Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Shibahara, Yuji*
KURNS Progress Report 2024, P. 31, 2025/06
no abstracts in English
Fukuda, Kodai; Obara, Toru*; Suyama, Kenya
Nuclear Technology, 211(5), p.963 - 973, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe
FeNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(3), p.300 - 307, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) Er(n,
Er(n, )
)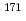 Er and
Er and  Hf(n,
Hf(n, )
) Hf reactions
Hf reactionsNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 14 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Fukuda, Kodai; Obara, Toru*
Nuclear Technology, 12 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0Yoshida, Go*; Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Nakamura, Hajime*; Miura, Taichi*; Toyoda, Akihiro*; Masumoto, Kazuyoshi*; Nakabayashi, Takayuki*; Matsuda, Makoto
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(10), p.1298 - 1307, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Watanabe, Miku*; Miyamoto, Goro*; Zhang, Y.*; Morooka, Satoshi; Harjo, S.; Kobayashi, Yasuhiro*; Furuhara, Tadashi*
ISIJ International, 64(9), p.1464 - 1476, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:57.76(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Li, L.*; Miyamoto, Goro*; Zhang, Y.*; Li, M.*; Morooka, Satoshi; Oikawa, Katsunari*; Tomota, Yo*; Furuhara, Tadashi*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 184, p.221 - 234, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:52.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) -odd/
-odd/ -odd interactions on the 0.75 eV
-odd interactions on the 0.75 eV  -wave resonance in
-wave resonance in 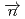 +
+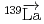 forward transmission determined using a pulsed neutron beam
forward transmission determined using a pulsed neutron beamNakabe, Rintaro*; Auton, C. J.*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Gudkov, V.*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ide, Ikuo*; Ino, Takashi*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Kambara, Wataru*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(4), p.L041602_1 - L041602_4, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:18.90(Physics, Nuclear) -wave resonance of
-wave resonance of 
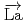 +
+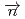
Okudaira, Takuya*; Nakabe, Rintaro*; Auton, C. J.*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Gudkov, V.*; Ide, Ikuo*; Ino, Takashi*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Kambara, Wataru*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(4), p.044606_1 - 044606_9, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:74.11(Physics, Nuclear) Nb by activation method and half-life of
Nb by activation method and half-life of  Nb by mass analysis
Nb by mass analysisNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1361 - 1371, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:59.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)The thermal-neutron capture cross section (
 ) and resonance integral (I
) and resonance integral (I ) for
) for  Nb among nuclides for decommissioning were measured by an activation method and the half-life of
Nb among nuclides for decommissioning were measured by an activation method and the half-life of  Nb by mass analysis. Niobium-93 samples were irradiated with a hydraulic conveyer installed in the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Gold-aluminum, cobalt-aluminum alloy wires were used to monitor thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indexes at an irradiation position. A 25-
Nb by mass analysis. Niobium-93 samples were irradiated with a hydraulic conveyer installed in the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Gold-aluminum, cobalt-aluminum alloy wires were used to monitor thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indexes at an irradiation position. A 25- m-thick gadolinium foil was used to sort out reactions ascribe to thermal-and epi-thermal neutrons. Its thickness provided a cut-off energy of 0.133 eV. In order to attenuate radioactivity of
m-thick gadolinium foil was used to sort out reactions ascribe to thermal-and epi-thermal neutrons. Its thickness provided a cut-off energy of 0.133 eV. In order to attenuate radioactivity of 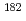 Ta due to impurities, the Nb samples were cooled for nearly 2 years. The induced radio activity in the monitors and Nb samples were measured by
Ta due to impurities, the Nb samples were cooled for nearly 2 years. The induced radio activity in the monitors and Nb samples were measured by  -ray spectroscopy. In analysis based on Westcott's convention, the
-ray spectroscopy. In analysis based on Westcott's convention, the 
 and I
and I values were derived as 1.11
values were derived as 1.11 0.04 barn and 10.5
0.04 barn and 10.5 0.6 barn, respectively. After the
0.6 barn, respectively. After the  -ray measurements, mass analysis was applied to the Nb sample to obtain the reaction rate. By combining data obtained by both
-ray measurements, mass analysis was applied to the Nb sample to obtain the reaction rate. By combining data obtained by both  -ray spectroscopy and mass analysis, the half-life of
-ray spectroscopy and mass analysis, the half-life of  Nb was derived as (2.00
Nb was derived as (2.00 0.15)
0.15) 10
10 years.
years.
