Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hatae, Takaki; Naito, Osamu; Kitamura, Shigeru; Sakuma, Takeshi*; Hamano, Takashi*; Nakatsuka, Masahiro*; Yoshida, Hidetsugu*
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 49, p.S160 - S164, 2006/12
no abstracts in English
Hatae, Takaki; Kondoh, Takashi; Naito, Osamu; Nakatsuka, Masahiro*; Yoshida, Hidetsugu*
Proceedings of 12th International Symposium on Laser-Aided Plasma Diagnostics (LAPD-12) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/09
no abstracts in English
Hatae, Takaki; Nakatsuka, Masahiro*; Yoshida, Hidetsugu*
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 80(10), p.870 - 882, 2004/10
A high performance phase conjugate mirror by stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS-PCM) is applied to Thomson scattering diagnostics in JT-60U for the first time. To improve the measurement performance, two developments were performed with SBS-PCM. First, we developed a new optical design to provide a double-pass scattering scheme with SBS-PCM. A laser beam passing through the plasma is reflected by the SBS-PCM, and a reflected beam returned back through the same path as coming one by the phase conjugate effect, and passed through the plasma again. The double path Thomson scattering scheme demonstrated in JT-60U plasma that a factor of 1.6 increase of the scattered light in contrast with single-pass scattering. Second, an improvement of the output power of YAG laser system using the SBS-PCM was performed. As a result, average power was increased over 8 times in contrast with conventional system, and was achieved up to 368 W (7.4 J  50 Hz). A multi-pass Thomson scattering scheme is also proposed based on the results of double-pass scattering.
50 Hz). A multi-pass Thomson scattering scheme is also proposed based on the results of double-pass scattering.
Yamauchi, Toshihiko
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 43(9A), p.6473 - 6474, 2004/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)The output pattern of He-Ne laser that passes through the optical glass fiber bundle used for free electron laser etc. depends on the weight of load (modulation of transverse mode). The increment of pattern radius exponentially increases with the load. It is considered that the micro bending causes this increment. Next, the estimated delay time also exponentially increases with the weight of load, and the estimated delay time is the extent of pico-second.

Nagao, Tatsuya*; Igarashi, Junichi
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 72(9), p.2381 - 2384, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:54.40(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We examine the mechanism of the X-ray diffraction process by including the Thomson scattering (TS) term in addition to the resonant X-ray scattering (RXS) term near the Ce L absorption edge in the antiferroquadrupole (AFQ) ordering phase of CeB . Assuming the AFQ order in the 4f states but without any lattice distortion, we obtain the TS intensity comparable to the RXS intensity, owing to the anisotropic charge distribution of 4f states. The present calculation reproduces well the interference pattern between the TS and RXS terms for the (5/2,3/2,3/2) spot observed in the recent experiment. The result suggests that the TS signal as well as the main peak of the RXS signal are a direct reflection of the AFQ order in CeB
. Assuming the AFQ order in the 4f states but without any lattice distortion, we obtain the TS intensity comparable to the RXS intensity, owing to the anisotropic charge distribution of 4f states. The present calculation reproduces well the interference pattern between the TS and RXS terms for the (5/2,3/2,3/2) spot observed in the recent experiment. The result suggests that the TS signal as well as the main peak of the RXS signal are a direct reflection of the AFQ order in CeB .
.
 -particle diagnostics by CO
-particle diagnostics by CO laser collective Thomson scattering in ITER
laser collective Thomson scattering in ITERKondoh, Takashi; Richards, R. K.*; Hutchinson, D. P.*; Sugie, Tatsuo; Costley, A. E.*; Miura, Yukitoshi; Lee, S.*
Proceedings of 30th EPS Conference on Controlled Fusion and Plasma Physics (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2003/07
In order to understand the behavior of alpha-particles which are the dominant heat source in a burning plasma, it is necessary to measure the spatial distribution of the number of the alpha-particles and their energy spectrum. A collective Thomson scattering (CTS) system based on a pulsed CO laser is being developed and is under consideration for alpha-particle measurements on ITER. Heating beam ions (E = 1 MeV) are normally co-injected and have a similar velocity with alpha-particles in ITER. The CTS measurement can not, in general, distinguish beam ions and alpha-particles which have the same velocity. A vertical scattering geometry to distinguish between beam ions and alpha-particles is proposed. Calculations have shown that the vertically viewing CTS can resolve counter-travelling alphas without being masked by beam ions. Preliminary design of a beam line and a receiver system with the vertical scattering geometry has been developed. A proof-of-principle test on the CTS system using the JT-60U plasma is being conducted.
laser is being developed and is under consideration for alpha-particle measurements on ITER. Heating beam ions (E = 1 MeV) are normally co-injected and have a similar velocity with alpha-particles in ITER. The CTS measurement can not, in general, distinguish beam ions and alpha-particles which have the same velocity. A vertical scattering geometry to distinguish between beam ions and alpha-particles is proposed. Calculations have shown that the vertically viewing CTS can resolve counter-travelling alphas without being masked by beam ions. Preliminary design of a beam line and a receiver system with the vertical scattering geometry has been developed. A proof-of-principle test on the CTS system using the JT-60U plasma is being conducted.
