Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamazaki, Dai; Maruyama, Ryuji; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Akutsu-Suyama, Kazuhiro*; Miyata, Noboru*; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 9(2), p.20_1 - 20_12, 2024/06
Tamura, Itaru; Kashima, Yoichi; Soyama, Kazuhiko
JAEA-Research 2014-029, 12 Pages, 2015/03
Neutron guide tubes, which are installed near reactor cores, are damaged by neutrons and  rays irradiation. Those glass substrates which contain boron material are affected by (n,
rays irradiation. Those glass substrates which contain boron material are affected by (n,  ) reaction, and ionization effect of
) reaction, and ionization effect of  rays on material strength decrease duration of use of neutron guide tubes. In order to increase resistance to radiation, we have fabricated a supermirror with Ni-P metallic substrate. The substrate roughness with 0.2 - 0.3 nm (rms) was produced by super- polishing. The neutron reflectivity reached 76 % for an m=3 supermirror.
rays on material strength decrease duration of use of neutron guide tubes. In order to increase resistance to radiation, we have fabricated a supermirror with Ni-P metallic substrate. The substrate roughness with 0.2 - 0.3 nm (rms) was produced by super- polishing. The neutron reflectivity reached 76 % for an m=3 supermirror.
Maruyama, Ryuji; Yamazaki, Dai; Ebisawa, Toru*; Hino, Masahiro*; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 385-386(2), p.1256 - 1258, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:71.22(Physics, Condensed Matter)Neutron supermirror has become an important device to transport, bending and focusing a neutron beam. We have developed it using ion beam sputtering (IBS) instrument since it enables us to produce good quality layers with high density and small grain size. We have also investigated ion-polishing technique, which suppresses the interface roughness of multilayers. We have now installed new IBS instrument with effective deposit area of 500 mm in diameter for the realization of supermirror guide and bender with large effective critical angle. In this presentation, the performance of the supermirrors fabricated with it and the future development of neutron optical devices using supermirrors will be discussed.
Osakabe, Toyotaka; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Review of Scientific Instruments, 76(7), p.073102_1 - 073102_5, 2005/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:24.96(Instruments & Instrumentation)Neutron focusing is an indispensable technique used to compensate for weak signals in experiments under extreme conditions with tiny samples. We describe the development of a thermal neutron focusing device for a typical triple-axis neutron spectrometer. The device has a length of 400 mm and is placed between the second collimator and the sample position. The focal length is 150 mm from the downstream end of the device. The optic has 18 pieces of the circular blade consisting of 3m NiC/Ti neutron supermirrors. The extensions of the end of each blade meet at the sample position, namely the focal point. Neutrons undergo successive reflection through the same angle from the inner surface of each blade and arrive at the sample position. The test results show that the gain of the neutron intensity at the sample position increases by a factor of two or more for the neutron energy below 30.5 meV.
Tamura, Itaru; Suzuki, Masatoshi; Hazawa, Tomoya; Moriai, Atsushi; Hori, Naohiko; Sasajima, Fumio; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 529(1-3), p.234 - 237, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.32(Instruments & Instrumentation)Thermal neutron guides at JRR-3 reactor have been upgraded from Nickel mirrors to Ni/Ti multilayer supermirrors. We performed the characteristics experiment of neutron beams transmitted through supermirror neutron guides. Neutron fluxes at the end of the thermal neutron guides were measured by the gold foil activation method on March 2003. We have confirmed that neutron fluxes at the end of thermal neutron guide increases by 6 times. The neutron spectra were also measured at the end of the thermal neutron guides by the time-of-flight method. The wavelength range for the neutron beam is extended and the shorter wavelength neutrons, which had been filtered by the characteristics of curved neutron guides before upgrade, were observed. In this paper, we have performed several Monte Carlo simulation codes using the McStas package in the consideration of the performance of fabricated supermirrors and its alignment errors for the purpose of estimation of instruments performance. We discuss the comparison of the experimental results with results of simulation.
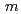 -Qc supermirror by ion polishing
-Qc supermirror by ion polishingSoyama, Kazuhiko; Tsunoda, Haruhiko*; Murakami, Katsuhiko*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 529(1-3), p.73 - 77, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.37(Instruments & Instrumentation)An ion polishing technique has been applied to supermirror coating in order to enhance neutron reflectivity. A Ni/Ti supermirror with a critical value of 3Qc and the total number of layers of 407 was coated in combination with ion polishing. The dependencies of Ar ion polishing time, ion acceleration energy and incidence angle on the interface roughness were studied and optimized by using X-ray and neutron reflectometry. The reflectivity of the supermirror was measured at the JRR-3 reflectometer of cold beam line. It has reached 90% at the external critical angle, although the non polished one has the reflectivity of 80%.
ion polishing time, ion acceleration energy and incidence angle on the interface roughness were studied and optimized by using X-ray and neutron reflectometry. The reflectivity of the supermirror was measured at the JRR-3 reflectometer of cold beam line. It has reached 90% at the external critical angle, although the non polished one has the reflectivity of 80%.
Bin, C.; Soyama, Kazuhiko
JAERI-Conf 2001-002, p.592 - 599, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
Soyama, Kazuhiko; Murakami, Katsuhiko*
JAERI-Conf 2001-002, p.551 - 556, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
Soyama, Kazuhiko; ; ; Ebisawa, Toru*; Tasaki, Seiji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 35(11), p.750 - 758, 1998/11
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:59.72(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Soyama, Kazuhiko; ; Ebisawa, Toru*
JAERI-Research 98-067, 61 Pages, 1998/10
no abstracts in English
; ; ; Kaieda, Keisuke
KAERI/GP-128/98, p.205 - 221, 1998/00
no abstracts in English
Soyama, Kazuhiko; ; Ichikawa, Hiroki;
Genshiryoku Kogyo, 43(10), p.36 - 41, 1997/10
no abstracts in English
Soyama, Kazuhiko; Suzuki, Masatoshi
ASRR-V: Proc., 5th Asian Symp. on Research Reactors, 2, p.894 - 900, 1996/00
no abstracts in English
Soyama, Kazuhiko; Suzuki, Masatoshi; Kodaira, Tsuneo; Ebisawa, Toru*; ; Tasaki, Seiji*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 213-214, p.951 - 953, 1995/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.14(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
Yamazaki, Dai; Maruyama, Ryuji; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Harada, Masahide; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Nagano, Mikinori*; Tabata, Takaaki*; Mitsushima, Naoki*; Yamamura, Kazuya*
no journal, ,
We have been developing focusing supermirrors by depositing a supermirror on a precisely figured aspheric surface. Surface of a quartz substrate is figured using the "numerically-controlled local wet etching" technique. The figured surface shows a figure error of less than 1 micrometer p-v and an RMS roughness of less than 0.2 nm. Deposition of NiC/Ti supermirror (m=4) with ion beam sputtering keeps the figure error within several micrometers p-v and the roughness almost unchanged. A one-dimensional elliptical supermirror of 400mm in length was developed and it successfully achieved focused peak width (FWHM) of 0.128 mm and peak intensity 52 times that of unfocused (divergent) beam. We also tried two-dimensional focusing using two (vertical and lateral) focusing mirrors in a Kirkpatric-Baez configuration and successfully focused the beam to a spot of 0.5 mm in diameter.