Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Li, C.-Y.; 内堀 昭寛; 高田 孝; Pellegrini, M.*; Erkan, N.*; 岡本 孝司*
第25回動力・エネルギー技術シンポジウム講演論文集(インターネット), 4 Pages, 2021/07
溶融炉心の原子炉容器内保持を達成するためには、デブリベッドの安定冷却と再臨界回避が重要である。本研究では、異なる物質から構成され、密度成層化したデブリベッドの挙動を評価するため、数値流体力学(CFD),個別要素法(DEM),モンテカルロ法を連成させた解析手法を構築した。本解析手法により、デブリベッドにおける密度成層化の挙動等を解析できることを確認した。
竹田 武司
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-019, 58 Pages, 2021/01
ROSA-IV計画において、大型非定常実験装置(LSTF)を用いた実験(実験番号: SB-SL-01)が1990年3月27日に行われた。ROSA/LSTFSB-SL-01実験では、加圧水型原子炉(PWR)の主蒸気管破断(MSLB)事故を模擬した。このとき、両ループの蒸気発生器(SG)二次側への補助給水(AFW)とともに、非常用炉心冷却系である高圧注入(HPI)系から両ループの低温側配管内への冷却材注入を仮定した。MSLBにより、破断ループのSGは急減圧し、破断ループのSG二次側広域水位は低下した。しかし、破断ループのSG二次側へのAFWにより、破断ループのSG二次側広域水位は回復した。一次系圧力は、MSLB直後一時的に若干低下したが、SG主蒸気隔離弁の閉止に従い16.1MPaまで上昇した。一次系圧力が10MPa以下に低下した数分後、HPI系から両ループの低温側配管内へ冷却材を手動注入した。一次系圧力は、HPI系からの冷却材注入により上昇したが、加圧器逃し弁の開放により16.2MPa以下に維持された。実験中、炉心はサブクール水で満たされた。健全ループでは、流れが停滞し、HPI系からの冷却材注入時に低温側配管での温度成層が観察された。一方、破断ループでは、顕著な自然循環が継続した。HPI系からの冷却材の連続注入による継続的な炉心冷却を確認して実験を終了した。取得した実験データは、PWRのMSLBを伴う多重故障事故時の回復操作および手順の検討に役立てることができる。本報告書は、ROSA/LSTFSB-SL-01実験の手順、条件および実験で観察された主な結果をまとめたものである。
安部 諭; Studer, E.*; 石垣 将宏; 柴本 泰照; 与能本 泰介
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 368, p.110785_1 - 110785_14, 2020/11
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:78.21(Nuclear Science & Technology)The hydrogen behavior in a nuclear containment vessel is one of the significant issues raised when discussing the potential of hydrogen combustion during a severe accident. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) is a powerful tool for better understanding the turbulence transport behavior of a gas mixture, including hydrogen. Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) is a practical-use approach for simulating the averaged gaseous behavior in a large and complicated geometry, such as a nuclear containment vessel; however, some improvements are required. We implemented the dynamic modeling for  based on the previous studies into the OpenFOAM ver 2.3.1 package. The experimental data obtained by using a small scale test apparatus at Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) was used to validate the RANS methodology. Moreover, Large-Eddy Simulation (LES) was performed to phenomenologically discuss the interaction behavior. The comparison study indicated that the turbulence production ratio by shear stress and buoyancy force predicted by the RANS with the dynamic modeling for
based on the previous studies into the OpenFOAM ver 2.3.1 package. The experimental data obtained by using a small scale test apparatus at Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) was used to validate the RANS methodology. Moreover, Large-Eddy Simulation (LES) was performed to phenomenologically discuss the interaction behavior. The comparison study indicated that the turbulence production ratio by shear stress and buoyancy force predicted by the RANS with the dynamic modeling for  was a better agreement with the LES result, and the gradual decay of the turbulence fluctuation in the stratification was predicted accurately. The time transient of the helium molar fraction in the case with the dynamic modeling was very closed to the VIMES experimental data. The improvement on the RANS accuracy was produced by the accurate prediction of the turbulent mixing region, which was explained with the turbulent helium mass flux in the interaction region. Moreover, the parametric study on the jet velocity indicates the good performance of the RANS with the dynamic modeling for
was a better agreement with the LES result, and the gradual decay of the turbulence fluctuation in the stratification was predicted accurately. The time transient of the helium molar fraction in the case with the dynamic modeling was very closed to the VIMES experimental data. The improvement on the RANS accuracy was produced by the accurate prediction of the turbulent mixing region, which was explained with the turbulent helium mass flux in the interaction region. Moreover, the parametric study on the jet velocity indicates the good performance of the RANS with the dynamic modeling for  on the slower erosive process. This study concludes that the dynamic modeling for
on the slower erosive process. This study concludes that the dynamic modeling for  is a useful and practical approach to improve the prediction accuracy.