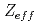 spatial profile from background light in incoherent Thomson scattering diagnostic
spatial profile from background light in incoherent Thomson scattering diagnosticNaito, Osamu; Hatae, Takaki
JAERI-Research 2002-033, 9 Pages, 2003/03
A simulation study on the feasibility of inferring spatial 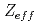 profile along with electron temperature and density in Thomson scattering diagnostic is presented. The background signal, which is usually discarded after subtracted from the Thomson scattered signal, is used in the reconstruction procedure. If the contribution from line radiation to the background signal is by one order of magnitude smaller than that from bremsstrahlung, a fairly accurate
profile along with electron temperature and density in Thomson scattering diagnostic is presented. The background signal, which is usually discarded after subtracted from the Thomson scattered signal, is used in the reconstruction procedure. If the contribution from line radiation to the background signal is by one order of magnitude smaller than that from bremsstrahlung, a fairly accurate 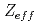 profile can be reconstructed.
profile can be reconstructed.
 laser for ion energy spectrum measurements in JT-60U
laser for ion energy spectrum measurements in JT-60UKondoh, Takashi; Miura, Yukitoshi; Lee, S.*; Richards, R. K.*; Hutchinson, D. P.*; Bennett, C. A.*
Review of Scientific Instruments, 74(3), p.1642 - 1645, 2003/03
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:67.54(Instruments & Instrumentation)Measurements of energy spectrum and density profile of confined alpha-particles are required for ITER. Several methods have been proposed, however, a measurement technique hasn't been established yet. A collective Thomson scattering (CTS) system based on a pulsed CO laser is being developed to demonstrate feasibility of alpha-particle diagnostics for ITER. The pulse laser (15J, 1
laser is being developed to demonstrate feasibility of alpha-particle diagnostics for ITER. The pulse laser (15J, 1 m, 0.6
m, 0.6  m) and a wide band (~ 8GHz) heterodyne receiver with a quantum-well infrared photodetector (QWIP) have been developed and installed in the JT-60U tokamak. Stray light is reduced by a notch filter with hot CO
m) and a wide band (~ 8GHz) heterodyne receiver with a quantum-well infrared photodetector (QWIP) have been developed and installed in the JT-60U tokamak. Stray light is reduced by a notch filter with hot CO gas. Heterodyne receiver is absolutely calibrated using large area blackbody radiation source. Scattered signal from JT-60U plasma has not detected because of electrical noise originated from discharge of the pulsed laser and stray signal caused by impurity of the spectrum of the pulsed laser.
gas. Heterodyne receiver is absolutely calibrated using large area blackbody radiation source. Scattered signal from JT-60U plasma has not detected because of electrical noise originated from discharge of the pulsed laser and stray signal caused by impurity of the spectrum of the pulsed laser.
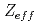 spatial profile in incoherent Thomson scattering diagnostic
spatial profile in incoherent Thomson scattering diagnosticNaito, Osamu; Hatae, Takaki
Review of Scientific Instruments, 74(3), p.1374 - 1376, 2003/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)A simulation study on the feasibility of inferring spatial 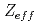 profile along with electron temperature and density in Thomson scattering diagnostic is presented. The background signal, which is usually discarded after subtracted from the Thomson scattered signal, is used in the reconstruction procedure. If the background signal consists predominantly of bremsstrahlung radiation, a fairly accurate
profile along with electron temperature and density in Thomson scattering diagnostic is presented. The background signal, which is usually discarded after subtracted from the Thomson scattered signal, is used in the reconstruction procedure. If the background signal consists predominantly of bremsstrahlung radiation, a fairly accurate 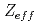 profile can be reconstructed. Additional benefit of including background signal in the reconstruction is the reduction of errors in the inferred electron temperature and density.
profile can be reconstructed. Additional benefit of including background signal in the reconstruction is the reduction of errors in the inferred electron temperature and density.