Okita, Shoichiro; Goto, Minoru
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/10
Wu, P.*; Murai, Naoki; Li, T.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Xia, K.*; Peng, K.*; Zhang, Y.*; et al.
New Journal of Physics (Internet), 25(1), p.013032_1 - 013032_11, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Nakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(11), p.1388 - 1398, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:14.04(Nuclear Science & Technology)The present study selected  Np among radioactive nuclides and aimed to measure the thermal-neutron capture cross-section for
Np among radioactive nuclides and aimed to measure the thermal-neutron capture cross-section for  Np in a well-thermalized neutron field by an activation method. A
Np in a well-thermalized neutron field by an activation method. A  Np standard solution was used for irradiation samples. A thermal-neutron flux at an irradiation position was measured with neutron flux monitors:
Np standard solution was used for irradiation samples. A thermal-neutron flux at an irradiation position was measured with neutron flux monitors:  Sc,
Sc,  Co,
Co,  Mo,
Mo,  Ta and
Ta and  Au. The
Au. The  Np sample and flux monitors were irradiated together for 30 minutes in the graphite thermal column equipped with the Kyoto University Research Reactor. The similar irradiation was carried out twice. After the irradiations, the
Np sample and flux monitors were irradiated together for 30 minutes in the graphite thermal column equipped with the Kyoto University Research Reactor. The similar irradiation was carried out twice. After the irradiations, the  Np samples were quantified using 312-keV gamma ray emitted from
Np samples were quantified using 312-keV gamma ray emitted from  Pa in a radiation equilibrium with
Pa in a radiation equilibrium with  Np. The reaction rates of
Np. The reaction rates of  Np were obtained from gamma-ray peak net counts given by
Np were obtained from gamma-ray peak net counts given by  Np, and then the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of
Np, and then the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of  Np was found to be 173.8
Np was found to be 173.8 4.4 barn by averaging the results obtained by the two irradiations. The present result was in agreement with the reported data given by a time-of-flight method within the limit of uncertainty.
4.4 barn by averaging the results obtained by the two irradiations. The present result was in agreement with the reported data given by a time-of-flight method within the limit of uncertainty.
 Np(n,
Np(n,  ) reaction with TC-Pn in KUR
) reaction with TC-Pn in KURNakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Shibahara, Yuji*
KURNS Progress Report 2021, P. 93, 2022/07
In terms of nuclear transmutation studies of minor actinides in nuclear wastes, the present work selected  Np among them and aimed to measure the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of
Np among them and aimed to measure the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of  Np using a well-thermalized neutron field by a neutron activation method because there have been discrepancies among reported cross-section data. A
Np using a well-thermalized neutron field by a neutron activation method because there have been discrepancies among reported cross-section data. A  Np standard solution was used for irradiation samples. The thermal-neutron flux at an irradiation position was measured with flux monitors:
Np standard solution was used for irradiation samples. The thermal-neutron flux at an irradiation position was measured with flux monitors:  Sc,
Sc,  Co,
Co,  Mo,
Mo,  Ta and
Ta and  Au. The
Au. The  Np sample was irradiated together with the flux monitors for 30 minutes in the graphite thermal column equipped in the Kyoto University Research Reactor. The similar irradiation was repeated once more to confirm the reproducibility of the results. After irradiation, the
Np sample was irradiated together with the flux monitors for 30 minutes in the graphite thermal column equipped in the Kyoto University Research Reactor. The similar irradiation was repeated once more to confirm the reproducibility of the results. After irradiation, the  Np samples were quantified using 312-keV gamma-ray emitted from
Np samples were quantified using 312-keV gamma-ray emitted from  Pa in radiation equilibrium with
Pa in radiation equilibrium with  Np. The reaction rates of
Np. The reaction rates of  Np were obtained from the peak net counts of gamma-rays emitted from generated
Np were obtained from the peak net counts of gamma-rays emitted from generated  Np, and then the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of
Np, and then the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of  Np was found to be 173.8
Np was found to be 173.8 4.7 barn by averaging the results obtained by the two irradiations. The present result was in agreement with the reported data given by a time-of-flight method within a limit of uncertainty.
