Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Auh, Y. H.*; Neal, N. N.*; Arole, K.*; Regis, N. A.*; Nguyen, T.*; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Radovic, M.*; Green, M. J.*; et al.
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 17(21), p.31392 - 31402, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Tomota, Yo*; Harjo, S.; Xu, P. G.; Morooka, Satoshi; Gong, W.; Wang, Y.*
Metals, 15(6), p.610_1 - 610_19, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 phases in undoped and Ca-modified sodium niobates
phases in undoped and Ca-modified sodium niobatesAso, Seiyu*; Matsuo, Hiroki*; Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Morikawa, Daisuke*; Tsuda, Kenji*; Oyama, Kenji*; Ishigaki, Toru*; Noguchi, Yuji*
Physical Review B, 111(17), p.174114_1 - 174114_12, 2025/05
We investigate the crystal structures, phase transitions, and phase stability of undoped and Ca-modified NaNbO through a combined analysis of high-resolution synchrotron radiation X-ray and neutron diffraction, convergent-beam electron diffraction, and density functional theory (DFT) calculations. It is demonstrated that the antiferroelectric (AFE)-
through a combined analysis of high-resolution synchrotron radiation X-ray and neutron diffraction, convergent-beam electron diffraction, and density functional theory (DFT) calculations. It is demonstrated that the antiferroelectric (AFE)- phase is stabilized over a wide temperature range of 200 to 800 K by Ca modification, and that the NaNbO
phase is stabilized over a wide temperature range of 200 to 800 K by Ca modification, and that the NaNbO is stabilized by temperature-driven isostatic pressure accompanied by lattice expansion, whereas the Ca-modified NaNbO
is stabilized by temperature-driven isostatic pressure accompanied by lattice expansion, whereas the Ca-modified NaNbO is induced by composition-induced chemical pressure along with lattice shrinkage.
is induced by composition-induced chemical pressure along with lattice shrinkage.
 under hydrostatic pressure; A Combined neutron, X-ray, Raman, and first-principles calculation study
under hydrostatic pressure; A Combined neutron, X-ray, Raman, and first-principles calculation studyEfthimiopoulos, I.*; Klotz, S.*; Kunc, K.*; Baptiste, B.*; Chauvigne, P.*; Hattori, Takanori
Physical Review B, 111(13), p.134103_1 - 134103_13, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We present a comprehensive study of the high pressure behaviour of ReO using X-ray and neutron diffraction, Raman scattering and first-principles calculations to 15 GPa. We show that the ambient pressure
using X-ray and neutron diffraction, Raman scattering and first-principles calculations to 15 GPa. We show that the ambient pressure 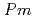
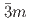 structure converts at 0.7 GPa in a continuous phase transition directly to a cubic phase with space group
structure converts at 0.7 GPa in a continuous phase transition directly to a cubic phase with space group 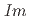
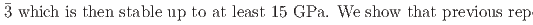 and rhombohedral
and rhombohedral 
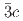 structures in this pressure range are an artifact due to an alteration of the sample by high-flux synchrotron X-ray radiation. The structural pressure dependence of the
structures in this pressure range are an artifact due to an alteration of the sample by high-flux synchrotron X-ray radiation. The structural pressure dependence of the 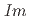
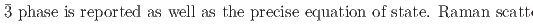 O samples are presented. The data shed light onto the unusual transition and densification mechanism due to progressive tilting of essentially rigid ReO
O samples are presented. The data shed light onto the unusual transition and densification mechanism due to progressive tilting of essentially rigid ReO octahedra.
octahedra.
Suzuki, Seiya; Katsube, Daiki*; Yano, Masahiro; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Terasawa, Tomoo; Ozawa, Takahiro*; Fukutani, Katsuyuki; Kim, Y.*; Asaoka, Hidehito; Yuhara, Junji*; et al.
Small Methods, 9(3), p.2400863_1 - 2400863_9, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:30.18(Chemistry, Physical) Sm synchrotron-radiation-based M
Sm synchrotron-radiation-based M ssbauer and
ssbauer and  SR studies of Sm
SR studies of Sm Ru
Ru Ge
Ge
Tsutsui, Satoshi; Ito, Takashi; Nakamura, Jin*; Yoshida, Mio*; Kobayashi, Yoshio*; Yoda, Yoshitaka*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Koda, Akihiro*; Higashinaka, Ryuji*; Aoki, Dai*; et al.
