1, p.730 - 733, 1996/00
no abstracts in English
; ; ; ; ; Matoba, Toru
JAERI-Tech 95-041, 12 Pages, 1995/08
no abstracts in English
Kondoh, Takashi; JT-60 Team
Physics of Plasmas, 1(5), p.1489 - 1496, 1994/05
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:56.67(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Kimura, Toyoaki; JT-60 Team
Proc. of the 14th Symp. on Fusion Engineering,Vol. 2, p.860 - 866, 1992/00
no abstracts in English
 p bootstrap tokamak reactor
p bootstrap tokamak reactorKikuchi, Mitsuru
JAERI-M 89-164, 33 Pages, 1989/10
no abstracts in English