Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -,
-,  - and X-ray spectra
- and X-ray spectraOshima, Masumi*; Goto, Jun*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Asai, Masato; Shinohara, Hirofumi*; Suzuki, Katsuyuki*; Shen, H.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(4), p.379 - 388, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The spectrum determination method (SDM) is the method to determine radioactivities by analyzing full spectral shape of  - or
- or  rays through least-squares fitting by referring to standard
rays through least-squares fitting by referring to standard  - and
- and  spectra. In this paper, we have newly applied the SDM to a unified spectrum composed of two spectra measured with a Ge detector and a liquid scintillation counter. By analyzing the unified spectrum, uncertainties of deduced radioactivities have been improved. We applied this method to the unified spectrum including 40 radionuclides with equal intensities, and have deduced their radioactivities correctly.
spectra. In this paper, we have newly applied the SDM to a unified spectrum composed of two spectra measured with a Ge detector and a liquid scintillation counter. By analyzing the unified spectrum, uncertainties of deduced radioactivities have been improved. We applied this method to the unified spectrum including 40 radionuclides with equal intensities, and have deduced their radioactivities correctly.
Oshima, Masumi*; Goto, Jun*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Shinohara, Hirofumi*; Suzuki, Katsuyuki*; Sano, Yuichi*; Asai, Masato; Haraga, Tomoko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(7), p.871 - 882, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:17.48(Nuclear Science & Technology)Previously we reported a simple algorithmic method of spectral determination method (SDM), which is based on the first principle that a  -ray spectrum obtained for a sample is a linear superposition of individual spectra of the radioactive nuclides included in the sample and demonstrated that the method is valid for
-ray spectrum obtained for a sample is a linear superposition of individual spectra of the radioactive nuclides included in the sample and demonstrated that the method is valid for  -ray determination. Here we apply it to the spectra obtained by liquid scintillation counter (LSC). In LSC measurements quenching is generally observed and we at first developed its correction method to standard spectra. The SDM code reported in the previous investigation is used to analyze the LSC spectra. Based on the analyses done by using the measured spectra, we concluded that the SDM method is valid in the LSC spectra similarly to the
-ray determination. Here we apply it to the spectra obtained by liquid scintillation counter (LSC). In LSC measurements quenching is generally observed and we at first developed its correction method to standard spectra. The SDM code reported in the previous investigation is used to analyze the LSC spectra. Based on the analyses done by using the measured spectra, we concluded that the SDM method is valid in the LSC spectra similarly to the  -ray spectra studied in the previous investigation.
-ray spectra studied in the previous investigation.
 ,
,  , and X-ray spectrum analysis
, and X-ray spectrum analysisOshima, Masumi*; Goto, Jun*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Asai, Masato; Kin, Tadahiro*; Shinohara, Hirofumi*
Isotope News, (790), p.19 - 23, 2023/12
When analyzing samples that contain many radionuclides at various concentrations, such as radioactive waste or fuel debris, it is difficult to apply general spectrum analysis methods and is necessary to chemically separate each nuclide before quantifying it. The chemical separation is especially essential for analysis using a liquid scintillation counter (LSC). In this report, the authors explain the newly developed spectral determination method (SDM) in which the entire spectrum is fitted to quantify radioactivity of nuclides mixed in a sample. By applying the SDM to  - and X-ray spectrum measured by LSC and
- and X-ray spectrum measured by LSC and  -ray spectrum measured by Ge detector simultaneously, the authors demonstrated that radioactivity of 40 radionuclides mixed in a sample at concentrations varying by two orders could be quantified, which is useful to simplify chemical separation process in radionuclide quantification.
-ray spectrum measured by Ge detector simultaneously, the authors demonstrated that radioactivity of 40 radionuclides mixed in a sample at concentrations varying by two orders could be quantified, which is useful to simplify chemical separation process in radionuclide quantification.