is a useful and practical approach to improve the prediction accuracy.
Hamdani, A.; 安部 諭; 石垣 将宏; 柴本 泰照; 与能本 泰介
Proceedings of 18th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-18) (USB Flash Drive), p.5463 - 5479, 2019/08
The present study introduces thermal mixing and stratification produced by heated air jet located at the bottom level of the containment vessel. The investigation was carried out experimentally and numerically in the large containment vessel called CIGMA (Containment InteGral effects Measurement Apparatus). The experiments were conducted with external surface cooling and various air jet inlet temperatures. The containment cooling was done by flooding the water on the external side of half-upper of a vessel. To identify their influence on the thermal mixing and stratification phenomena, the investigation focuses on mixing convection which occurred in the cooled region of a containment vessel. Temperature distribution and jet velocity were measured by thermocouple and Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) respectively. Numerical simulation was performed using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) code OpenFOAM to investigate the detail effects of external cooling on the fluid flow and thermal characteristics in the test vessel. CFD results showed a good agreement with experimental data on both temperature and velocity. Both temperature and velocity of hot air jet decayed rapidly downstream jet nozzle. Thermal stratification was observed by visualization of temperature contour maps over a cross-section in the containment vessel. Vigorous mixing was also noticed in the upper region of the containment vessel. Effect of external cooling on mixing and the thermal stratification were presented and discussed.
安部 諭; 石垣 将宏; 柴本 泰照; 与能本 泰介
Proceedings of 12th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-12) (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2018/10
At Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), small scale experiment, named VIMES (VIsualization and MEasurement system on stratification behavior) experiment, has been performed since 2014. In this paper, we introduce the influence of grating type obstacle to the VIMES experiment. Two types of grating obstacle were constructed based on the aperture area ratio. The obstacles were placed at the intermediate position between the jet nozzle exit and bottom of the initial stratification. Experimental results showed that the vertical jet was strongly affected by the grating obstacle. Due to the rectifying effect, the radial spreading was suppressed and the velocity magnitude on the jet center line became larger than that in case without the grating obstacle. Meanwhile, due to the resistance effect, the integral momentum flux of the vertical jet was decayed with decrease of the aperture area ratio. It means that in case with the grating obstacle the integral jet penetration strength was decayed, although the local jet penetration to the stratification was stronger than that in case without the grating obstacle. Also, the slower stratification breakup could be observed with decrease of the aperture area ratio, indicating that stratification breakup rate to be discussed in detail considering every possible effect of a jet penetration.
安部 諭; 石垣 将宏; 柴本 泰照; 与能本 泰介
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 289, p.231 - 239, 2015/08
被引用回数:23 パーセンタイル:87.9(Nuclear Science & Technology)Density stratification in the reactor containment vessel is an important phenomenon on an issue of hydrogen safety. The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has started the ROSA-SA project on containment thermal hydraulics. As a part of the activity, we participated in the third international CFD benchmark exercise (IBE-3) focused on density stratification erosion by a vertical buoyant jet in containment vessel. This paper shows our approach for the IBE-3, focusing on the turbulence transport phenomena in eroding the density stratification and introducing modified turbulence models for improvement of the CFD analyses. For this analysis, we modified the CFD code OpenFOAM by using two turbulence models; the Kato and Launder modification to estimate turbulent kinetic energy production around a stagnation point, and the Katsuki model to consider turbulence damping in density stratification. As a result, the modified code predicted well the experimental data. The importance of turbulence transport modeling is also discussed using the calculation results.