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.55_1 - 55_9, 2024/12
 Sm synchrotron-radiation-based M
Sm synchrotron-radiation-based M ssbauer spectroscopy of Sm-based heavy fermion compounds
ssbauer spectroscopy of Sm-based heavy fermion compoundsTsutsui, Satoshi; Higashinaka, Ryuji*; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Kobayashi, Yoshio*; Nakamura, Jin*; Ito, Takashi; Yoda, Yoshitaka*; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Aoki, Yuji*; Sato, Hideyuki*
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.9_1 - 9_10, 2024/12
 F
FKatsumata, Tetsuhiro*; Suzuki, Ryo*; Sato, Naoto*; Oda, Ryoya*; Motoyama, Shingo*; Suzuki, Shumpei*; Nakashima, Mamoru*; Inaguma, Yoshiyuki*; Mori, Daisuke*; Aimi, Akihisa*; et al.
Chemistry of Materials, 36(8), p.3697 - 3704, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:30.18(Chemistry, Physical)A perovskite-type oxynitride BaFeO F was prepared by high-pressure synthesis. Since the SHG signal was observed in the obtained material, suggesting the existence of spontaneous polarization, the mechanism of polarization was investigated by synchrotron high-energy X-ray diffraction. The obtained pair distribution functions were fitted, and a local polarization mechanism with different orientations was found. Since BaFeO
F was prepared by high-pressure synthesis. Since the SHG signal was observed in the obtained material, suggesting the existence of spontaneous polarization, the mechanism of polarization was investigated by synchrotron high-energy X-ray diffraction. The obtained pair distribution functions were fitted, and a local polarization mechanism with different orientations was found. Since BaFeO F is also a magnetic material, a magnetic domain and a ferroelectric domain are considered to coexist.
F is also a magnetic material, a magnetic domain and a ferroelectric domain are considered to coexist.
funabiki, Yuta*; Iyota, Muneyoshi*; Shobu, Takahisa; Matsuda, Tomoki*; Hayashi, Yujiro*; Sano, Tomokazu*; 8 of others*
Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 115, p.40 - 55, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:78.76(Engineering, Manufacturing)Li, X.*; Zhu, R.*; Xin, J.*; Luo, M.*; Shang, S.-L.*; Liu, Z.-K.*; Yin, C.*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Dippenaar, R. J.*; Higo, Yuji*; et al.
CALPHAD; Computer Coupling of Phase Diagrams and Thermochemistry, 84, p.102641_1 - 102641_6, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Thermodynamics)Miura, Yasufumi*; Suzuki, Kenji*; Morooka, Satoshi; Shobu, Takahisa
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 8(1), p.1_1 - 1_14, 2024/03
 X-ray synchrotron diffraction
X-ray synchrotron diffractionLi, H.*; Liu, Y.*; Zhao, W.*; Liu, B.*; Tominaga, Aki; Shobu, Takahisa; Wei, D.*
International Journal of Plasticity, 165, p.103612_1 - 103612_20, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:94.81(Engineering, Mechanical)In order to clarify the strength properties of Co-free maraging steel,  tensile experiment using high energy synchrotron X-ray diffraction was performed. Diffraction profiles from the martensitic and austenitic phases were obtained, and their strength and width were observed to vary as loading. Analysis of the diffraction profiles showed that the content of martensite in the as-aged material decreased slowly at low stress levels and decreased rapidly at high stress levels. On the other hand, the austenite phase in the as-solution materials was significantly transformed the martensite phase as the stress increased. It was clarified to be responsible for their respective strength properties.
tensile experiment using high energy synchrotron X-ray diffraction was performed. Diffraction profiles from the martensitic and austenitic phases were obtained, and their strength and width were observed to vary as loading. Analysis of the diffraction profiles showed that the content of martensite in the as-aged material decreased slowly at low stress levels and decreased rapidly at high stress levels. On the other hand, the austenite phase in the as-solution materials was significantly transformed the martensite phase as the stress increased. It was clarified to be responsible for their respective strength properties.
