Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Tc for Compton camera imaging
Tc for Compton camera imagingHatsukawa, Yuichi; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Nagai, Yasuki; Tanimori, Toru*; Sonoda, Shinya*; Kabuki, Shigeto*; et al.
no journal, ,
In recent years, the Compton camera which is originally developed for the astrophysical studies was applied for medical diagnostic usage. For the Compton camera imaging require technetium isotopes emitting higher energy  -rays. Two Tc isotopes,
-rays. Two Tc isotopes,  Tc (T
Tc (T = 60 d; E
= 60 d; E = 204, 582 and 835 keV) and
= 204, 582 and 835 keV) and 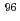 Tc(T
Tc(T = 4.28 d, E
= 4.28 d, E = 778 and 812 keV) are candidates for Compton camera imaging. Compton camera imaging can realize high position resolution without collimator. Because of no collimator using, the Compton camera makes higher
= 778 and 812 keV) are candidates for Compton camera imaging. Compton camera imaging can realize high position resolution without collimator. Because of no collimator using, the Compton camera makes higher  -ray detection efficiency. Compared with SPECT with
-ray detection efficiency. Compared with SPECT with  Tc, the Compton camera imaging technique can be expected that radiation exposure deduce to 1/5-1/10. In this study, technetium-95m was produced by the
Tc, the Compton camera imaging technique can be expected that radiation exposure deduce to 1/5-1/10. In this study, technetium-95m was produced by the  Mo(p,n)
Mo(p,n) Tc reaction.
Tc reaction.