M ri, A.*; Mazurek, M.*; Ota, Kunio; Siitari-Kauppi, M.*; Eichinger, F.*; Leuenberger, M.*
ri, A.*; Mazurek, M.*; Ota, Kunio; Siitari-Kauppi, M.*; Eichinger, F.*; Leuenberger, M.*
Minerals (Internet), 11(10), p.1072_1 - 1072_17, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:37.55(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Sakai, Kenji; Oi, Motoki; Teshigawara, Makoto; Naoe, Takashi; Haga, Katsuhiro; Watanabe, Akihiko*
Journal of Neutron Research, 22(2-3), p.337 - 343, 2020/10
For operating a spallation neutron source and a muon target safely and efficiently, a general control system (GCS) operates within Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF). GCS administers operation and interlock processes of many instruments under various operation status. Since the first beam injection in 2008, it has operated stably without any serious troubles for more than ten years. GCS has a data storage server storing operational data on status around target stations. It has functioned well to detect and investigate unusual situations by checking data in this server. For continuing stable operation of MLF in future, however, introduction of abnormality sign determination system (ASDS) will be necessary for picking up potential abnormalities of target stations caused by radiation damages, time-related deterioration and so on. It will judge abnormalities from slight state transitions of target stations based on analysis with various operational data throughout proton beams, target stations, and secondary beams during long-term operations. This report mentions present status of GCS, conceptual design of ASDS, and installation of an integral data storage server which can deal with various data for ASDS integrally.
Kawaguchi, Munemichi; Miyahara, Shinya; Uno, Masayoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(8), p.874 - 884, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.50(Nuclear Science & Technology)As parts of severe accident studies in sodium-cooled fast reactor, experiments were performed to investigate the termination mechanism of sodium-concrete reaction (SCR). In the experiment, the reaction time was controlled to investigate the distribution change of sodium (Na) and the reaction products in the pool and around the reaction front. In the results, the Na around the reaction front decreased from the enough amount with the reaction time. The concentrations were 18-24 wt.% for Na, and 22-18 wt.% for Si after the termination. From the thermodynamics calculations, the stable materials around the reaction front comprised more than 90 wt.% solid products such as Na SiO
SiO , and no Na. Further, the distribution of Na and reaction products could be explained by a steady-state sedimentation-diffusion model. At the early stage of SCR, the reaction products were suspended as particles in the Na pool because of the high H
, and no Na. Further, the distribution of Na and reaction products could be explained by a steady-state sedimentation-diffusion model. At the early stage of SCR, the reaction products were suspended as particles in the Na pool because of the high H -generation rate. As the concrete ablation proceeds, they start settling down due to the decreased H
-generation rate. As the concrete ablation proceeds, they start settling down due to the decreased H -generation rate, thereby allowing SCR termination. It was concluded that SCR termination was caused by the sediment of the reaction products and the lack of Na around the reaction front.
-generation rate, thereby allowing SCR termination. It was concluded that SCR termination was caused by the sediment of the reaction products and the lack of Na around the reaction front.
Kawaguchi, Munemichi; Doi, Daisuke; Seino, Hiroshi; Miyahara, Shinya
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(12), p.2098 - 2107, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:43.87(Nuclear Science & Technology)A sodium concrete reaction (SCR) is one of the important phenomena to cause the structural concrete ablation and the release of H gas in the case of sever accident of sodium cooled fast reactors. In this study, the long-time SCR test had been carried out to investigate the self-termination mechanism. The results showed the SCR terminated even if the enough amount of Na remained on the concrete. The quantitative data were collected on the SCR terminating such as temperature and H
gas in the case of sever accident of sodium cooled fast reactors. In this study, the long-time SCR test had been carried out to investigate the self-termination mechanism. The results showed the SCR terminated even if the enough amount of Na remained on the concrete. The quantitative data were collected on the SCR terminating such as temperature and H generation. The reaction products, which became the small solids in liquid Na were transferred with slurry state by generated H
generation. The reaction products, which became the small solids in liquid Na were transferred with slurry state by generated H bubbles. Though the Na transfers actively and ablated the concrete surface with the high H
bubbles. Though the Na transfers actively and ablated the concrete surface with the high H generation rate, the mass exchange coefficient defined as
generation rate, the mass exchange coefficient defined as 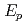 decreased and the reaction products settled gradually with decreasing the H
decreased and the reaction products settled gradually with decreasing the H generation rate. Therefore, the Na concentration decreased at the reaction front and resulted in the SCR terminating naturally.
generation rate. Therefore, the Na concentration decreased at the reaction front and resulted in the SCR terminating naturally.