久保 真治; 秋野 詔夫; 田中 周*; 亀岡 利行*; 岡田 裕紀*
日本機械学会論文集,B, 64(623), p.336 - 344, 1998/07
我々の開発した新しい熱媒体である、マイクロカプセル化相変化物質スラリー(MCPCMスラリー)を用いた自然対流熱伝達実験を行う準備のため、容器内に温度成層と循環流等がある場合の加熱体の熱伝達特性を測定した。加熱体は水平円柱であり、容器内に一本、あるいは垂直に二本並べて設置した。作動流体にはシリコンオイルと純水を用いた。熱伝達率を評価する際に、代表周囲流体温度の測定位置(深さ)の熱伝達整理式への影響を調べた。循環流や加熱体の熱的干渉が小さい場合には、容器内に温度成層があっても適当な代表流体温度を選べば、従来の無限空間における自然対流熱伝達の整理式を適用できた。それらが大きい場合には、現象に対して自然対流熱伝達の整理式を適用することは難しかった。
中村 秀夫; 久木田 豊; L.S.Ghan*; R.R.Schultz*
Proc. of 1997 Int. Meeting on Advanced Reactors Safety, 0, p.1245 - 1252, 1997/06
AP600炉における蒸気発生器(SG)の伝熱管多数本同時破断事象を模擬した実験を、改造したROSA-V/LSTF(体積比1/30.5)を用いて行った。その結果、静的安全系である静的余熱除去系(PRHR)と炉心補給水タンク(CMT)の、いずれも自然循環による熱除去が、原子炉スクラムとほぼ同時の起動後すぐに炉心崩壊熱出力を大きく上回り( 2倍)、1次系圧力をSG2次系圧力近くまで短時間で低下させたため、運転員操作が無くても炉心をサブクール水中に維持できることが分かった。更にその熱除去は、高温配管(hot leg)温度をSG2次系より低下させ、2次系圧力を逃がし弁開の設定値以下に維持した。しかし、PRHRからの低温の冷却水は、他のROSA/AP600小破断模擬実験同様、低温配管(cold leg)に大きな温度差(
2倍)、1次系圧力をSG2次系圧力近くまで短時間で低下させたため、運転員操作が無くても炉心をサブクール水中に維持できることが分かった。更にその熱除去は、高温配管(hot leg)温度をSG2次系より低下させ、2次系圧力を逃がし弁開の設定値以下に維持した。しかし、PRHRからの低温の冷却水は、他のROSA/AP600小破断模擬実験同様、低温配管(cold leg)に大きな温度差( 100K)の温度成層を生じることが分かった。
100K)の温度成層を生じることが分かった。
近藤 昌也; 与能本 泰介; 浅香 英明; 久木田 豊*; R.Schultz*
Proc. of 1997 Int. Meeting on Advanced Reactors Safety, 0, p.217 - 224, 1997/06
ウェスティングハウス社製のAP600炉に関する総合模擬実験中に見られた炉心補給水タンク(CMT)の熱水力挙動についてRELAP5/Mod3(Ver.3.2)を用いて解析した。解析の結果、CMT自然循環流量は良好に予測できること、CMT上部の軸方向の混合が計算できないために温度成層を予測するには問題があることを明らかにした。また、CMT壁の過大な熱容量は、ADS(自動減圧系)の故障により減圧速度が極端に小さい場合や、比較的破断口が大きなために温度成層が発達する前に注入が始まる場合において、CMT注入挙動に影響を与えることを明らかにした。これらの実験では、CMT壁面において蒸気が凝縮し、CMT注入速度を制限した。
大貫 晃
第1回オーガナイズド混相流フォーラム講演論文集, p.73 - 82, 1997/00
21世紀に予想される発展途上国での電力需要の急上昇及び各国での労働力不足に対処するため、国内外で受動的安全設備を取り入れた次世代軽水炉の設計研究が進められている。この研究を進める上で重要な課題の一つに熱流動解析の精度向上がある。本報では、原研原子力コード委員会原子炉熱流動解析コード高度化専門部会での調査結果をもとに受動的安全設備を有する次世代軽水炉の熱流動解析の現状と課題をまとめた。大きな課題として、不凝縮性ガスのトレース及び信頼性の高い多次元解析ツールの開発が指摘された。
亀岡 利行*; 岡田 裕紀*; 久保 真治; 秋野 詔夫; 田中 周*; 高瀬 和之
可視化情報学会誌, 18(68), p.1 - 8, 1997/00
容器内に水平に設置した二本の加熱円柱の自然対流実験を行った。二本の円柱の配置に、水平に並べた状態よりズレを与えて、下円柱から立ち上がるサーマルプリュームが上円柱の熱伝導に影響する効果を調べた。感温液晶法による温度分布の可視化と、熱電対等を用いた測定の併用により、以下のことが明らかとなった。上円柱の熱伝達率は、特異に増減することがあり、これは下円柱からのプリュームが上円柱を横切ったり、接近したりすることと対応していた。上円柱の境界層が下円柱のプリュームと干渉して、その熱伝達率が促進するか劣化するかは二本の円柱の位置のズレの大きさと関係していた。
中村 秀夫; 久木田 豊; R.A.Shaw*; R.R.Schultz*
Proc. of ASME JSME 4th Int. Conf. on Nuclear Engineering 1996 (ICONE-4), 1(PART A), p.237 - 244, 1996/00
JSME 4th Int. Conf. on Nuclear Engineering 1996 (ICONE-4), 1(PART A), p.237 - 244, 1996/00
ROSA-AP600実験で観察された蓄圧注入系与圧用窒素(N )ガスのPRHRとCMTへの蓄積条件と、各々の機器の除熱能力に及ぼす影響を、実施した14実験からまとめると共に、CMT内の濃度変化を推定した。AP600では事象の終盤に、蓄圧注入系からN