Shiwaku, Hideaki; Marushita, Motoharu*
JAEA-Research 2022-015, 39 Pages, 2023/05
We designed the hard X-ray undulator beamline BL22XU, which is dedicated to Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) at SPring-8 (now Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA)). BL22XU is used for XAFS (X-ray Absorption Fine Structure) analysis experiments to develop separation and extraction materials for radioactive waste treatment and to elucidate their chemical behavior, magnetic research experiments using a diffractometer, and experiments under extreme conditions using a high-pressure press and a diamond anvil cell. The available X-ray energy range was set from 3 to 70 keV. To design the optics of the beamline, the reflectivity of the mirrors, the diffraction width of the monochromatic crystal, and the absorptance of the Be window were calculated. In addition, ray tracing was performed to optimize the materials for optics, dimensions, and location. The delay time of the ADL (Acoustic Delay Line) was also examined to ensure the safety in the use of radioactive materials. The operation of BL22XU "JAEA Actinide Science I" has already started. By collaborating BL22XU and BL23SU "JAEA Actinide Science II," which uses a soft X-ray undulator as a light source, we solve the problems to promote nuclear sciences. Since the monochromator was upgraded in 2018-2019, initial planning and measured data are documented here again.
Iyota, Muneyoshi*; Matsuda, Tomoki*; Sano, Tomokazu*; Shigeta, Masaya*; Shobu, Takahisa; Yumoto, Hirokatsu*; Koyama, Takahisa*; Yamazaki, Hiroshi*; Semba, Yasunori*; Ohashi, Haruhiko*; et al.
Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 94, p.424 - 434, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:69.06(Engineering, Manufacturing)Yamazaki, Yasuhiro*; Shinomiya, Keisuke*; Okumura, Tadaharu*; Suzuki, Kenji*; Shobu, Takahisa; Nakamura, Yuiga*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(2), p.14_1 - 14_12, 2023/05
Suzuki, Kenji*; Miura, Yasufumi*; Shiro, Ayumi*; Toyokawa, Hidenori*; Saji, Choji*; Shobu, Takahisa; Morooka, Satoshi
Zairyo, 72(4), p.316 - 323, 2023/04
 synchrotron X-ray scattering and nanoindentation test
synchrotron X-ray scattering and nanoindentation testIm, S.*; Jee, H.*; Suh, H.*; Kanematsu, Manabu*; Morooka, Satoshi; Choe, H.*; Nishio, Yuhei*; Machida, Akihiko*; Kim, J.*; Lim, S.*; et al.
Construction and Building Materials, 365, p.130034_1 - 130034_18, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:77.68(Construction & Building Technology)Hirano, Tatsumi*; Maeda, Takehiro*; Murata, Tetsuyuki*; Yamaki, Takahiro*; Matsubara, Eiichiro*; Shobu, Takahisa; Shiro, Ayumi*; Yasuda, Ryo*; Takamatsu, Daiko*
SPring-8/SACLA Riyo Kenkyu Seikashu (Internet), 11(1), p.49 - 57, 2023/02
Tamura, Fumihiko; Omori, Chihiro*; Yoshii, Masahito*; Tomizawa, Masahito*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Sugiyama, Yasuyuki*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Kobayashi, Aine*; Okita, Hidefumi
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.175 - 178, 2023/01
J-PARC MR delivers high intensity proton beams to the neutrino experiment. Eight bunches with high peak currents are extracted from the MR by the extraction kicker, therefore the neutrino beam has the similar structure. Intermediate Water Cherenkov Detector (IWCD) will be installed for the future experiments and the IWCD requires a time structure with low peaks. We consider bunch manipulation at flattop of the MR for reducing the peak current. It should be quickly done to avoid the significant loss of the beam power. The beam gap for the kicker rise time must be kept. We propose a non-adiabatic bunch manipulation using the multiharmonic rf voltage. The longitudinal impedance in the MR can affect the beam stability. The feasibility of the manipulation is discussed by using the longitudinal simulations.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:73.20(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.