Okubo, Ayako; Kimura, Yoshiki; Shinohara, Nobuo; Toda, Nobufumi; Funatake, Yoshio; Watahiki, Masaru; Sakurai, Satoshi; Kuno, Yusuke
JAEA-Technology 2015-001, 185 Pages, 2015/03
Nuclear forensics is the analysis of intercepted illicit nuclear or radioactive material and any associated material to provide evidence for nuclear attribution by determining origin, history, transit routes and purpose involving such material. Nuclear forensics activity includes sampling of the illicit material, analysis of the samples and evaluation of the attribution by comparing the analyzed data with database or numerical simulation. Because the nuclear forensics technologies specify the origin of the nuclear materials used illegal dealings or nuclear terrorism, it becomes possible to identify and indict offenders, hence to enhance deterrent effect against such terrorism. Worldwide network on nuclear forensics can contribute to strengthen global nuclear security regime. In this paper, the results of research and development of fundamental nuclear forensics technologies performed in Japan Atomic Energy Agency during the fiscal term of 2011-2013 were reported.
Suyama, Kenya; Mochizuki, Hiroki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 42(7), p.661 - 669, 2005/07
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:68.27(Nuclear Science & Technology)Burnup is important value for criticality safety evaluation of spent nuclear fuel. Nd-148 method is one of most important method to evaluate the burnup of post irradiation examination (PIE) samples, and well known that it has good accuracy. However, the evaluated burnup values could be perturbed by the neutron capture reaction of Nd-147 and Nd-148. And in the analysis of PIE data from PWR, the calculation results of Nd-148 have approximately more than 1% deviation from experiment. In this study, the contribution of neutron capture reaction of Nd-147 and Nd-148 to Nd-148 amount are discussed. Especially for Nd-147 contribution, it is shown that the current evaluated cross section of Nd-147 is not supported and the new evaluation is consistent with the analysis of PIE data. Possible perturbed amount of Nd-148 by both reactions is less than 0.7% for normal reactor operation condition, and it is approximately 0.1% for 30 GWd/t (BWR) and 40 GWd/t (PWR). Finally, we confirm again that Nd-148 method is good evaluation method.
Morita, Kenji*; Ishikawa, Dai*; Yuhara, Junji*; Nakamura, Daisuke*; Soda, Kazuo*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Narumi, Kazumasa; Naramoto, Hiroshi; Saito, Kazuo*
JAERI-Review 99-025, TIARA Annual Report 1998, p.179 - 181, 1999/10
no abstracts in English
Yoshino, Ryuji; Nakamura, Yukiharu; Neyatani, Yuzuru
Nuclear Fusion, 36(3), p.295 - 307, 1996/00
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:71.56(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Nagai, Ryoji; Kobayashi, Hideki*; Sasaki, Shigemi; Sawamura, Masaru; Sugimoto, Masayoshi; ; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Okubo, Makio; Minehara, Eisuke; ; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 358, p.403 - 406, 1995/00
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:75.46(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
; ;
Fresenius' Z.Anal.Chem., 323, p.225 - 227, 1986/00
None
Bunseki Kagaku, 33(6), p.336 - 338, 1984/00
no abstracts in English
; ; Shiba, Koreyuki
J.Phys.,E, 17, p.339 - 341, 1984/00
no abstracts in English
;
Anal. Chem., 55(13), p.2059 - 2062, 1983/00
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:63.78(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English

 Mo using differential pulse polarography
Mo using differential pulse polarographyR.K.Barnes*; E.L.R.Hetheringtone*;
Int.J.Appl.Radiat.Isot., 34(3), p.603 - 606, 1983/00
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:43.74(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English


 Eu activity
Eu activity; ; ; ;
Nuclear Instruments and Methods, 203, p.273 - 280, 1982/00
no abstracts in English
; Iwamoto, K.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 13(3), p.132 - 138, 1976/03
Times Cited Count:1no abstracts in English
Nuclear Instruments and Methods, 114(1), p.65 - 69, 1974/01
no abstracts in English