)ガスのPRHRとCMTへの蓄積条件と、各々の機器の除熱能力に及ぼす影響を、実施した14実験からまとめると共に、CMT内の濃度変化を推定した。AP600では事象の終盤に、蓄圧注入系からN ガスが一次系に流入する。その際、PRHRにはADS作動後ホットレグに水位が形成された場合にのみ、CMTには、コールドレグに水位が形成され、かつ均圧ラインが順流の時に各々流入、蓄積することがわかった。ただし、このようなN
ガスが一次系に流入する。その際、PRHRにはADS作動後ホットレグに水位が形成された場合にのみ、CMTには、コールドレグに水位が形成され、かつ均圧ラインが順流の時に各々流入、蓄積することがわかった。ただし、このようなN ガスの蓄積は通常ADS作動後に生じるため、系への影響は小さいことがわかった。CMTへの蓄積は逆に、円滑な冷却材の注入を促すことがわかった。更に気相密度の安定成層を仮定し、温度分布から求めたCMT内N
ガスの蓄積は通常ADS作動後に生じるため、系への影響は小さいことがわかった。CMTへの蓄積は逆に、円滑な冷却材の注入を促すことがわかった。更に気相密度の安定成層を仮定し、温度分布から求めたCMT内N ガス最大蓄積量は、蓄圧注入系から放出される相当部分に達する可能性があることを示した。
ガス最大蓄積量は、蓄圧注入系から放出される相当部分に達する可能性があることを示した。
渡辺 正; M.Wang*; 久木田 豊
JAERI-M 93-039, 26 Pages, 1993/03
ROSA-IV/LSTFを用いて行われた蒸気発生器伝熱管損傷事象(SGTR)に関する安全解析の想定条件にほぼ沿った実験(実験番号SB-SG-07)の解析を、RELAP5/MOD2コードを用いて行い、SGTR事象に特徴的な現象に対するコードの予測性能の評価を行った。解析結果は実験における重要なパラメータの変化を良好に再現した。ただし、本解析では破断ライン内流体初期温度をホットレグ流体温度より低く設定したところ、破断流量は破断直後やや過大評価された。また、加圧器逃し弁(PORV)開による1次系減圧時の加圧器水位の上昇は過小評価され、PORV閉後の1次系圧力上昇は過大評価された。RELAP5/MOD2を用いたSGTR事象解析によって、水平層状流の判定基準、垂直層状流の界面熱伝達モデルなどの問題点が明らかとなった。
笹倉 浩
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 54(5), p.1769 - 1781, 1985/00
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Physics, Multidisciplinary)不均一スワール流について、不安定モード(m,k)の複素角位相速度は、直径b-a+( -
- )|
)| |、中心の座標{(b+a+(
|、中心の座標{(b+a+( +
+ )
) )/2,0}の半円C(
)/2,0}の半円C( )の中に存在しなければならぬことが示される。ここで、a,b及び
)の中に存在しなければならぬことが示される。ここで、a,b及び ,
, は回転速度及び軸速度の下限と上限である。
は回転速度及び軸速度の下限と上限である。 は波数比k/mである。すべての不安定モードの角位相速度の範囲は、2つの半円C(
は波数比k/mである。すべての不安定モードの角位相速度の範囲は、2つの半円C(
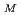 )とC(
)とC(
 )並びに接線t
)並びに接線t
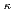
 とt
とt
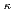
 (若し接線が存在するならば)とに囲まれた、上半面における総領域として作図される。ここで、t
(若し接線が存在するならば)とに囲まれた、上半面における総領域として作図される。ここで、t
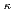 はC(O)とC(
はC(O)とC( )との接線を意味する。比
)との接線を意味する。比 の最大値
の最大値
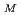 と最小値
と最小値
 は不安定条件から決定される。回転による成層、レイレイ・シンジの判別式及び軸方向流の諸効果が組み入れられるならば、半円は半楕円に変形される。
は不安定条件から決定される。回転による成層、レイレイ・シンジの判別式及び軸方向流の諸効果が組み入れられるならば、半円は半楕円に変形される。
須藤 彩子; 水迫 文樹*; 星野 国義*; 佐藤 拓未; 永江 勇二; 倉田 正輝
no journal, ,
In order to obtain the knowledge on the phase relationship and stratification behavior of oxide debris under the slow solidification condition, liquefaction/solidification tests of simulated oxide debris were performed by using a high frequency induction furnace. As the oxides components from the core melt and structural materials, sintered pellets of UO -ZrO
-ZrO -sim-FPs and powder of FeO and B