Hatae, Takaki; JT-60 Team
Proceedings of 6th Japan-Australia Workshop on Plasma Diagnostics (CD-ROM), 16 Pages, 2002/00
The diagnostic system of JT-60U is composed of about 50 individual diagnostic devices. Recently, the detailed radial profile measurements of plasma parameters such as electron temperature, electron density, ion temperature, plasma rotation, and plasma current (safety factor q) have been improved. As a result, the understanding of internal structure of plasmas has advanced. In particular, detailed studies of the internal transport barrier could be performed in reversed magnetic shear plasmas. Furthermore, a "current hole" or a nearly zero current density at the plasma center was discovered in JT-60U plasmas by using a motional stark effect (MSE) system. Several diagnostic signal have been linked to actuators such as neutral beam injectors, the gas feed system, and the electron cyclotron heating system establishing the real-time control of electron temperature, neutron yield, radiated power, and electron temperature gradient, and thus improving plasma performance.
 laser in JT-60U
laser in JT-60UKondoh, Takashi; Lee, S.; Hutchinson, D. P.*; Richards, R. K.*
Review of Scientific Instruments, 72(1), p.1143 - 1146, 2001/01
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:58.73(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
 laser in JT-60U
laser in JT-60UKondoh, Takashi; Lee, S.; Miura, Yukitoshi
Proceedings of 10th International Symposium on Laser-Aided Plasma Diagnostics, p.109 - 114, 2001/00
A collective Thomson scattering (CTS) diagnostic system based on a CO laser has come into operation to establish measurement technique of ion temperature and fast alpha particle in fusion plasmas. A pulsed CO2 laser (wavelength 10.6
laser has come into operation to establish measurement technique of ion temperature and fast alpha particle in fusion plasmas. A pulsed CO2 laser (wavelength 10.6 m, beam energy 15 J, pulse width 1
m, beam energy 15 J, pulse width 1 s) and a heterodyne receiver were developed by Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) and were installed in the JT-60U tokamak. Commissioning of the CTS system by injecting the CO
s) and a heterodyne receiver were developed by Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) and were installed in the JT-60U tokamak. Commissioning of the CTS system by injecting the CO laser into the plasmas has been proceeded.
laser into the plasmas has been proceeded.
Hatae, Takaki; Naito, Osamu
Proceedings of 10th International Symposium on Laser-Aided Plasma Diagnostics, p.160 - 166, 2001/00
In recent strong electron heating experiments in JT-60U, it seems that central 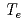 rises above
rises above  15 keV which is measured by Ruby laser and YAG laser Thomson scattering systems. However, error bars are relatively large and it is difficult to measure the very high
15 keV which is measured by Ruby laser and YAG laser Thomson scattering systems. However, error bars are relatively large and it is difficult to measure the very high 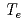 beyond
beyond  15 keV with high accuracy because the electron temperature region exceeds that of the original design. To improve the measurement performance in very high
15 keV with high accuracy because the electron temperature region exceeds that of the original design. To improve the measurement performance in very high 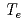 , we have tried the combination of existing Ruby laser system and YAG laser system. From simulations, it was found that (1) changing the form of the spectrum with the other laser is an effective way for very high
, we have tried the combination of existing Ruby laser system and YAG laser system. From simulations, it was found that (1) changing the form of the spectrum with the other laser is an effective way for very high 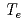 measurement, (2) furthermore the combined system in YAG laser scattering is well optimized at
measurement, (2) furthermore the combined system in YAG laser scattering is well optimized at 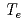
 20keV and relative error is reduced significantly compared with original system.
20keV and relative error is reduced significantly compared with original system.
Hatae, Takaki; Yoshida, Hidetoshi; Yamauchi, Toshihiko; Naito, Osamu
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 76(9), p.868 - 873, 2000/09
no abstracts in English
 laser system
laser systemKondoh, Takashi; Lee, S.; Miura, Yukitoshi
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 76(9), p.883 - 887, 2000/09
no abstracts in English
Hatae, Takaki; Nagashima, Akira; Kitamura, Shigeru; ; Yoshida, Hidetoshi*; Naito, Osamu; Yamashita, Osamu; Shimizu, Kazuaki; ; Kondoh, Takashi
Review of Scientific Instruments, 70(1), p.772 - 775, 1999/01
Times Cited Count:64 Percentile:93.70(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Yoshida, Hidetoshi; Naito, Osamu; Yamashita, Osamu; Kitamura, Shigeru; ; ; ; ; Hatae, Takaki; Nagashima, Akira; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 70(1), p.751 - 754, 1999/01
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:69.45(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Yoshida, Hidetoshi; Naito, Osamu; ; Kitamura, Shigeru; Hatae, Takaki; Nagashima, Akira
Review of Scientific Instruments, 70(1), p.747 - 750, 1999/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:42.46(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Naito, Osamu; Yoshida, Hidetoshi; Hatae, Takaki; Nagashima, Akira
Physics of Plasmas, 4(4), p.1171 - 1172, 1997/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:16.38(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Yoshida, Hidetoshi; Naito, Osamu; Matoba, Toru; Yamashita, Osamu; Kitamura, Shigeru; Hatae, Takaki; Nagashima, Akira
Review of Scientific Instruments, 68(2), p.1152 - 1161, 1997/02
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:69.48(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English