4.7 barn by averaging the results obtained by the two irradiations. The present result was in agreement with the reported data given by a time-of-flight method within a limit of uncertainty.
Hashimoto, Shunsuke*; Nakajima, Kenji; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Shibata, Kaoru; Yamada, Takeshi*
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 342, p.117580_1 - 117580_8, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:23.35(Chemistry, Physical)Quasi-elastic neutron scattering (QENS) and pulsed-field-gradient nuclear magnetic resonance (PFGNMR) analyses of a nanofluid composed of silicon dioxide (SiO ) nanoparticles and a base fluid of ethylene glycol aqueous solution were performed. The aim was to elucidate the mechanism increase in the thermal conductivity of the nanofluid above its theoretical value. The obtained experimental results indicate that SiO
) nanoparticles and a base fluid of ethylene glycol aqueous solution were performed. The aim was to elucidate the mechanism increase in the thermal conductivity of the nanofluid above its theoretical value. The obtained experimental results indicate that SiO particles may decrease the self-diffusion coefficient of the liquid molecules in the ethylene glycol aqueous solution because of their highly restricted motion around these nanoparticles. At a constant temperature, the thermal conductivity increases as the self-diffusion coefficient of the liquid molecules decreases in the SiO
particles may decrease the self-diffusion coefficient of the liquid molecules in the ethylene glycol aqueous solution because of their highly restricted motion around these nanoparticles. At a constant temperature, the thermal conductivity increases as the self-diffusion coefficient of the liquid molecules decreases in the SiO nanofluids.
nanofluids.
Nakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(10), p.1061 - 1070, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:70.62(Nuclear Science & Technology)In a well-thermalized neutron field, it is principally possible to drive a thermal-neutron capture cross-section without considering an epithermal neutron component. This was demonstrated by a neutron activation method using the graphite thermal column (TC-Pn) of the Kyoto University Research Reactor. First, in order to confirm that the graphite thermal column was a well-thermalized neutron field, neutron irradiation was performed with neutron flux monitors:  Au,
Au,  Co,
Co,  Sc,
Sc,  Cu, and
Cu, and  Mo. The TC-Pn was confirmed to be extremely thermalized on the basis of Westcott's convention, because the thermal-neutron flux component took a constant value regardless of the sensitivity of each flux monitor to epithermal neutrons. Next, as a demonstration, the thermal-neutron capture cross section of
Mo. The TC-Pn was confirmed to be extremely thermalized on the basis of Westcott's convention, because the thermal-neutron flux component took a constant value regardless of the sensitivity of each flux monitor to epithermal neutrons. Next, as a demonstration, the thermal-neutron capture cross section of  Ta(n,
Ta(n, )
)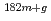 Ta reaction was measured using the graphite thermal column, and then derived to be 20.5
Ta reaction was measured using the graphite thermal column, and then derived to be 20.5 0.4 barn, which supported the evaluated value of 20.4
0.4 barn, which supported the evaluated value of 20.4 0.3 barn. The
0.3 barn. The  Ta nuclide could be useful as a flux monitor that complements the sensitivity between
Ta nuclide could be useful as a flux monitor that complements the sensitivity between  Au and
Au and  Mo monitors.