-sim-FPs and powder of FeO and B C were prepared. The powder mixture and crashed sintered oxides were heated to 2600
C were prepared. The powder mixture and crashed sintered oxides were heated to 2600 C in Ar atmosphere in the first step (partial liquefaction), and then solidified at two different cooling rates; furnace cooling (No.1) and slow cooling (5
C in Ar atmosphere in the first step (partial liquefaction), and then solidified at two different cooling rates; furnace cooling (No.1) and slow cooling (5 C /min, No.2). For the corium microstructure study, solidified samples were subjected to elemental analysis by SEM/EDX. Cross sectional images of both samples showed that the oxide layer and metallic layer were separately solidified. EDX analysis of oxide layer of No.1 sample revealed four phases; (U
C /min, No.2). For the corium microstructure study, solidified samples were subjected to elemental analysis by SEM/EDX. Cross sectional images of both samples showed that the oxide layer and metallic layer were separately solidified. EDX analysis of oxide layer of No.1 sample revealed four phases; (U Zr
Zr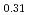 Fe
Fe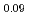 )O
)O , (Zr
, (Zr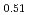 U
U Fe
Fe )O
)O , ZrO
, ZrO and Fe metal. The tendency of re-distribution of oxide elements observed in No.2 was similar to that of No.1, however, the grain-growth of (Zr,U)O
and Fe metal. The tendency of re-distribution of oxide elements observed in No.2 was similar to that of No.1, however, the grain-growth of (Zr,U)O phase occurred at the bottom region of the oxide layer. In these results, the phases detected in both samples were in reasonable accordance with those evaluated by the UO
phase occurred at the bottom region of the oxide layer. In these results, the phases detected in both samples were in reasonable accordance with those evaluated by the UO -ZrO
-ZrO -FeO phase diagram.
-FeO phase diagram.
Hamdani, A.; 安部 諭; 石垣 将宏; 柴本 泰照; 与能本 泰介
no journal, ,
Gas density stratification build-up and its propagation/erosion, which is regarded as a benchmark of hydrogen behavior in a severe accident, were experimentally and numerically studied by using buoyant jet in the containment vessel. The experiments were conducted with external surface cooling and high-temperature air-jet inlet up to 435 degrees Celcius. The CFD simulation was also performed, and the data on temperature and velocity profile were used for the validation.