Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hotta, Akitoshi*; Morita, Akinobu*; Kajimoto, Mitsuhiro*; Maruyama, Yu
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 16(3), p.139 - 152, 2017/09
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Nakamura, Hideo; Maruyama, Yu*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 236(19-21), p.2010 - 2025, 2006/10
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:82.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)A computer code JASMINE-pre was developed for the prediction of premixing conditions of fuel-coolant interactions and the debris bed formation behavior relevant to severe accidents of light water reactors. JASMINE-pre consists of three melt component models: melt jet, melt particles and melt pool, coupled with a two-phase flow model derived from the ACE-3D code developed at JAERI. Simulations of the FARO corium quenching experiments with a saturated water pool and with a subcooled water pool were performed with JASMINE-pre and 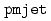 . JASMINE-pre reproduced the pressurization and fragmentation behaviors observed in the experiments with a reasonable accuracy. The results by pmjet showed qualitatively the same trend with JASMINE-pre in the fragmentation behavior.
. JASMINE-pre reproduced the pressurization and fragmentation behaviors observed in the experiments with a reasonable accuracy. The results by pmjet showed qualitatively the same trend with JASMINE-pre in the fragmentation behavior.
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Maruyama, Yu; Usami, Tsutomu*; Nakamura, Hideo
JAERI-Research 2005-017, 173 Pages, 2005/08
A series of experiments on the break-up of high temperature oxide and steel melt jets in a water pool was conducted. The objective was to obtain data for the jet break-up length and size distribution of the droplets produced by the jet break-up, and information on the influence of material properties. Also, we tried to obtain additional information giving a clue to the mechanism governing the melt jet break-up, such as flow intensity of the steam column surrounding the melt jet, and its relation with the droplet size. In the experiments, zirconia-alumina mixture and stainless steel melt jets with diameter  17mm and velocity
17mm and velocity  7.8m/s at the water surface were dropped into a deep (2.1m) or shallow (0.6m) water pool with various subcool. From the results of the present experiments and also by referring other experimental data from literature, we obtained empirical correlation equations for the jet break-up length, the fraction of jet broken-up in a shallow pool where the jet was not completely broken-up, and the droplet size.
7.8m/s at the water surface were dropped into a deep (2.1m) or shallow (0.6m) water pool with various subcool. From the results of the present experiments and also by referring other experimental data from literature, we obtained empirical correlation equations for the jet break-up length, the fraction of jet broken-up in a shallow pool where the jet was not completely broken-up, and the droplet size.
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Takagi, Seiji; Muramatsu, Ken; Nakamura, Hideo; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of 2005 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP '05) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2005/05
The containment failure probability due to ex-vessel steam explosions were evaluated for a BWR Mk-II model plant. The evaluation was made for two scenarios: a steam explosion in the pedestal area, or in the suppression pool. A probabilistic approach, Latin Hypercube Sampling (LHS), was applied for the evaluation of steam explosion loads, in which a steam explosion simulation code JASMINE was used as a physics model. The fragility curves connecting the steam explosion loads and containment failure were developed based on simplified assumptions on the containment failure scenarios. The mean conditional probabilities of containment failure per occurrence of a steam explosion were 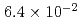 for suppression pool and
for suppression pool and 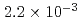 for pedestal area. Note that the results depend on the assumed range of input parameters and fragility curves that involve conservatism and simplification.
for pedestal area. Note that the results depend on the assumed range of input parameters and fragility curves that involve conservatism and simplification.
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Nakamura, Hideo; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics, Operations and Safety (NUTHOS-6) (CD-ROM), 18 Pages, 2004/10
A steam explosion simulation code JASMINE is under development at JAERI for the assessment of steam explosion impacts on the integrity of containment vessel during severe accidents in light water reactors. Selected alumina and corium steam explosion experiments, KROTOS-44, 42, 37 and FARO-L33 were simulated with JASMINE code. The experimentally observed difference of the steam explosion intensity with the two materials, alumina and corium, was reproduced in the simulations without changing the model parameters related to the fine fragmentation process, but based on the difference in the premixing behavior predicted by the simulations. The simulation of corium experiments showed more fraction of the melt droplets frozen during premixing, as well as more void fraction, and those two points were likely to be the primary reasons of weak interactions in corium experiments.