Mo monitors.
 Am(n,
Am(n, )
)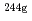 Am and
Am and  Am(n,
Am(n, )
)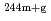 Am reactions
Am reactionsNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(3), p.259 - 277, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:42.20(Nuclear Science & Technology)Research and development were made for accuracy improvement of neutron capture cross section data on  Am among minor actinides. First, the emission probabilities of decay
Am among minor actinides. First, the emission probabilities of decay  rays were obtained with high accuracy, and the amount of the ground state of
rays were obtained with high accuracy, and the amount of the ground state of  Am produced by reactor neutron irradiation of
Am produced by reactor neutron irradiation of  Am was examined by
Am was examined by  -ray measurement. Next, the total amount of isomer and ground states was examined by
-ray measurement. Next, the total amount of isomer and ground states was examined by  -ray measurement. Thermal-neutron capture cross sections and resonance integrals were derived both for the
-ray measurement. Thermal-neutron capture cross sections and resonance integrals were derived both for the  Am(n,
Am(n, )
)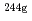 Am and for
Am and for  Am(n,
Am(n, )
)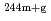 Am reactions.
Am reactions.
Okita, Shoichiro; Tasaki, Seiji*; Abe, Yutaka*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 19(3), p.178 - 184, 2020/09
The Kyoto University Accelerator-based Neutron Source (KUANS) is a compact neutron source that is mainly used for spectrometer and detector development. In addition, it is also suited for experiments to study the neutronic design of moderators owing to the relatively low neutron generation yield by  Be(p,n). We present a neutronic design of the neutron moderator on a reentrant-hole configuration for KUANS to enhance the neutron emission, and some experiments are conducted at KUANS for verification. A polyethylene moderator on a reentrant-hole configuration is designed by PHITS calculation and is introduced to KUANS to obtain intense oblong neutron beams. The intensity of the pulsed neutron beam is experimentally measured. The results reveal that the intensity becomes approximately 1.9 times stronger than that of the conventional rectangular design. In addition, the ratio of its intensity to the conventional intensity increases to approximately threefold as the neutron wavelength increases. It is interesting to note that the longer the neutron wavelength, the more efficiently they are extracted from the inside of the moderator owing to the existence of the reentrant-hole configuration.
Be(p,n). We present a neutronic design of the neutron moderator on a reentrant-hole configuration for KUANS to enhance the neutron emission, and some experiments are conducted at KUANS for verification. A polyethylene moderator on a reentrant-hole configuration is designed by PHITS calculation and is introduced to KUANS to obtain intense oblong neutron beams. The intensity of the pulsed neutron beam is experimentally measured. The results reveal that the intensity becomes approximately 1.9 times stronger than that of the conventional rectangular design. In addition, the ratio of its intensity to the conventional intensity increases to approximately threefold as the neutron wavelength increases. It is interesting to note that the longer the neutron wavelength, the more efficiently they are extracted from the inside of the moderator owing to the existence of the reentrant-hole configuration.
 Am(n,
Am(n, )
)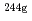 Am,
Am, 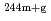 Am reactions
Am reactionsNakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Shibahara, Yuji*
KURNS Progress Report 2019, P. 132, 2020/08
Research and development were made for accuracy improvement of neutron capture cross section data on  Am among minor actinides. First, the emission probabilities of decay
Am among minor actinides. First, the emission probabilities of decay  rays were obtained with high accuracy, and the amount of the ground state of
rays were obtained with high accuracy, and the amount of the ground state of  Am produced by reactor neutron irradiation of
Am produced by reactor neutron irradiation of  Am was examinded by
Am was examinded by  -ray measurement. Next, the total amount of isomer and ground states was examoned by
-ray measurement. Next, the total amount of isomer and ground states was examoned by  -ray measurement.
-ray measurement.