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Maruyama, Yu*; Nakamura, Hideo
JAERI-Research 2002-021, 36 Pages, 2002/11
Silicon is a material which is easily oxidized like zirconium which is one of the LWR core materials. Also, its steam explosion behavior is a concern in semi-conductor industries where its melt is handled. In this study, steam explosion behavior of silicon melt and contribution of oxidation reaction in a steam explosion were investigated. Two cases of experiments were performed by dropping silicon melt into a water pool and both produced spontaneous steam explosions. Energy conversion ratio was 4--9% which was similar or slightly larger compared with previous experiments with thermite melt. Fragmentation of the melt was finer than previous experiments and the mass median diameter of the debris was 65--85 m. An oxide layer of about 5
m. An oxide layer of about 5 m thick was fond on the debris surface indicating possibility of oxidation of several % of the melt.
m thick was fond on the debris surface indicating possibility of oxidation of several % of the melt.
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Nakamura, Hideo; Hirano, Masashi
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Dai-8-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu, p.209 - 214, 2002/06
Through a review of experimental works on steam explosions and consideration on the uncertainty in the methodology for plant scale analysis of each stage of the phenomena, it was identified that the molten jet breakup process in premixing has an important uncertainty caused by lack of experimental knowledge. Based on this perspective, an experimental work are under planning at Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI), in which the premixing stage of steam explosions in a deep water pool is modeled by high temperature oxide melts. Melt material and scale of the experiment were examined in terms of the simulation capability of the jet breakup mechanism in a plant scale phenomena. Materials and geometrical scale considered adequate were found.
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Maruyama, Yu*; Nakamura, Hideo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(1), p.53 - 58, 2002/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:46.86(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Yang, Y.; Nilsuwankosit, S.; Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Maruyama, Yu; Nakamura, Hideo; Hashimoto, Kazuichiro
JAERI-Data/Code 2000-035, 86 Pages, 2000/12
no abstracts in English
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; ; Maruyama, Yu; Kudo, Tamotsu; Sugimoto, Jun
JAERI-Data/Code 99-017, 34 Pages, 1999/03
no abstracts in English
; Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Maruyama, Yu; H.Park*; Y.Yang*; Sugimoto, Jun
Nucl. Eng. Des., 189(1-3), p.205 - 221, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:49.07(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Mishima, Kaichiro*; Hibiki, Takashi*; ; ; Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Sugimoto, Jun
Proc. of Int. Seminar on Vapor Explosions and Explosive Eruptions, p.101 - 109, 1997/00
no abstracts in English
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Yamano, N.; Maruyama, Yu; Kudo, Tamotsu; Sugimoto, Jun
Proc. of ASME JSME 4th Int. Conf. on Nuclear Engineering 1996 (ICONE-4), 1(PART B), p.903 - 915, 1996/00
JSME 4th Int. Conf. on Nuclear Engineering 1996 (ICONE-4), 1(PART B), p.903 - 915, 1996/00
no abstracts in English
Maruyama, Yu; Yamano, N.; Kudo, Tamotsu; Hidaka, Akihide; Sugimoto, Jun
NEA/CSNI/R(95)3, 0, p.223 - 240, 1995/07
no abstracts in English
Sugimoto, Jun
Dennetsu Kenkyu, 34(133), p.52 - 59, 1995/04
no abstracts in English
Yamano, Norihiro; Maruyama, Yu; Kudo, Tamotsu; Hidaka, Akihide; Sugimoto, Jun
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 155(1-2), p.369 - 389, 1995/04
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:96.15(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
; ; Maruyama, Yu; Yamano, N.; Sugimoto, Jun
Transactions of 13th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT-13), 4, p.359 - 370, 1995/00
no abstracts in English
Fuketa, Toyoshi;
Nucl. Eng. Des., 146, p.181 - 194, 1994/00
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:62.84(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Sugimoto, Jun; Yamano, N.; Maruyama, Yu; Kudo, Tamotsu; Soda, Kunihisa
Safety Options for Future Pressurized Water Reactors, 0, 14 Pages, 1994/00
no abstracts in English
Sugimoto, Jun; Yamano, N.; Maruyama, Yu; Hidaka, Akihide; Soda, Kunihisa
JAERI-M 92-035, 20 Pages, 1992/03
no abstracts in English